Researchers have discovered a link between high blood pressure and tellurium, a contaminant found in various plant-based foods. The study highlights the importance of closely and consistently monitoring tellurium levels in different types of food.
The likelihood of developing high blood pressure increases with higher levels of tellurium, a contaminant transferred from mining and manufacturing activities to foods. Improved monitoring of tellurium levels in specific foods could help decrease high blood pressure in the general population. The results of a study examining the relationship between tellurium exposure and hypertension were published in the journalThe study was led by Nagoya University in Japan.
The study conducted by Professor Masashi Kato, Takumi Kagawa, and their colleagues involved 2,592 Japanese adults. It revealed that higher levels of tellurium in urine were associated with higher blood pressure and a greater occurrence of hypertension. The results were the same in both mice and humans.
"We found that despite raising tellurium levels in the urine, cereal/legume intake did not directly increase the risk of hypertension," said Takumi Kagawa."Cereals/legumes may contain many diverse nutrients that can mitigate the risk of hypertension despite high levels of tellurium.
Heart Disease Cholesterol Vitamin D Food Endangered Plants Mice Food And Agriculture
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Researchers explore the interplay between high-affinity DNA and carbon nanotubesSingle-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) hold promise for biomedicine and nanoelectronics, yet the functionalization with single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) remains a challenge. Researchers using high-affinity ssDNA sequences identified through high-throughput selection.
Researchers explore the interplay between high-affinity DNA and carbon nanotubesSingle-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) hold promise for biomedicine and nanoelectronics, yet the functionalization with single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) remains a challenge. Researchers using high-affinity ssDNA sequences identified through high-throughput selection.
Read more »
 Researchers realize multi-heterojunctioned plastics with high thermoelectric figure of meritOrganic thermoelectric materials hold great promise as flexible energy sources for the Internet of Things and wearable electronics. However, their relatively low dimensionless figure of merit (ZT) compared to traditional materials has been a major obstacle, limiting their use in thermoelectric power generation and solid-state cooling.
Researchers realize multi-heterojunctioned plastics with high thermoelectric figure of meritOrganic thermoelectric materials hold great promise as flexible energy sources for the Internet of Things and wearable electronics. However, their relatively low dimensionless figure of merit (ZT) compared to traditional materials has been a major obstacle, limiting their use in thermoelectric power generation and solid-state cooling.
Read more »
 Researchers develop high-sensitivity technique to detect mercury in soilEnvironmental pollution by heavy metals is a major social problem. Among these metals, mercury (Hg) is strictly controlled due to its high toxicity. Focusing on soil, which is closely related to our daily lives, the environmental standard for mercury is set at less than 0.5 µg/L (µg is a unit of 1 millionth of a gram).
Researchers develop high-sensitivity technique to detect mercury in soilEnvironmental pollution by heavy metals is a major social problem. Among these metals, mercury (Hg) is strictly controlled due to its high toxicity. Focusing on soil, which is closely related to our daily lives, the environmental standard for mercury is set at less than 0.5 µg/L (µg is a unit of 1 millionth of a gram).
Read more »
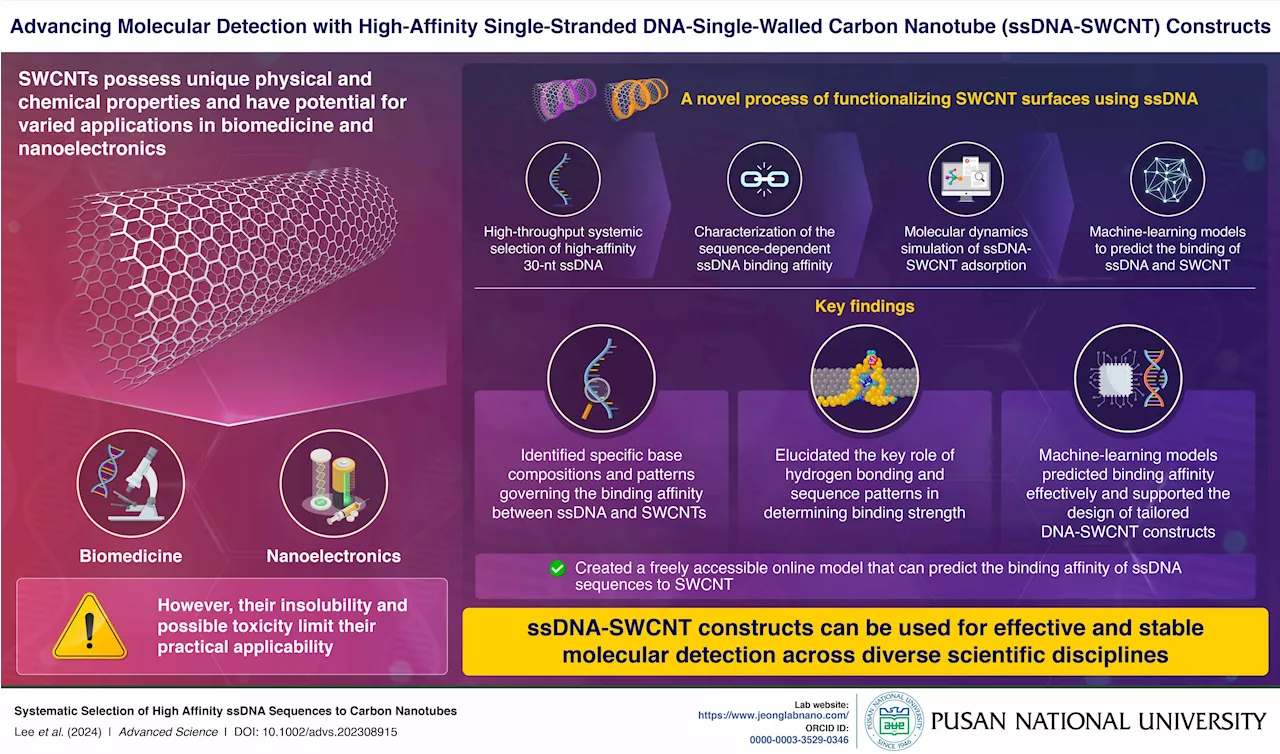 Researchers explore interplay between high-affinity DNA and carbon nanotubesSingle-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) have emerged as promising candidates for applications in biotechnology and nanoelectronics due to their exceptional physical and chemical properties. Despite their potential, challenges like insolubility and toxicity have hindered their widespread use.
Researchers explore interplay between high-affinity DNA and carbon nanotubesSingle-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) have emerged as promising candidates for applications in biotechnology and nanoelectronics due to their exceptional physical and chemical properties. Despite their potential, challenges like insolubility and toxicity have hindered their widespread use.
Read more »
 High-Frequency, Low-Power: Researchers Develop Switch To Revolutionize 6G CommunicationsScience, Space and Technology News 2024
High-Frequency, Low-Power: Researchers Develop Switch To Revolutionize 6G CommunicationsScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
 New inverted perovskite solar cell boosts 25% efficiency, 98% stabilityResearchers develop high-entropy hybrid perovskite solar cells with better efficiency and stability, promising industrial scalability.
New inverted perovskite solar cell boosts 25% efficiency, 98% stabilityResearchers develop high-entropy hybrid perovskite solar cells with better efficiency and stability, promising industrial scalability.
Read more »
