Endogenous exosomes act as decoys for SARS-CoV-2 Exosomes SARSCoV2 Coronavirus Disease COVID Tolllikereceptors Autophagic Interferons PLOSBiology UZH_ch UZH_Virology
Study: SARS-CoV-2 takes the bait: Exosomes as endogenous decoys. Image Credit: Meletios Verras / Shutterstock
In a study, researchers at the University of Zurich, Switzerland, identified a subset of exosomes, termed defensosomes, secreted specifically during bacterial infection. These defensosomes incorporated surface receptors to the levels typically expressed on cells and were decoys for bacterial toxins, which otherwise would have mediated toxicity through interactions with receptors on living cells.
SARS-CoV-2 infection triggers the secretion of ACE2-coated defensosomes Next, they showed that SARS-CoV-2 could trigger the secretion of ACE2-coated exosomes in cell-based assays in vitro. This induction was comparable to bacterial induction in that both required autophagy components of the host and was recapitulated by some immune stimuli.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Is there any impact of COVID-19 vaccines on the fertility of men and women of reproductive age?Is there any impact of COVID-19 vaccines on the fertility of men and women of reproductive age? Unicatt COVID19 coronavirus covid ferility SARSCoV2 reproductivehealth
Is there any impact of COVID-19 vaccines on the fertility of men and women of reproductive age?Is there any impact of COVID-19 vaccines on the fertility of men and women of reproductive age? Unicatt COVID19 coronavirus covid ferility SARSCoV2 reproductivehealth
Read more »
 In Denmark, Omicron reinfections reveal ineffective post-COVID-19 immunityIn Denmark, Omicron reinfections reveal ineffective post-COVID-19 immunity Denmark immunity Omicron Coronavirus Disease COVID HerdImmunity medrxivpreprint cwru TAMU StanfordMed ColumbiaMed
In Denmark, Omicron reinfections reveal ineffective post-COVID-19 immunityIn Denmark, Omicron reinfections reveal ineffective post-COVID-19 immunity Denmark immunity Omicron Coronavirus Disease COVID HerdImmunity medrxivpreprint cwru TAMU StanfordMed ColumbiaMed
Read more »
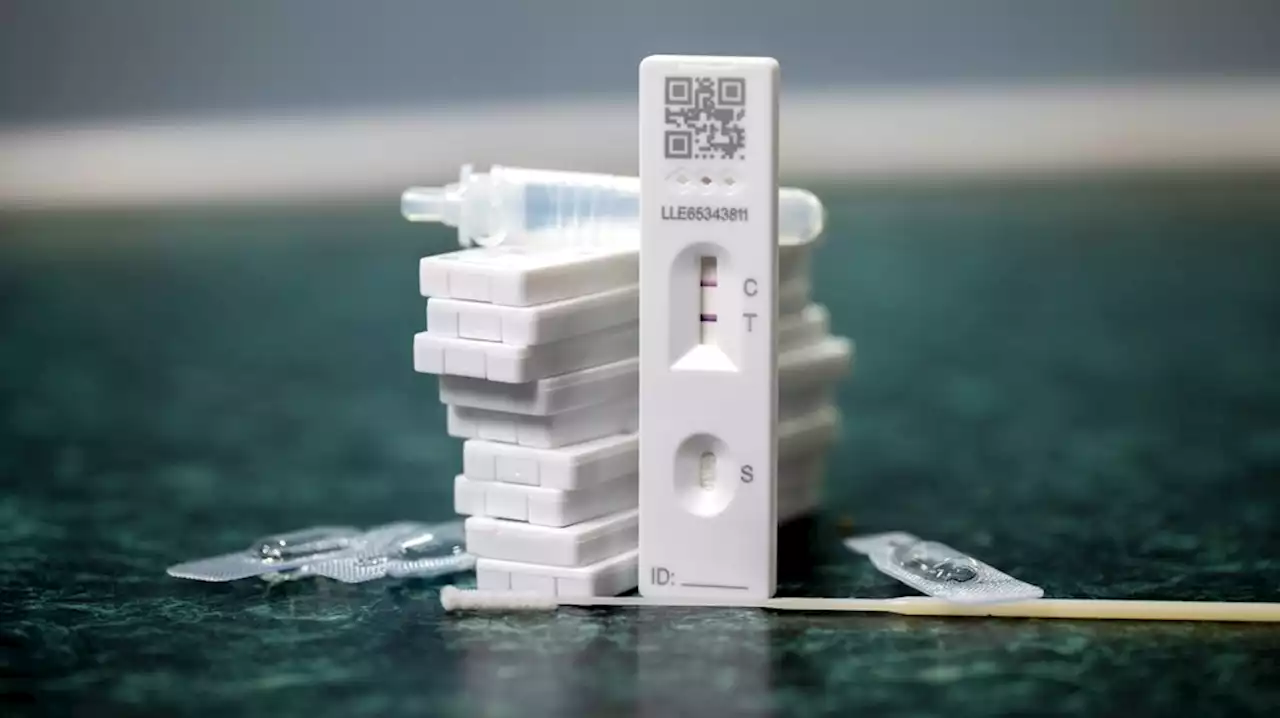 The relationship between antigen concentration and diagnostic test performance for SARS-CoV-2 on different types of samplesThe relationship between antigen concentration and diagnostic test performance for SARS-CoV-2 on different types of samples medrxivpreprint PPI_Insights UW SARSCoV2 COVID19 coronavirus covid antigen diagnostictest
The relationship between antigen concentration and diagnostic test performance for SARS-CoV-2 on different types of samplesThe relationship between antigen concentration and diagnostic test performance for SARS-CoV-2 on different types of samples medrxivpreprint PPI_Insights UW SARSCoV2 COVID19 coronavirus covid antigen diagnostictest
Read more »
 Molecular engineered low-cost highly effective RBD-based COVID vaccineIn a recent study posted to the bioRxiv* preprint server, an international team of researchers developed a second-generation severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) receptor binding domain (RBD) antigen (RBD-J6) by molecular engineering with two additional amino acid (aa) substitutions (S383D and L518D mutations) in a hydrophobic cryptic RBD core epitope to enhance stability and expression against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs).
Molecular engineered low-cost highly effective RBD-based COVID vaccineIn a recent study posted to the bioRxiv* preprint server, an international team of researchers developed a second-generation severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) receptor binding domain (RBD) antigen (RBD-J6) by molecular engineering with two additional amino acid (aa) substitutions (S383D and L518D mutations) in a hydrophobic cryptic RBD core epitope to enhance stability and expression against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs).
Read more »
