Earth can regulate its own temperature over millennia, new study finds MIT ScienceAdvances
confirms that the planet harbors a"stabilizing feedback" mechanism that acts over hundreds of thousands of years to pull the climate back from the brink, keepingJust how does it accomplish this? A likely mechanism is"silicate weathering"—a geological process by which the slow and steady weathering of silicate rocks involvesthat ultimately draw carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere and into ocean sediments, trapping the gas in rocks.
to see whether the data revealed any patterns characteristic of stabilizing phenomena that reined in global temperatures on a geologic timescale.swings are dampened over timescales of hundreds of thousands of years. The duration of this effect is similar to the timescales over which silicate weathering is predicted to act.
Scientists have previously seen hints of a climate-stabilizing effect in the Earth's carbon cycle: Chemical analyses of ancient rocks have shown that the flux of carbon in and out of Earth's surface environment has remained relatively balanced, even through dramatic swings in global temperature. Furthermore, models of silicate weathering predict that the process should have some stabilizing effect on the global climate.
"This whole study is only possible because there have been great advances in improving the resolution of these deep-sea temperature records," Arnscheidt notes."Now we have data going back 66 million years, with data points at most thousands of years apart."To the data, the team applied the mathematical theory of stochastic differential equations, which is commonly used to reveal patterns in widely fluctuating datasets.
"To some extent, it's like your car is speeding down the street, and when you put on the brakes, you slide for a long time before you stop," Rothman says."There's a timescale over which frictional resistance, or a stabilizing feedback, kicks in, when the system returns to a steady state." "There's an idea that chance may have played a major role in determining why, after more than 3 billion years, life still exists," Rothman offers.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
Baby Fever: What to Do If Baby's Temperature SpikesWorried your child might have a baby fever? Learn what causes fever in babies and signs to look out for, plus what to do if baby has a fever and how to take baby's temperature properly.
Read more »
 G20 agrees to pursue efforts to limit temperature rise to 1.5°C - declarationLeaders at the G20 meeting in Bali on Wednesday agreed to pursue efforts to limit the rise in global temperatures to 1.5C, including speeding up efforts to phase down unabated use of coal.
G20 agrees to pursue efforts to limit temperature rise to 1.5°C - declarationLeaders at the G20 meeting in Bali on Wednesday agreed to pursue efforts to limit the rise in global temperatures to 1.5C, including speeding up efforts to phase down unabated use of coal.
Read more »
 G20 agrees to pursue efforts to limit temperature rise to 1.5CLeaders at the G20 meeting in Bali on Wednesday agreed to pursue efforts to limit the rise in global temperatures to 1.5 degrees Celsius and recognized the need to speed up efforts to phase down coal use, in a potential boost to the COP27 climate talks.
G20 agrees to pursue efforts to limit temperature rise to 1.5CLeaders at the G20 meeting in Bali on Wednesday agreed to pursue efforts to limit the rise in global temperatures to 1.5 degrees Celsius and recognized the need to speed up efforts to phase down coal use, in a potential boost to the COP27 climate talks.
Read more »
 G20 Summit: World leaders express resolve to limit temperature rise to 1.5CLeaders at the Group of 20 meeting in Bali agree to pursue efforts to limit the rise in global temperatures to 1.5C, including speeding up efforts to 'phase down' the unabated use of coal
G20 Summit: World leaders express resolve to limit temperature rise to 1.5CLeaders at the Group of 20 meeting in Bali agree to pursue efforts to limit the rise in global temperatures to 1.5C, including speeding up efforts to 'phase down' the unabated use of coal
Read more »
 A cold snap is coming to Houston this week. Here's how to prepareThe temperature overnight in Houston is expected to drop as low as 45 degrees, which may...
A cold snap is coming to Houston this week. Here's how to prepareThe temperature overnight in Houston is expected to drop as low as 45 degrees, which may...
Read more »
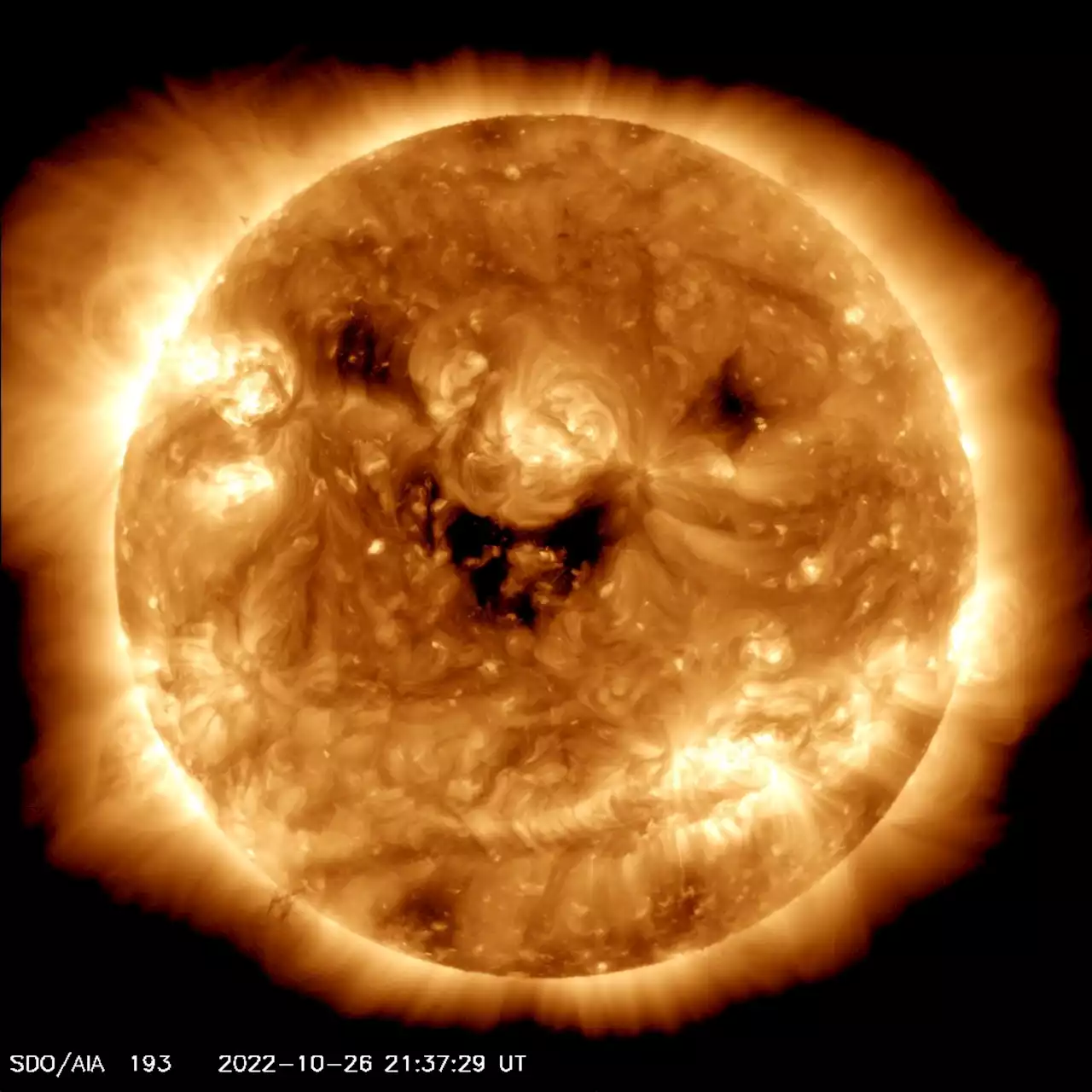 The Sun Could Hurl Powerful Storms at Earth From its Goofy SmileOur Sun is the very reason we’re alive. It provides warmth and the energy our planet needs to keep going. Now you can add photogenic to its illustrious résumé, as NASA recently photographed our giant ball of nuclear fusion doing something quite peculiar. “Say cheese!” NASA Sun & Space (NASASun) tweeted on October 26th. “Today, … Continue reading 'The Sun Could Hurl Powerful Storms at Earth From its Goofy Smile'
The Sun Could Hurl Powerful Storms at Earth From its Goofy SmileOur Sun is the very reason we’re alive. It provides warmth and the energy our planet needs to keep going. Now you can add photogenic to its illustrious résumé, as NASA recently photographed our giant ball of nuclear fusion doing something quite peculiar. “Say cheese!” NASA Sun & Space (NASASun) tweeted on October 26th. “Today, … Continue reading 'The Sun Could Hurl Powerful Storms at Earth From its Goofy Smile'
Read more »
