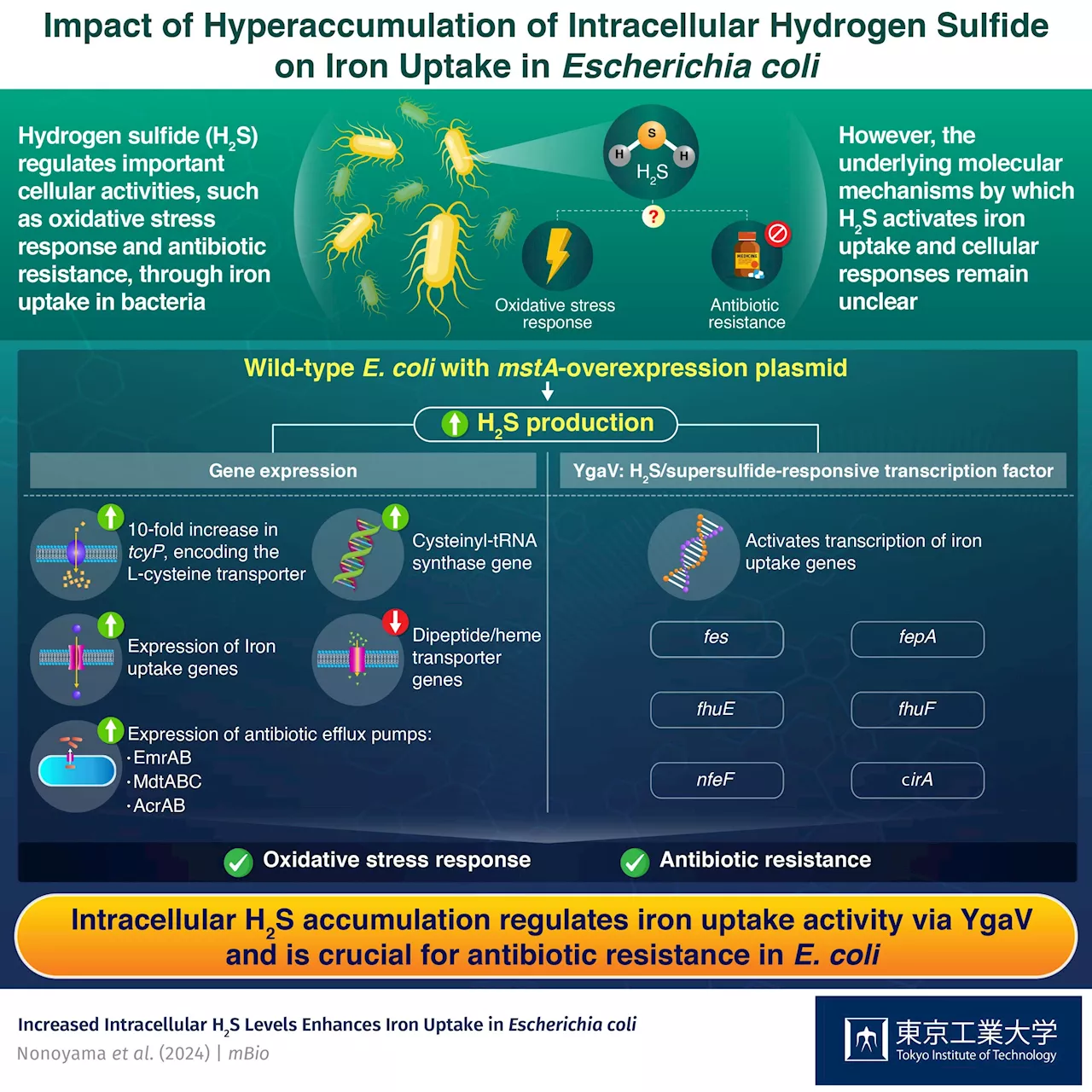
Antibiotic resistance and oxidative stress response are important biological mechanisms that help bacteria thrive, especially pathogenic bacteria like Escherichia coli. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a chemical messenger molecule, regulates several intracellular activities in bacteria such as responses to oxidative stress and antibiotics.
Exploring the role of hydrogen sulfide in the expression of iron uptake genes in E. coli retrieved 27 September 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-09-exploring-role-hydrogen-sulfide-iron.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.21 hours ago Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Physics News Science News Technology News Physics Materials Nanotech Technology Science
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Bill Gates-backed startup says a global gold rush for buried hydrogen is picking up momentumGeologic hydrogen — sometimes known as white, gold or natural hydrogen — refers to hydrogen gas that is found in its natural form beneath Earth’s…
Bill Gates-backed startup says a global gold rush for buried hydrogen is picking up momentumGeologic hydrogen — sometimes known as white, gold or natural hydrogen — refers to hydrogen gas that is found in its natural form beneath Earth’s…
Read more »
 Waging war on 'superbugs' in aged careThere's an urgent need for more careful antibiotic management to protect older people living in residential aged care from the dangerous spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria or 'superbugs', researchers warn.
Waging war on 'superbugs' in aged careThere's an urgent need for more careful antibiotic management to protect older people living in residential aged care from the dangerous spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria or 'superbugs', researchers warn.
Read more »
 Antibiotic Overuse in Nursing Homes Could Foster 'Superbugs'Senior residential homes are breeding grounds for antibiotic-resistant bacteria, due to overprescription of antibiotics, a new study says.
Antibiotic Overuse in Nursing Homes Could Foster 'Superbugs'Senior residential homes are breeding grounds for antibiotic-resistant bacteria, due to overprescription of antibiotics, a new study says.
Read more »
 Phage editing technology could lead to alternative treatments for antibiotic-resistant bacteriaAs antibiotic resistance becomes an increasingly serious threat to our health, the scientific and medical communities are searching for new medicines to fight infections. Researchers at Gladstone Institutes have just moved closer to that goal with a novel technique for harnessing the power of bacteriophages.
Phage editing technology could lead to alternative treatments for antibiotic-resistant bacteriaAs antibiotic resistance becomes an increasingly serious threat to our health, the scientific and medical communities are searching for new medicines to fight infections. Researchers at Gladstone Institutes have just moved closer to that goal with a novel technique for harnessing the power of bacteriophages.
Read more »
 Silver nanoparticles and a new sensing method can fight back against antibiotic-resistant biofilmsFrom safeguarding our food supply to preventing hospital infections, the battle against antibiotic-resistant bacteria is a growing challenge. Some bacteria can form biofilms, thick aggregates of millions of individual cells surrounded by protective mucus-like substances that easily adhere to surfaces.
Silver nanoparticles and a new sensing method can fight back against antibiotic-resistant biofilmsFrom safeguarding our food supply to preventing hospital infections, the battle against antibiotic-resistant bacteria is a growing challenge. Some bacteria can form biofilms, thick aggregates of millions of individual cells surrounded by protective mucus-like substances that easily adhere to surfaces.
Read more »
 For C. diff, antibiotic resistance comes at a costMichael Schubert is a veteran science and medicine communicator. He writes across all areas of the life sciences and medicine but specializes in the study of the very small — from the genes that make our bodies work to the chemicals that could support life on other planets. Mick holds graduate degrees in medical biochemistry and molecular biology.
For C. diff, antibiotic resistance comes at a costMichael Schubert is a veteran science and medicine communicator. He writes across all areas of the life sciences and medicine but specializes in the study of the very small — from the genes that make our bodies work to the chemicals that could support life on other planets. Mick holds graduate degrees in medical biochemistry and molecular biology.
Read more »