Flu vaccinations can prevent people living in the same household as infected individuals from contracting secondary influenza, particularly if the pathogen is influenza B virus.
About one in five people who live in the same household as an individual infected with the influenza virus develop secondary infections within a 7-day follow-up period, with children facing the highest risk. Vaccination lowers the risk of contracting the infection among household contacts.Researchers conducted a prospective cohort study of data between 2017 and 2020 to determine the estimated effectiveness of influenza vaccines in preventing secondary infections in household contacts.
The risk for secondary infection and vaccine effectiveness in preventing infection among household contacts was estimated overall and by virus type, subtype, and lineage.Nearly half of primary cases were from children and teens between ages 5 and 17 years. The overall risk for secondary infection among unvaccinated household contacts was 18.8%, with the highest risk observed among children younger than age 5 years .
Flu Influenza Vaccine Flu Vaccine Influenza Vaccination Flu Vaccination Immunizations Vaccination Vaccine Vaccines Children Child Childhood Pediatrics Kids Grant Adolescent Medicine Teens Teenage Teenager Adolescent Health Adolescents Adolescent Allergy Artificial Intelligence Deep Learning AI NPL Machine Learning ML Natural Language Processing
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Bird flu could become deadlier if it mixes with seasonal flu viruses, experts warnKamal Nahas is a freelance contributor based in Oxford, U.K. His work has appeared in New Scientist, Science and The Scientist, among other outlets, and he mainly covers research on evolution, health and technology. He holds a PhD in pathology from the University of Cambridge and a master's degree in immunology from the University of Oxford.
Bird flu could become deadlier if it mixes with seasonal flu viruses, experts warnKamal Nahas is a freelance contributor based in Oxford, U.K. His work has appeared in New Scientist, Science and The Scientist, among other outlets, and he mainly covers research on evolution, health and technology. He holds a PhD in pathology from the University of Cambridge and a master's degree in immunology from the University of Oxford.
Read more »
 H5N1 Detected in Pig Highlights the Risk of Bird Flu Mixing with Seasonal FluHumans and pigs could both serve as mixing vessels for a bird flu–seasonal flu hybrid, posing a risk of wider spread
H5N1 Detected in Pig Highlights the Risk of Bird Flu Mixing with Seasonal FluHumans and pigs could both serve as mixing vessels for a bird flu–seasonal flu hybrid, posing a risk of wider spread
Read more »
 Low COVID and Flu Vaccine Uptake Among Risk Groups in EuropeBuilding trust over time and reducing practical barriers for vaccines may increase uptake.
Low COVID and Flu Vaccine Uptake Among Risk Groups in EuropeBuilding trust over time and reducing practical barriers for vaccines may increase uptake.
Read more »
 What You Need to Know About FluMist, the Nasal Flu VaccineNow that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the at-home use of the flu vaccine spray FluMist, how do you know that it's the right choice for you and your family?
What You Need to Know About FluMist, the Nasal Flu VaccineNow that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the at-home use of the flu vaccine spray FluMist, how do you know that it's the right choice for you and your family?
Read more »
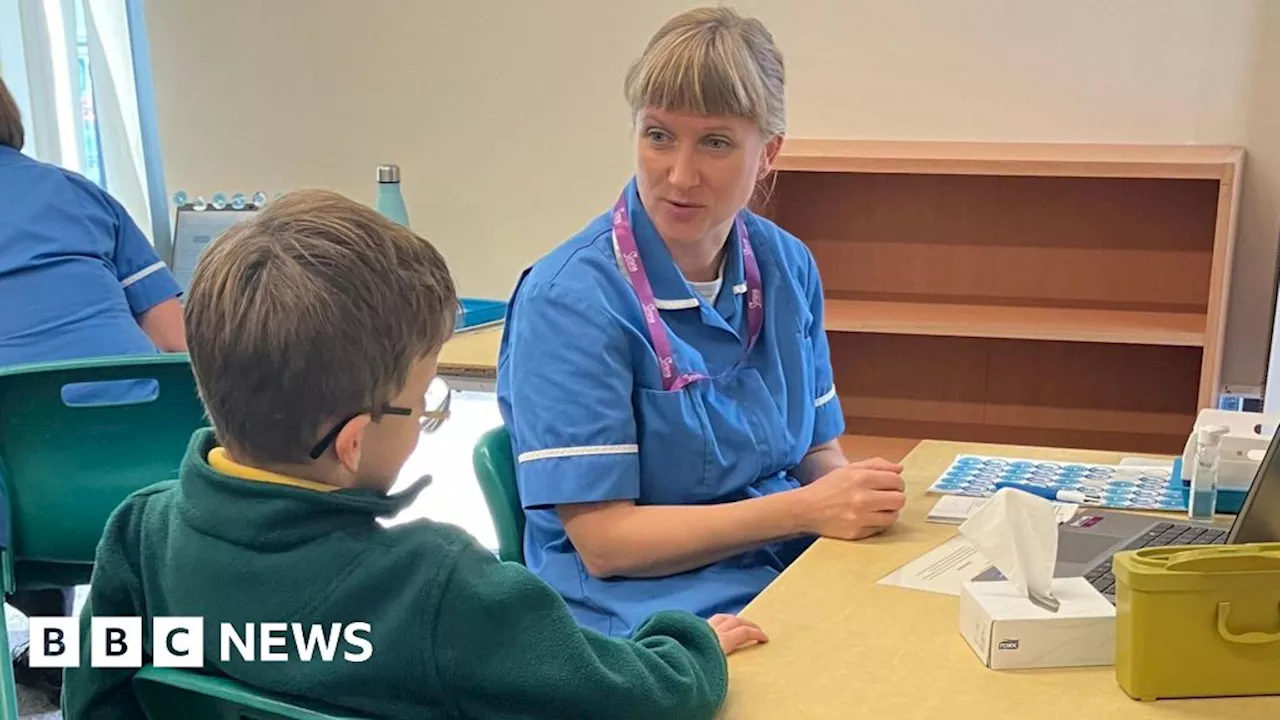 Bristol school children get vaccine to ease winter pressureChildren from reception to year 11 are being offered a flu vaccine.
Bristol school children get vaccine to ease winter pressureChildren from reception to year 11 are being offered a flu vaccine.
Read more »
 A Bird Flu Vaccine Might Come Too Late to Save Us from H5N1If the influenza virus infecting cattle workers starts a pandemic, help in the form of a vaccine is months away
A Bird Flu Vaccine Might Come Too Late to Save Us from H5N1If the influenza virus infecting cattle workers starts a pandemic, help in the form of a vaccine is months away
Read more »