Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) face nearly double the risk for osteoarticular infections compared with those without RA, with similar mortality risks in both groups.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) face nearly double the risk for osteoarticular infections compared with those without RA, with similar mortality risks in both groups. Bacteremia is linked to poor clinical outcomes in patients with RA; however, no well-sized studies have evaluated the risk for osteoarticular infections and mortality outcomes in patients with RA following bacteremia.
This Danish nationwide cohort study aimed to explore whether the cumulative incidence of osteoarticular infections and death would be higher in patients with RA than in those without RA after contracting bacteremia. The RA cohort had more women (62%) and a higher median age of participants (73 years) than the non-RA cohort (37% women; median age of participants, 70 years). The cumulative incidence of osteoarticular infections (eg, septic arthritis, psoas muscle abscess, or prosthetic joint infection) was nearly double in patients with RA compared with in those without RA (23.1% vs 12.5%; hazard ratio, 1.93; 95% CI, 1.54-2.41)
Rheumatoid Arthritis Osteoarticular Infections Mortality Bacteremia Clinical Outcomes
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Patients with IBD at Higher Risk for Myocarditis, Study FindsPatients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have a higher risk for myocarditis, especially severe myocarditis, than the general population, even 20 years after diagnosis, although absolute risks are low.
Patients with IBD at Higher Risk for Myocarditis, Study FindsPatients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have a higher risk for myocarditis, especially severe myocarditis, than the general population, even 20 years after diagnosis, although absolute risks are low.
Read more »
 Thousands of BCBSAZ patients out of network at Dignity Health, Aetna patients also at riskThousands are now out of network at Dignity, others at risk of losing coverage
Thousands of BCBSAZ patients out of network at Dignity Health, Aetna patients also at riskThousands are now out of network at Dignity, others at risk of losing coverage
Read more »
 Study Finds CPAP Machine Less Effective for Patients with Higher BMIsA new study suggests that a device used to treat sleep apnea may not be as effective for patients with higher body mass indexes (BMIs). The study found that patients with BMIs above 30 had a lower success rate with the device.
Study Finds CPAP Machine Less Effective for Patients with Higher BMIsA new study suggests that a device used to treat sleep apnea may not be as effective for patients with higher body mass indexes (BMIs). The study found that patients with BMIs above 30 had a lower success rate with the device.
Read more »
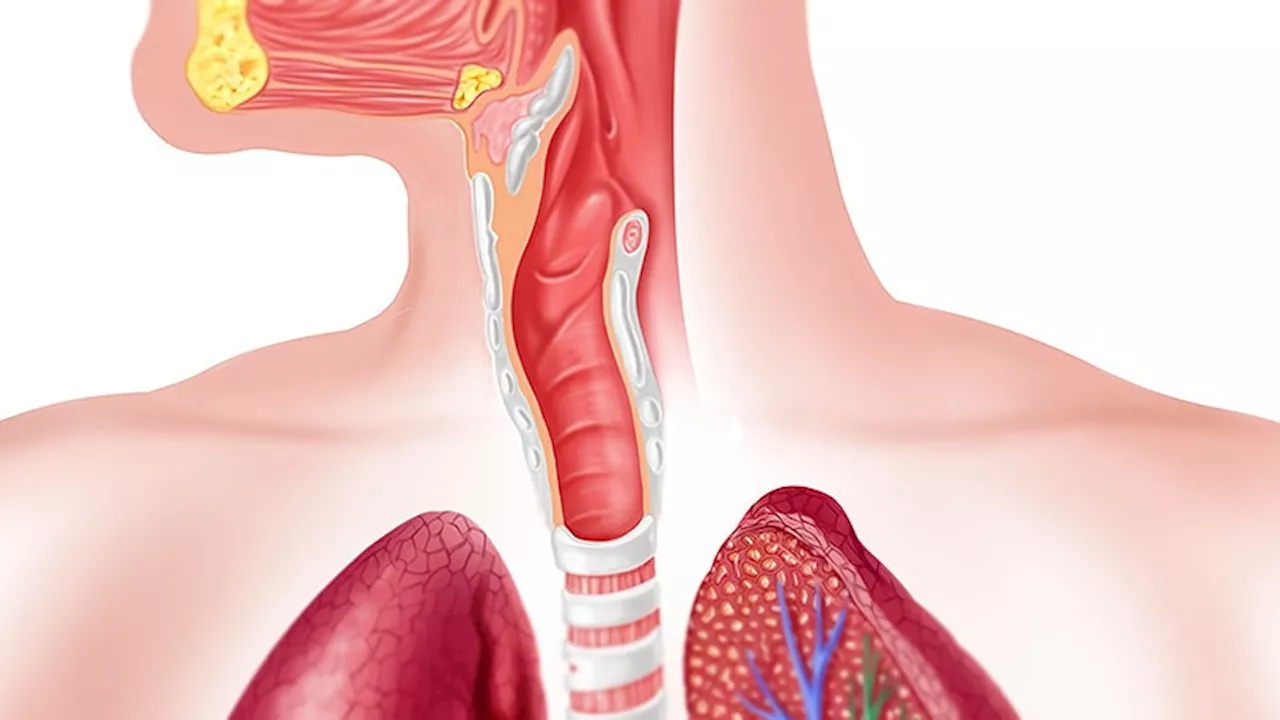 Twice-daily PPI dose leads to higher histologic response rates in EoE patientsA retrospective cohort study found that a twice-daily dose of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) is more effective in inducing histologic remission in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) compared to a once-daily dose. The study aimed to determine the optimal dosing strategy for PPI in EoE patients.
Twice-daily PPI dose leads to higher histologic response rates in EoE patientsA retrospective cohort study found that a twice-daily dose of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) is more effective in inducing histologic remission in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) compared to a once-daily dose. The study aimed to determine the optimal dosing strategy for PPI in EoE patients.
Read more »
 The Fed projects higher interest rates, and higher inflation, for longerThe central bank has always predicted higher interest rates for longer, but now it predicts even higher inflation.
The Fed projects higher interest rates, and higher inflation, for longerThe central bank has always predicted higher interest rates for longer, but now it predicts even higher inflation.
Read more »
 USD/MXN edges higher to near 16.70 on speculation of Fed prolonging higher cash ratesUSD/MXN expands gains for the second consecutive day on Friday, bouncing back from the eight-month low at 16.64 reached on Thursday.
USD/MXN edges higher to near 16.70 on speculation of Fed prolonging higher cash ratesUSD/MXN expands gains for the second consecutive day on Friday, bouncing back from the eight-month low at 16.64 reached on Thursday.
Read more »
