Science, Space and Technology News 2024
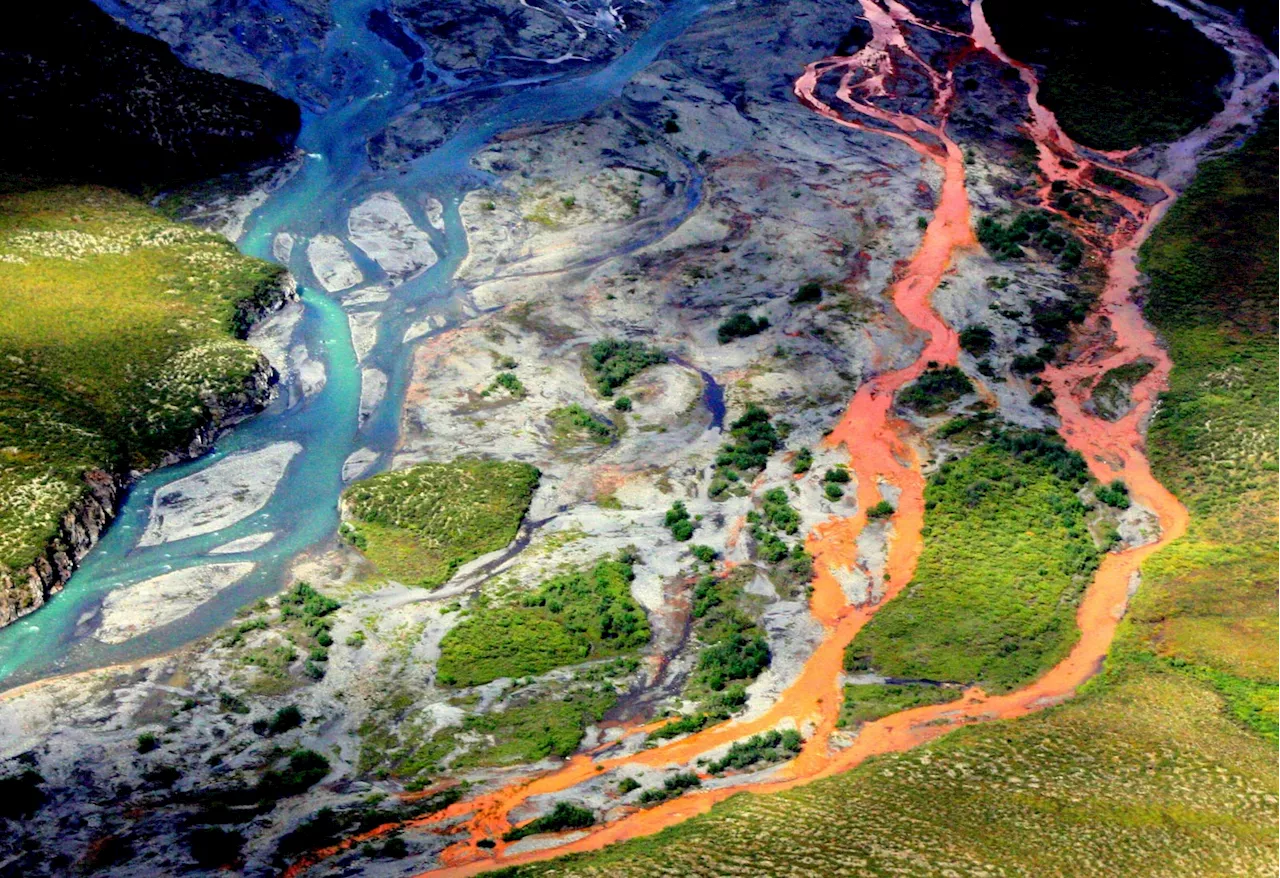
An aerial view of the rust-colored Kutuk River in Gates of the Arctic National Park in Alaska. Thawing permafrost is exposing minerals to weathering, increasing the acidity of the water, which releases metals like iron, zinc and copper. Credit: Ken Hill / National Park ServiceIn Alaska, numerous remote streams and rivers are shifting from their natural crystal-clear blue to an unsettling cloudy orange.
“The stained rivers are so big we can see them from space,” said Brett Poulin, an assistant professor of environmental toxicology at UC Davis who was a principal investigator in the research. “These have to be stained a lot to pick them up from space.” Poulin, who specializes in water chemistry, said the staining resembled the effects ofResearchers hypothesize that as the climate warms, permafrost thaws.
The problem is growing and affecting habitat, water quality, and other ecological systems, turning healthy areas into degraded habitats with fewer fish and. If rural communities rely on these rivers for drinking water, they could require treatment eventually, and the fishing stocks that feed local residents could be affected.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Rochelle and The SidewindersRochelle & The Sidewinders is an award-winning, high-energy blues band based out of Austin Texas. Formed during the summer of 2015, The Sidewinders have released two full-length CDs. The band won the Austin Blues Society’s “Heart Of Texas Blues Challenge” two years in a row and were semi-finalists in the 2018 International Blues Challenge.
Rochelle and The SidewindersRochelle & The Sidewinders is an award-winning, high-energy blues band based out of Austin Texas. Formed during the summer of 2015, The Sidewinders have released two full-length CDs. The band won the Austin Blues Society’s “Heart Of Texas Blues Challenge” two years in a row and were semi-finalists in the 2018 International Blues Challenge.
Read more »
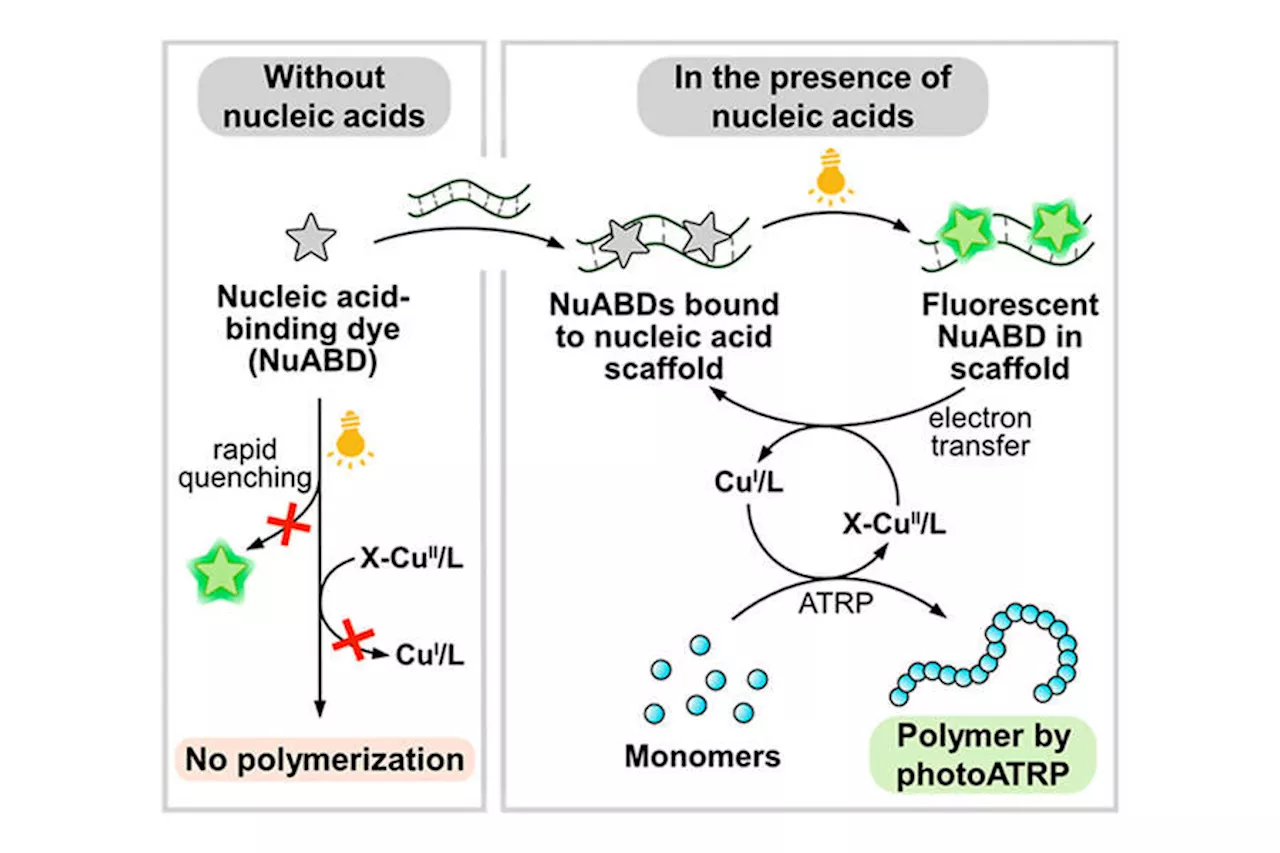 Chemists use nucleic acid binding dyes as photocatalysts for a popular polymerization methodResearchers in Carnegie Mellon University's Department of Chemistry have developed a nucleic-acid-based photocatalyst that can precisely control atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP), a popular method used to generate a wide range of materials with highly specific, tailored functionalities.
Chemists use nucleic acid binding dyes as photocatalysts for a popular polymerization methodResearchers in Carnegie Mellon University's Department of Chemistry have developed a nucleic-acid-based photocatalyst that can precisely control atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP), a popular method used to generate a wide range of materials with highly specific, tailored functionalities.
Read more »
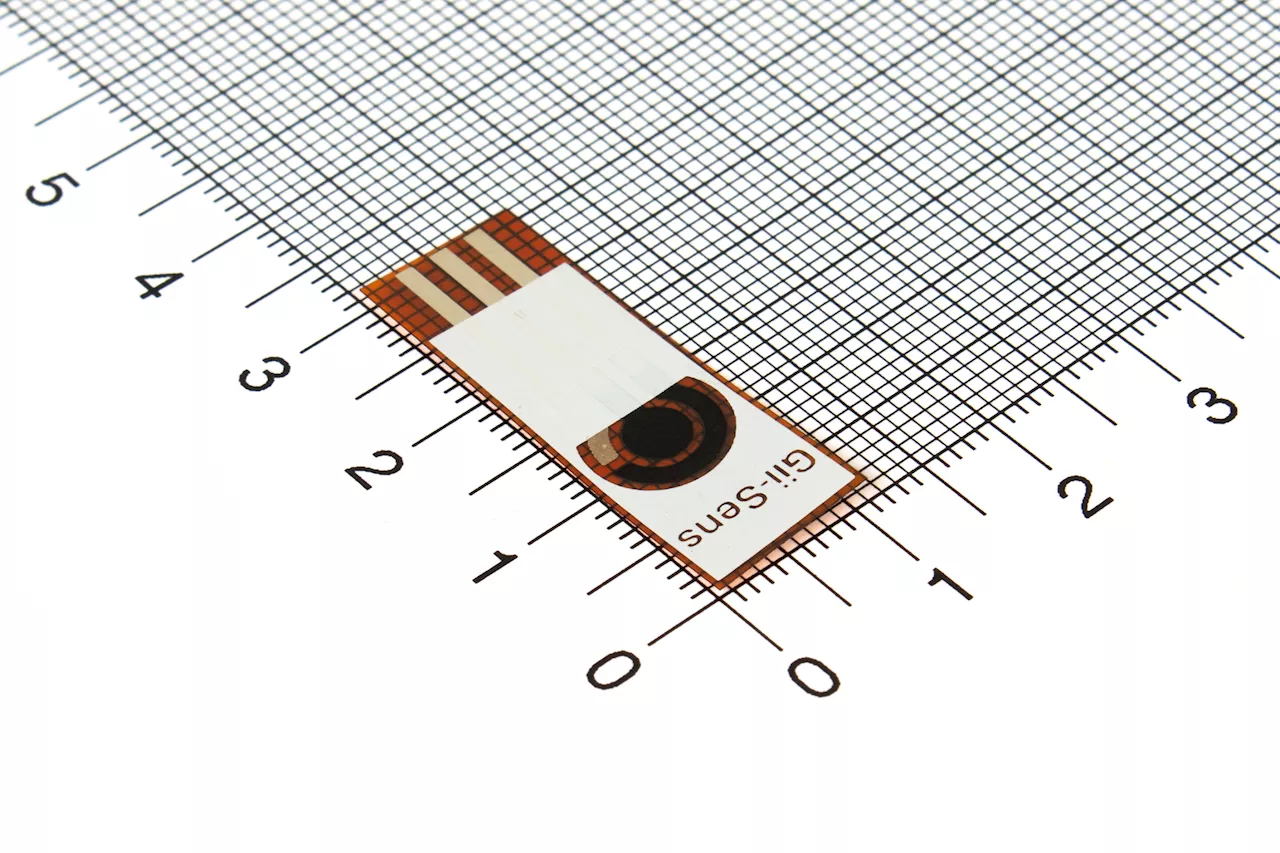 Scientists develop new battery-free lactic acid sensorScientists at Bath, have introduced a breakthrough carbon-based sensor for detecting lactic acid levels in saliva—avoiding the need for an electrical power source.
Scientists develop new battery-free lactic acid sensorScientists at Bath, have introduced a breakthrough carbon-based sensor for detecting lactic acid levels in saliva—avoiding the need for an electrical power source.
Read more »
 The Secret Weapon for Younger-Looking Skin: Is It Hyaluronic Acid?If your goal is glowing, youthful skin, dermatologists agree that hyaluronic acid has many benefits for skin, including deep hydration. Learn more about the science behind this powerful ingredient, how it can transform your complexion, and how to use it.
The Secret Weapon for Younger-Looking Skin: Is It Hyaluronic Acid?If your goal is glowing, youthful skin, dermatologists agree that hyaluronic acid has many benefits for skin, including deep hydration. Learn more about the science behind this powerful ingredient, how it can transform your complexion, and how to use it.
Read more »
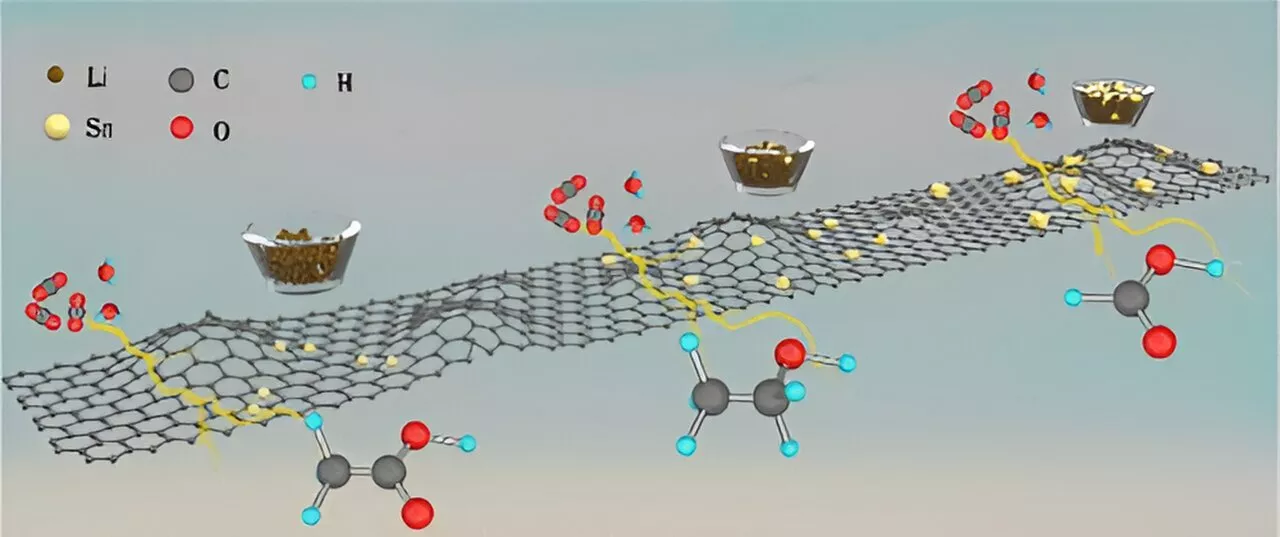 New catalyst transforms carbon dioxide from industrial emissions into commonly used chemicalsA low-cost, tin-based catalyst can selectively convert carbon dioxide to three widely produced chemicals—ethanol, acetic acid and formic acid.
New catalyst transforms carbon dioxide from industrial emissions into commonly used chemicalsA low-cost, tin-based catalyst can selectively convert carbon dioxide to three widely produced chemicals—ethanol, acetic acid and formic acid.
Read more »
 Will Hyaluronic Acid Supplements Help My Skin?The good news is that hyaluronic acid supplements are safe. The bad news is that there is very little evidence that they will improve your skin. But here is what does improve your skin, read on.
Will Hyaluronic Acid Supplements Help My Skin?The good news is that hyaluronic acid supplements are safe. The bad news is that there is very little evidence that they will improve your skin. But here is what does improve your skin, read on.
Read more »
