Scientists are using data from Hubble data of the famous Cygnus Loop supernova remnant to study how these remnants change over time.
Some of the most dramatic events in the universe are the deaths of massive stars. When stars far larger than our sun run out of fuel and explode in huge supernovas, these events not only let out huge blasts of energy but also change the environment around them. As the shockwave from the explosion travels outward millions of miles into space and slams into clouds dust and gas, it can create elaborate and beautiful structures called supernova remnants.
“Hubble is the only way that we can actually watch what’s happening at the edge of the bubble with such clarity,” said Ravi Sankrit of the Space Telescope Science Institute, lead author of the new research, in a statement. “The Hubble images are spectacular when you look at them in detail. They’re telling us about the density differences encountered by the supernova shocks as they propagate through space, and the turbulence in the regions behind these shocks.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Hubble spots expansion of 20,000-year-old supernova explosionHubble skillfully imaged the expanding shell of gas and dust of the Cygnus Loop into space.
Hubble spots expansion of 20,000-year-old supernova explosionHubble skillfully imaged the expanding shell of gas and dust of the Cygnus Loop into space.
Read more »
 Time-lapse video shows a supernova's aftermath ballooning into spaceA small sliver of the Cygnus Loop reveals new details about the iconic nebula.
Time-lapse video shows a supernova's aftermath ballooning into spaceA small sliver of the Cygnus Loop reveals new details about the iconic nebula.
Read more »
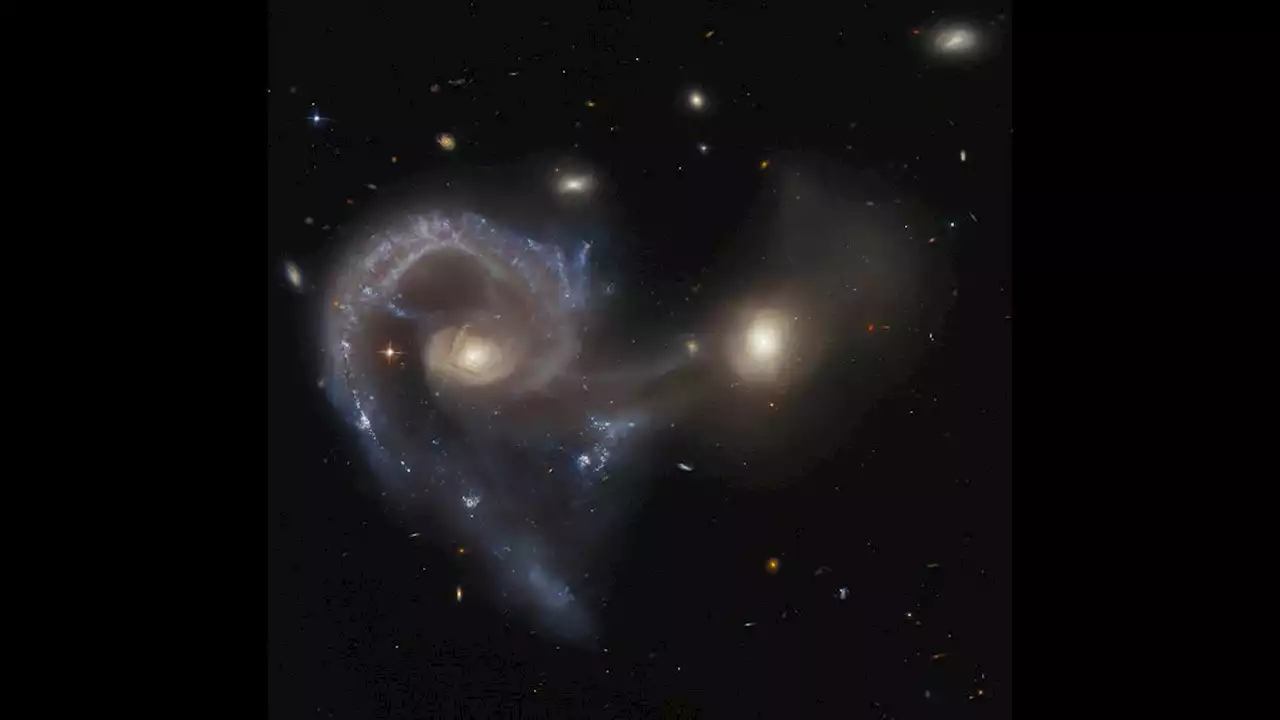 Space photo of the week: Hubble spies a spectacular galaxy crashArp 107 hosts a special spiraling 'Seyfert' galaxy connected to a smaller galaxy by a 'bridge' of dust and gas.
Space photo of the week: Hubble spies a spectacular galaxy crashArp 107 hosts a special spiraling 'Seyfert' galaxy connected to a smaller galaxy by a 'bridge' of dust and gas.
Read more »
 Loop Capital upgrades Burger King's parent company, says stock can rally more than 20%Loop Capital upgraded Burger King parent company Restaurant Brands International to buy.
Loop Capital upgrades Burger King's parent company, says stock can rally more than 20%Loop Capital upgraded Burger King parent company Restaurant Brands International to buy.
Read more »
 Scientists knew phenylephrine was useless—but you’ve been using it for decadesMore than 200 over-the-counter decongestants contain a key ingredient that was just revealed to be ineffective—and cold and flu season is just around the corner. Now what?
Scientists knew phenylephrine was useless—but you’ve been using it for decadesMore than 200 over-the-counter decongestants contain a key ingredient that was just revealed to be ineffective—and cold and flu season is just around the corner. Now what?
Read more »
