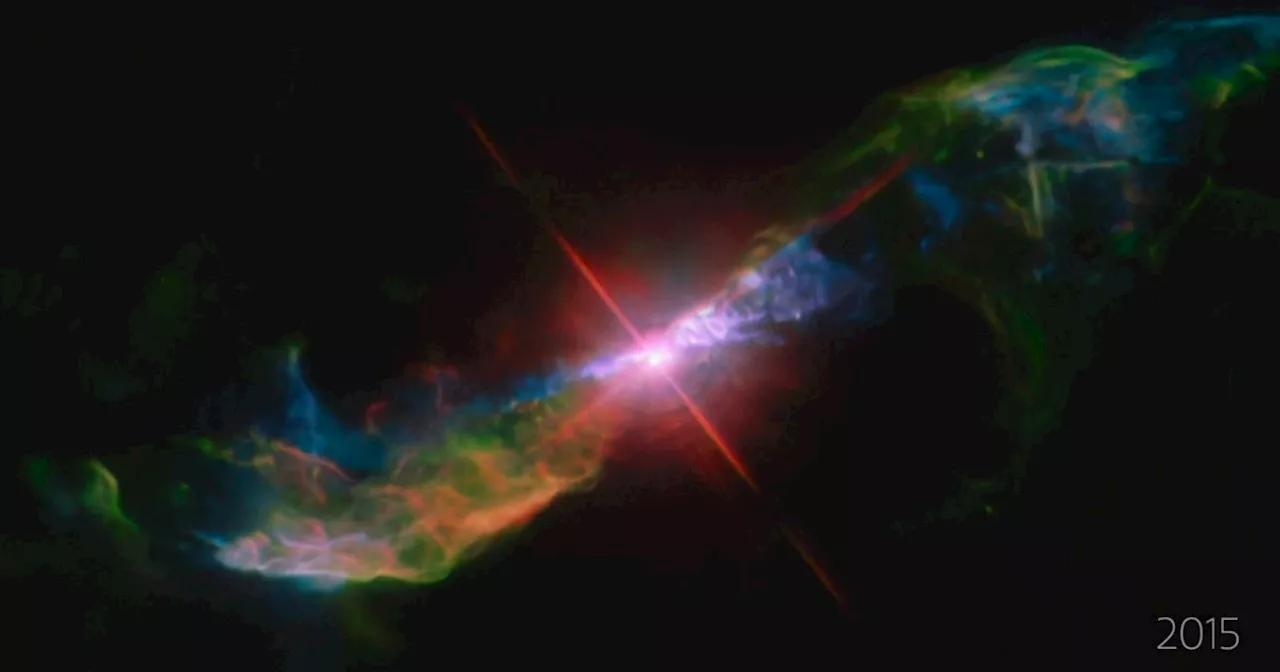
A gorgeous image from the Hubble Space Telescope shows a nearby star called R Aquarii that is the site of dramatic activity: violent eruptions of matter that is thrown out into the space around it.
Informally dubbed as a “stellar volcano” for the way it is throwing out matter like lava spewing from deep underground, the star makes for a stunning image, but it also holds an unexpected surprise. The star is not one single object, but two.
Known as a symbiotic variable star, it consists of a red giant and a white dwarf that orbit each other in an ongoing dance. The red giant pulses, with its temperature and brightness changing over a 390-day period. This intersects with the 44-year orbital period of the white dwarf. When the white dwarf starts to close in on the red giant, it sucks off some of its gas via gravity and builds up the disk around it until this collapses and explodes, throwing off jets of material.
“This outburst ejects powerful jets seen as filaments shooting out from the binary system, forming loops and trails as the plasma emerges in streamers,” Hubble scientists explain. “The plasma is twisted by the force of the explosion and channeled upwards and outwards by strong magnetic fields. The outflow appears to bend back on itself into a spiral pattern. The filaments are glowing in visible light because they are energized by blistering radiation from the stellar duo that is R Aquarii.
Recommended Videos You can see the pulses of the red giant in this video timeline of R Aquarii using data from Hubble collected between 2014 and 2023. It also shows the swirling material near the heart caused by previous jets. This gives an idea of just how large the effects from this star are, as the material travels as much as 248 billion miles from the central core region — that’s 2,500 times the distance between Earth and the sun.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
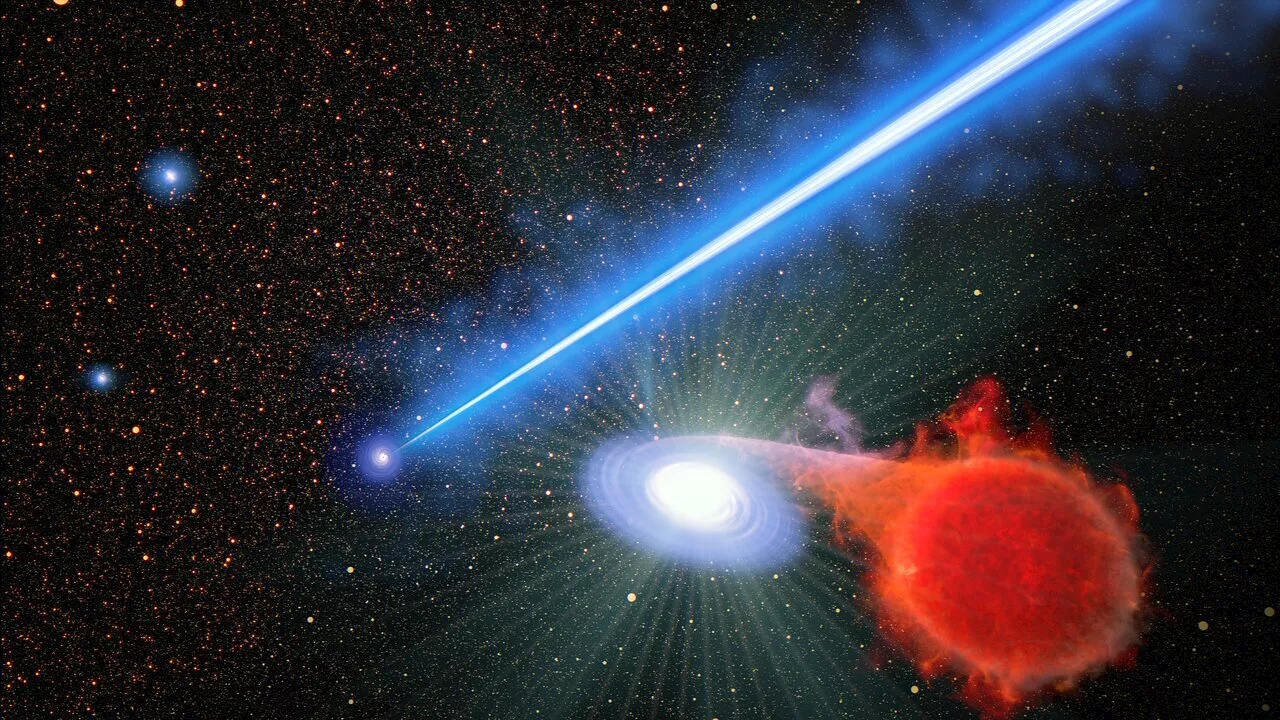 Hubble finds that a black hole beam promotes stellar eruptionsIn a surprise finding, astronomers using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope have discovered that the blowtorch-like jet from a supermassive black hole at the core of a huge galaxy seems to cause stars to erupt along its trajectory. The stars, called novae, are not caught inside the jet, but are apparently in a dangerous neighborhood nearby.
Hubble finds that a black hole beam promotes stellar eruptionsIn a surprise finding, astronomers using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope have discovered that the blowtorch-like jet from a supermassive black hole at the core of a huge galaxy seems to cause stars to erupt along its trajectory. The stars, called novae, are not caught inside the jet, but are apparently in a dangerous neighborhood nearby.
Read more »
 Jupiter's Great Red Spot is being squeezed, Hubble Telescope finds — and nobody knows why (video)Keith Cooper is a freelance science journalist and editor in the United Kingdom, and has a degree in physics and astrophysics from the University of Manchester.
Jupiter's Great Red Spot is being squeezed, Hubble Telescope finds — and nobody knows why (video)Keith Cooper is a freelance science journalist and editor in the United Kingdom, and has a degree in physics and astrophysics from the University of Manchester.
Read more »
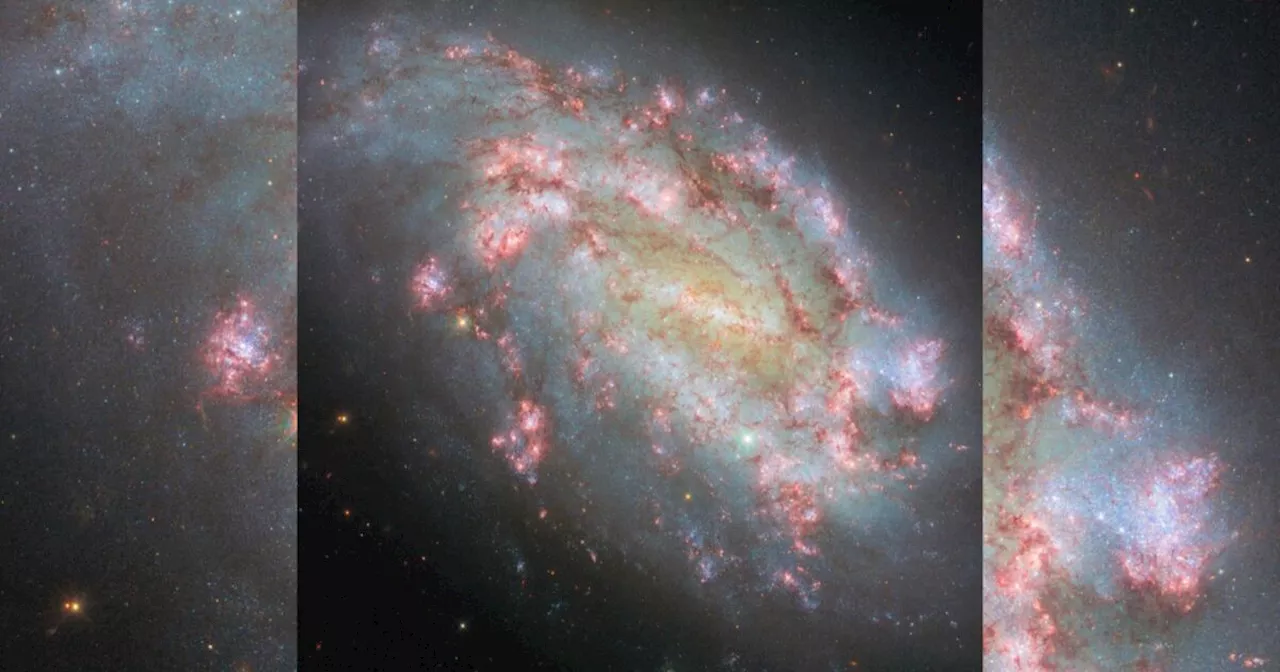 NASA's Hubble telescope reveals striking image of new multi-wavelength galaxyDoug covers topics from a national angle including politics, consumer issues, stories that cross borders, and news that catches the attention of U.S. lawmakers.
NASA's Hubble telescope reveals striking image of new multi-wavelength galaxyDoug covers topics from a national angle including politics, consumer issues, stories that cross borders, and news that catches the attention of U.S. lawmakers.
Read more »
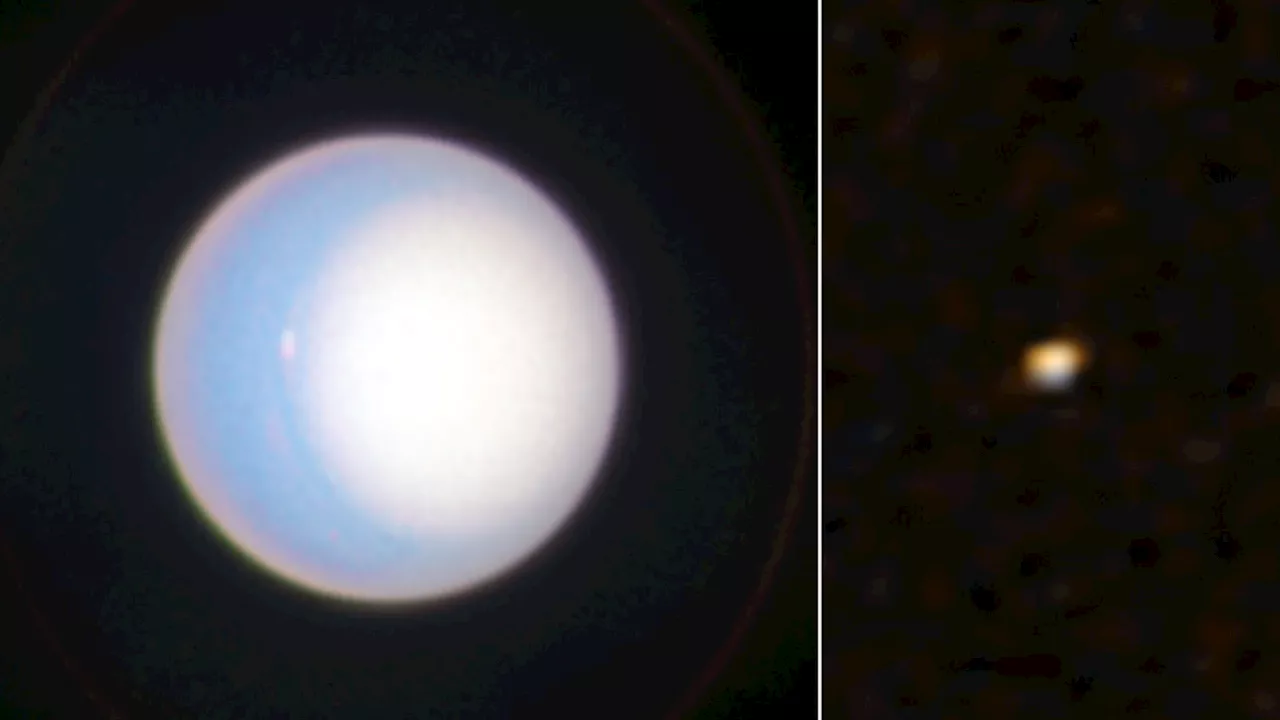 Hubble Telescope and New Horizons Pluto probe team up to image UranusRobert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.
Hubble Telescope and New Horizons Pluto probe team up to image UranusRobert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.
Read more »
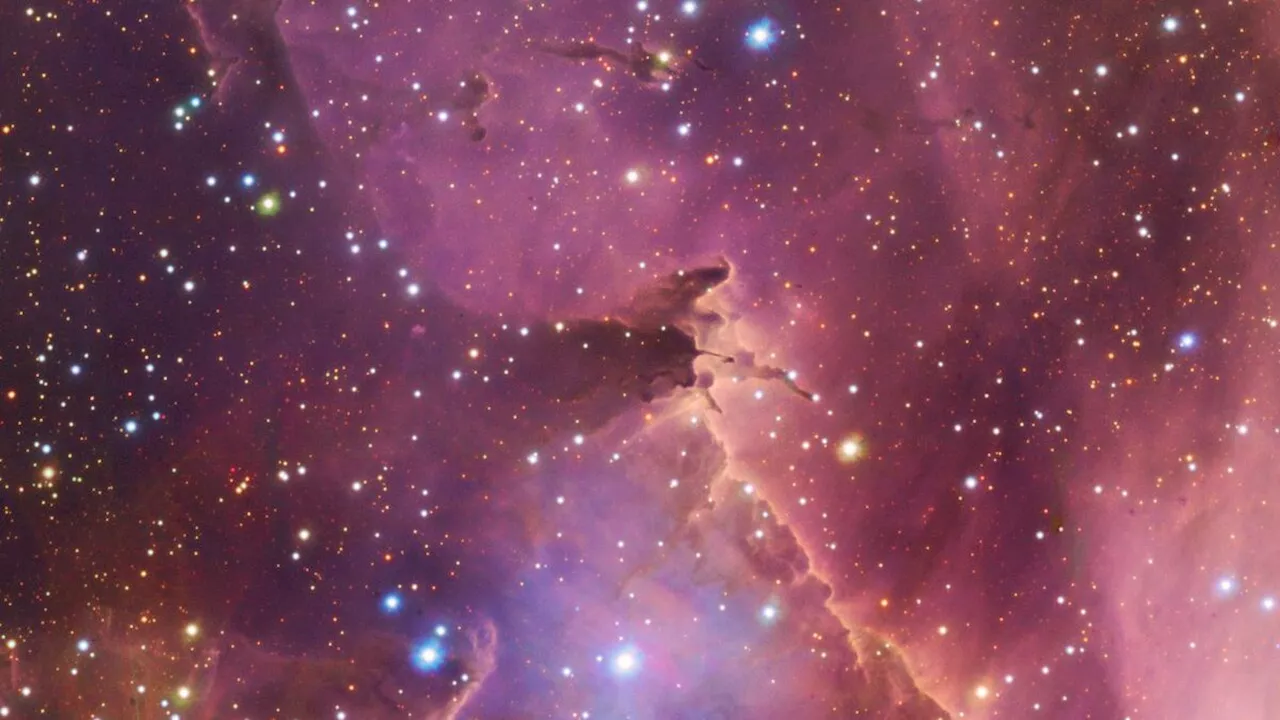 Find your way across countless young stars in this image of a faraway stellar nursery (image)Sharmila Kuthunur is a Seattle-based science journalist covering astronomy, astrophysics and space exploration. Follow her on X skuthunur.
Find your way across countless young stars in this image of a faraway stellar nursery (image)Sharmila Kuthunur is a Seattle-based science journalist covering astronomy, astrophysics and space exploration. Follow her on X skuthunur.
Read more »
 New RødeCaster Video Makes Video Production Easy For Content CreatorsMark Sparrow writes about consumer audio, computer gadgets and Apple Macs, He reviews tech that's fun, creative and productive.
New RødeCaster Video Makes Video Production Easy For Content CreatorsMark Sparrow writes about consumer audio, computer gadgets and Apple Macs, He reviews tech that's fun, creative and productive.
Read more »
