The mechanism facilitating the smooth movement of the oceanic lithosphere over the underlying asthenosphere (upper mantle) remains poorly understood. Recently, researchers from Japan investigated the effect of water on the seismic properties of olivine rocks, finding that water retention in the asthenosphere can induce sharp drops in shear wave velocity. This also explained other seismic changes observed at the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary. These findings provide invaluable insights into the diverse seismic activities on Earth.
The oceanic lithosphere, which constitutes the top layer including Earth's crust and mantle below the oceans, has long intrigued scientists due to its peculiar behavior. This layer appears to glide over a weaker region below called the asthenosphere, characterized by high seismic attenuation and low shear wave velocity.
In this regard, a team of researchers from Japan, led by Professor Takashi Yoshino from the Institute for Planetary Materials at Okayama University, has recently investigated the effect of water on the seismic properties of titanium-free olivine rocks, similar to those found in the asthenosphere.
The experiments revealed that water had a significant effect, enhancing the energy dispersion and reducing the elastic moduli of the rocks across a wide range of frequencies. Additionally, the researchers observed a seismic attenuation peak at higher frequencies of 1 to 5 seconds, which became more pronounced with increasing water content."The presence of water induces attenuation at higher frequencies, leading to a decrease in the velocity of seismic waves.
Notably, the researchers acknowledge that their conclusion assumes a negligible effect of iron on hydrogen-related defects in the rocks, indicating the need for further research to explore the anelastic properties of iron-bearing olivine rocks.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Japan’s Suzuki: Japan at a critical stage whether to spur consumption, wage growth“Japan at a critical stage whether to spur consumption or wage growth,” Japanese Finance Minister Shunichi Suzuki said on Tuesday. Suzuki added that i
Japan’s Suzuki: Japan at a critical stage whether to spur consumption, wage growth“Japan at a critical stage whether to spur consumption or wage growth,” Japanese Finance Minister Shunichi Suzuki said on Tuesday. Suzuki added that i
Read more »
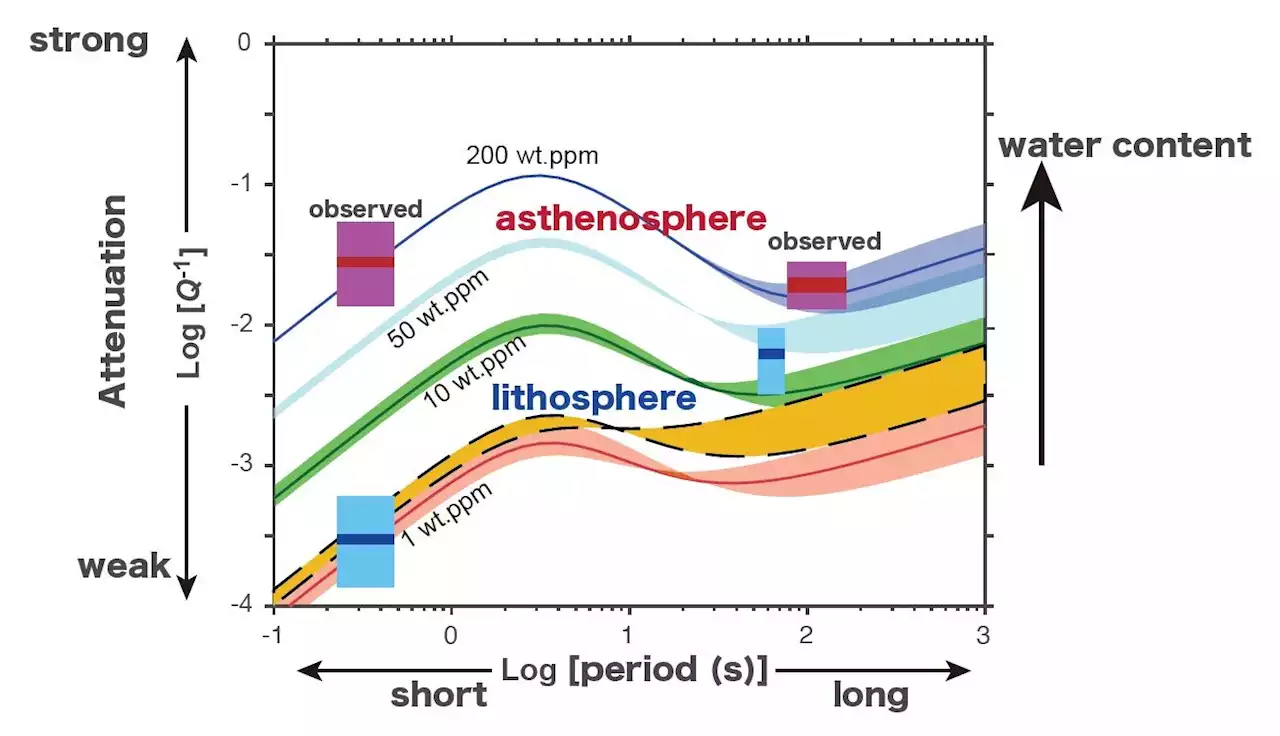 Exploring the effect of water on seismic wave attenuation in the upper mantleThe oceanic lithosphere, which constitutes the top layer including Earth's crust and mantle below the oceans, has long intrigued scientists due to its peculiar behavior. This layer appears to glide over a weaker region below called the asthenosphere, characterized by high seismic attenuation and low shear wave velocity.
Exploring the effect of water on seismic wave attenuation in the upper mantleThe oceanic lithosphere, which constitutes the top layer including Earth's crust and mantle below the oceans, has long intrigued scientists due to its peculiar behavior. This layer appears to glide over a weaker region below called the asthenosphere, characterized by high seismic attenuation and low shear wave velocity.
Read more »
 Why Aren’t Disabled Astronauts Exploring Space?Journeying into the future will require embracing disability—and recognizing its power in our changing world.
Why Aren’t Disabled Astronauts Exploring Space?Journeying into the future will require embracing disability—and recognizing its power in our changing world.
Read more »
10 Politicians Who Recently Ditched Democratic PartyPopular Dallas Mayor Eric Johnson on Friday became the latest in a string of politicians to defect from the Democratic Party due to frustrations or concerns with the direction it's headed.
Read more »
 Exploring the Convergence of Innovation in the Blockchain EcosystemIn this article, we will embark on a journey through this convergence, and explore how these seemingly unrelated elements are shaping the blockchain ecosystem.
Exploring the Convergence of Innovation in the Blockchain EcosystemIn this article, we will embark on a journey through this convergence, and explore how these seemingly unrelated elements are shaping the blockchain ecosystem.
Read more »
