It was, to put it mildly, a bad day on Earth when an asteroid smacked Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula 66 million years ago, causing a global calamity that erased three-quarters of the world's species and ended the age of dinosaurs.
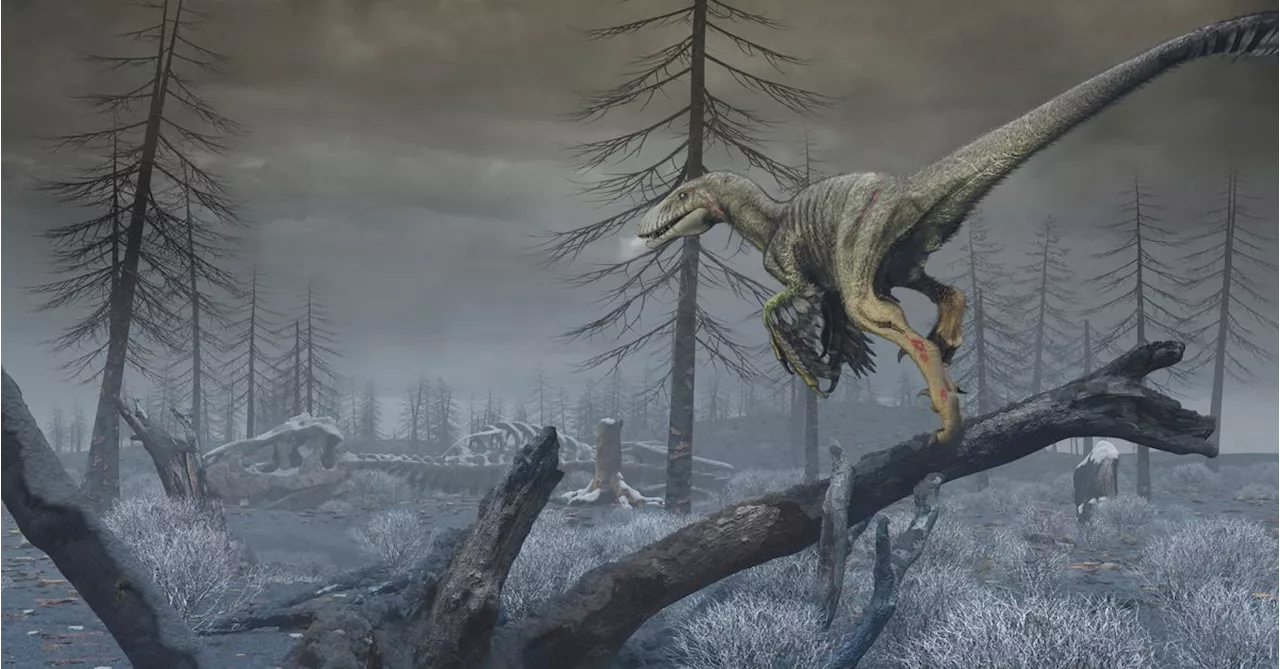
This artist's reconstruction depicts North Dakota in the first months following the impact of an asteroid off Mexico's coast 66 million years ago, showing a dark, dusty and cold world in which the last non-avian dinosaurs, illustrated by the species Dakotaraptor steini, were on the edge of...
Researchers on Monday revealed the potent role that dust from pulverized rock ejected into the atmosphere from the impact site may have played in driving extinctions, choking the atmosphere and blocking plants from harnessing sunlight for life-sustaining energy in a process called photosynthesis. The researchers ran paleoclimate simulations based on sediment unearthed at a North Dakota paleontological site called Tanis that preserved evidence of the post-impact conditions, including the prodigious dust fallout.
While prior research highlighted two other factors - sulfur released after the impact and soot from the wildfires - this study indicated dust played a larger role than previously known.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 New study explores role of post-impact dust in dinosaur extinctionInteresting Engineering is a cutting edge, leading community designed for all lovers of engineering, technology and science.
New study explores role of post-impact dust in dinosaur extinctionInteresting Engineering is a cutting edge, leading community designed for all lovers of engineering, technology and science.
Read more »
 Sun-blocking dust from asteroid impact drove the dinosaur extinctionThe Chicxulub impact 66 million years ago filled the sky with fine silicate dust, which blocked out sunlight and lingered for 15 years
Sun-blocking dust from asteroid impact drove the dinosaur extinctionThe Chicxulub impact 66 million years ago filled the sky with fine silicate dust, which blocked out sunlight and lingered for 15 years
Read more »
 In early 2029, Earth will likely lock into breaching key warming threshold, scientists calculateA new study says that in a little more than five years the world will likely be unable to stay below the internationally agreed temperature limit for global warming if it continues to burn fossil fuels at its current rate.
In early 2029, Earth will likely lock into breaching key warming threshold, scientists calculateA new study says that in a little more than five years the world will likely be unable to stay below the internationally agreed temperature limit for global warming if it continues to burn fossil fuels at its current rate.
Read more »
 In early 2029, Earth will likely lock into breaching key warming threshold, scientists calculateA new study says that in a little more than five years the world will likely be unable to stay below the internationally agreed temperature limit for global warming if it continues to burn fossil fuels at its current rate.
In early 2029, Earth will likely lock into breaching key warming threshold, scientists calculateA new study says that in a little more than five years the world will likely be unable to stay below the internationally agreed temperature limit for global warming if it continues to burn fossil fuels at its current rate.
Read more »
 New Marvel Book Designates MCU as Earth-616, Creating More Multiversal HeadachesSomewhere out there Iman Vellani is very upset about something, and she is not quite sure why.
New Marvel Book Designates MCU as Earth-616, Creating More Multiversal HeadachesSomewhere out there Iman Vellani is very upset about something, and she is not quite sure why.
Read more »
