The cellular therapy depletes CD19-positive B cells with the goal of 'resetting' the immune system to achieve durable remission.
The FDA cleared Cabaletta to begin a phase 1/2 clinical trial of CABA-201, the statement says, which will be the first trial accessing Cabaletta's Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cells for Autoimmunity approach. CABA-201, a 4-1BB-containing fully human CD19-CAR T cell investigational therapy, is designed to target and deplete CD19-positive B cells,"enabling an 'immune system reset' with durable remission in patients with SLE," according to the press release.
This upcoming open-label study will enroll two cohorts containing six patients each. One cohort will be patients with SLE and active LN, and the other will be patients with SLE without renal involvement. The therapy is designed as a one-time infusion and will be administered at a dose of 1.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Fast X Needs To Address An Unsolved Fast & Furious 9 MysteryFast X is busy trying to set up Fast and Furious 11, but there's a major loose end in F9 that the movie needs to resolve before anything else.
Fast X Needs To Address An Unsolved Fast & Furious 9 MysteryFast X is busy trying to set up Fast and Furious 11, but there's a major loose end in F9 that the movie needs to resolve before anything else.
Read more »
 Construction of multiple concentration gradients for single-cell level drug screening - Microsystems & NanoengineeringMicrosystems & Nanoengineering - Construction of multiple concentration gradients for single-cell level drug screening
Construction of multiple concentration gradients for single-cell level drug screening - Microsystems & NanoengineeringMicrosystems & Nanoengineering - Construction of multiple concentration gradients for single-cell level drug screening
Read more »
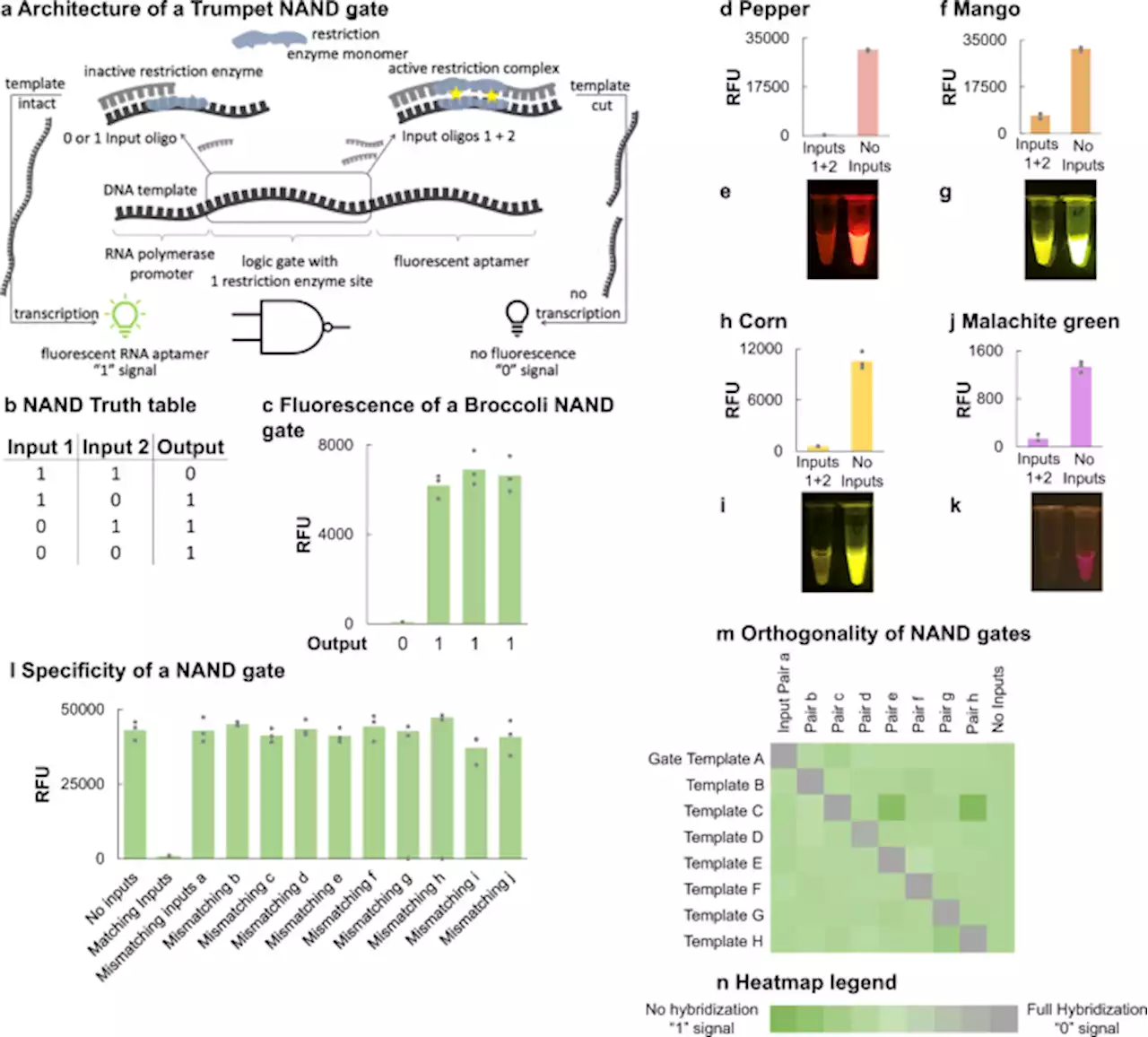 Trumpet is an operating system for simple and robust cell-free biocomputing - Nature CommunicationsBiological computation is becoming a viable and fast-growing alternative to traditional electronic computing. Here the authors present Trumpet, which uses DNA and enzymes to build logic gate circuits with amplified fluorescent readout.
Trumpet is an operating system for simple and robust cell-free biocomputing - Nature CommunicationsBiological computation is becoming a viable and fast-growing alternative to traditional electronic computing. Here the authors present Trumpet, which uses DNA and enzymes to build logic gate circuits with amplified fluorescent readout.
Read more »
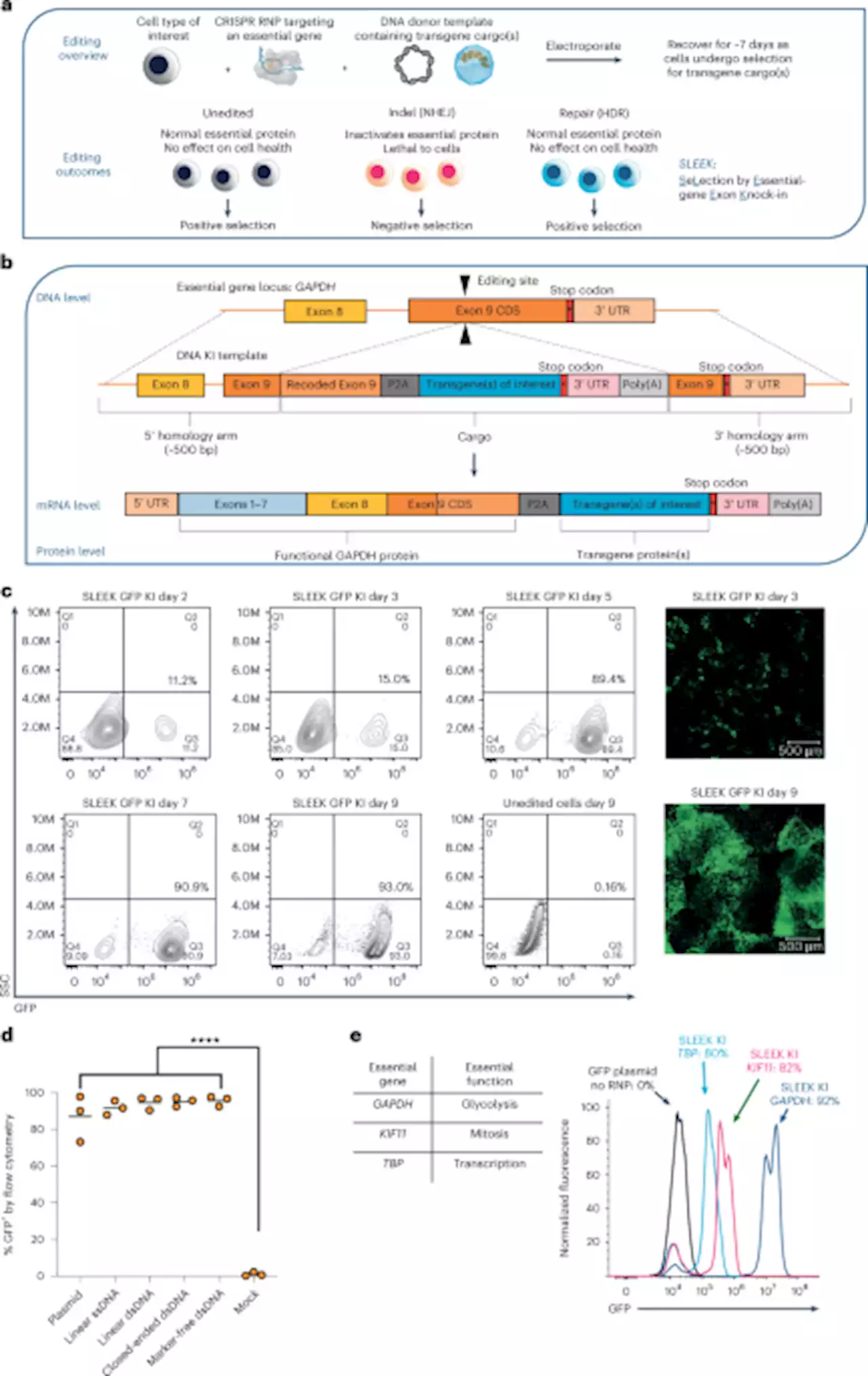 A highly efficient transgene knock-in technology in clinically relevant cell types - Nature BiotechnologyTransgene knock-ins into housekeeping genes lead to high efficiency of cell selection.
A highly efficient transgene knock-in technology in clinically relevant cell types - Nature BiotechnologyTransgene knock-ins into housekeeping genes lead to high efficiency of cell selection.
Read more »
A nucleotide binding–independent role for γ-tubulin in microtubule capping and cell division | Journal of Cell Biology | Rockefeller University PressBerman et al. examine the capping activity of the γ-TuRC. Using in vitro and cellular assays, they characterize how the γ-TuRC's nucleotide-independent capping
Read more »
