Study shows bacteria hijack crosstalk between nerve and immune cells to cause meningitis. A new study led by researchers at Harvard Medical School details the step-by-step cascade that allows bacteria to break through the brain’s protective layers — the meninges — and cause brain infection, or me
This time around, Chiu and Pinho-Ribeiro turned their attention to meningitis — another condition in which they suspected the relationship between nervous and immune systems plays a role.are three membranes that lie atop one another, wrapping the brain and spinal cord to shield the central nervous system from injury, damage, and infection. The outermost of the three layers — called dura mater — contains pain neurons that detect signals.
What exactly happens in the meninges when bacteria invade? How do they interact with the immune cells residing there? These questions remain poorly understood, the researchers said.In this particular study, the researchers focused on two pathogens —, leading causes of bacterial meningitis in humans. In a series of experiments, the team found that when bacteria reach the meninges, the pathogens trigger a chain of events that culminates in disseminated infection.
To confirm that the bacterially induced activation of pain neurons was the critical first step in disabling the brain’s defenses, the researchers checked what would happen to infected mice lacking pain neurons. In another experiment, the researchers used a chemical to block the RAMP1 receptor, preventing it from communicating with CGRP, the chemical released by activated pain neurons. The RAMP1 blocker worked both as preventive treatment before infection and as a treatment once infection had occurred.
One line of future research could examine whether CGRP and RAMP1 blockers could be used in conjunction with antibiotics to treat meningitis and augment protection. “There has to be an evolutionary reason why macrophages and pain neurons reside so closely together,” Chiu said. “With our study, we’ve gleaned what happens in the setting of bacterial infection, but beyond that, how do they interact during viral infection, in the presence of tumor cells, or the setting of brain injury? These are all important and fascinating future questions.”
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 A Harvard gut doctor shares 8 foods that cause bloating—and what she eats insteadEver feel bloated after eating a meal? You may be eating the wrong foods. Dr. Jacqueline Wolf, a gut doctor and Harvard Medical School professor, shares the foods she avoids that cause bloating—and what she eats instead.
A Harvard gut doctor shares 8 foods that cause bloating—and what she eats insteadEver feel bloated after eating a meal? You may be eating the wrong foods. Dr. Jacqueline Wolf, a gut doctor and Harvard Medical School professor, shares the foods she avoids that cause bloating—and what she eats instead.
Read more »
 Scientist exposes hidden bacteria all over your home — including staph, E. coliEveryday objects that look clean on the surface may have some dirty little secrets.
Scientist exposes hidden bacteria all over your home — including staph, E. coliEveryday objects that look clean on the surface may have some dirty little secrets.
Read more »
 Princeton, Harvard Grad Pete Hegseth Bashes Ivy League ‘Cartel’'If you went to the Ivy League, prove to me that you have any common sense at all,” Fox News host Pete Hegseth, who graduated from Princeton in 2003 and received a master’s degree from Harvard ten years later, said.
Princeton, Harvard Grad Pete Hegseth Bashes Ivy League ‘Cartel’'If you went to the Ivy League, prove to me that you have any common sense at all,” Fox News host Pete Hegseth, who graduated from Princeton in 2003 and received a master’s degree from Harvard ten years later, said.
Read more »
 Nanosyringes could inject drugs into specific cells in our bodiesResearchers have tweaked structures made by bacteria so that they can target human cells and inject proteins into them, a trick that could lead to targeted medical treatments
Nanosyringes could inject drugs into specific cells in our bodiesResearchers have tweaked structures made by bacteria so that they can target human cells and inject proteins into them, a trick that could lead to targeted medical treatments
Read more »
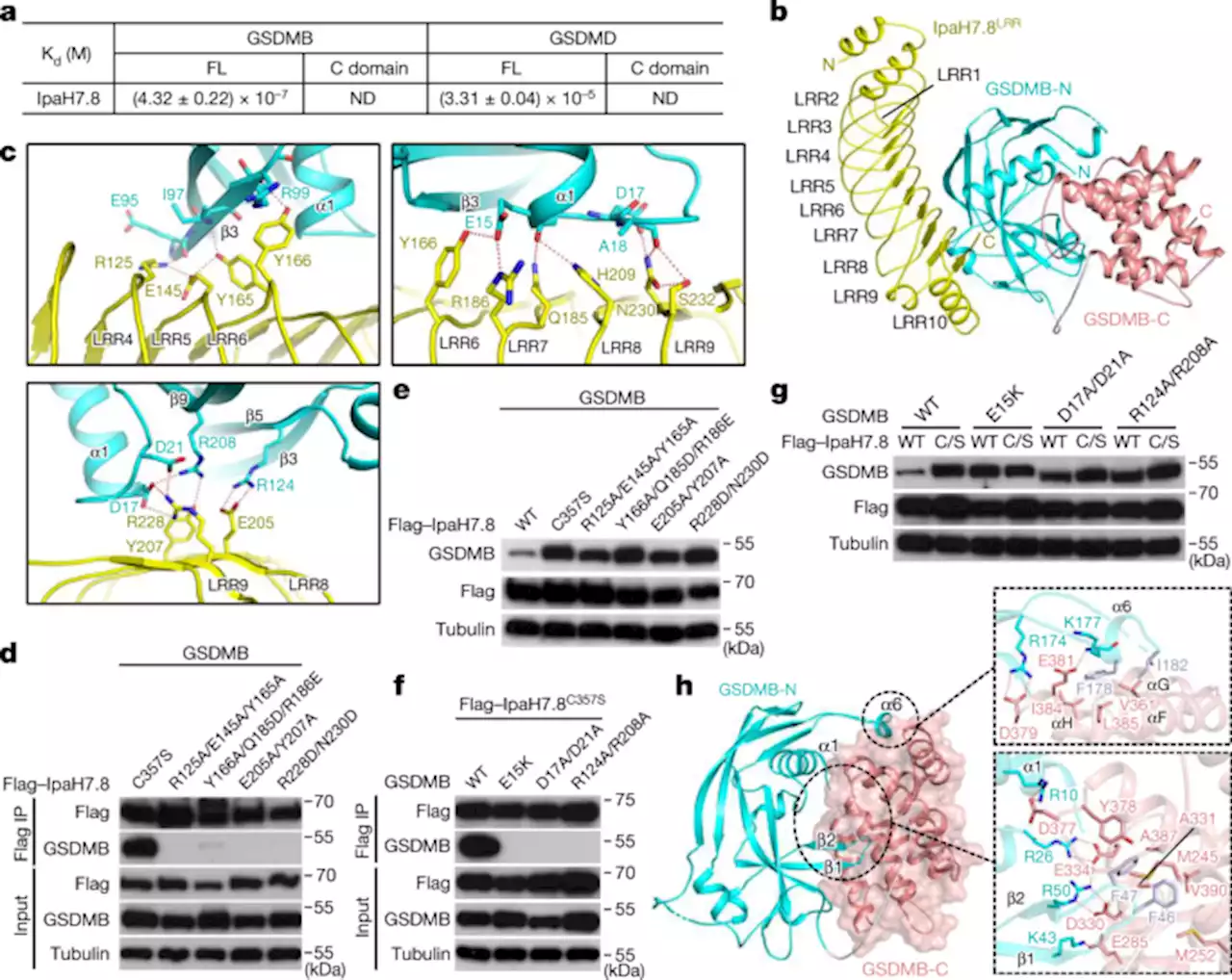 Structural mechanisms for regulation of GSDMB pore-forming activity - NatureThe cryo-EM structure of the GSDMB pore reveals mechanisms by which GSDMB pore-forming activity is regulated by pathogenic bacteria and mRNA splicing.
Structural mechanisms for regulation of GSDMB pore-forming activity - NatureThe cryo-EM structure of the GSDMB pore reveals mechanisms by which GSDMB pore-forming activity is regulated by pathogenic bacteria and mRNA splicing.
Read more »
 Cookie lovers warned to stop eating raw dough amid salmonella outbreak: CDCRaw, or unbaked, flour could be contaminated with the bacteria, which causes foodborne illness and leads to upset stomach, fever, chills, vomiting and cramps.
Cookie lovers warned to stop eating raw dough amid salmonella outbreak: CDCRaw, or unbaked, flour could be contaminated with the bacteria, which causes foodborne illness and leads to upset stomach, fever, chills, vomiting and cramps.
Read more »