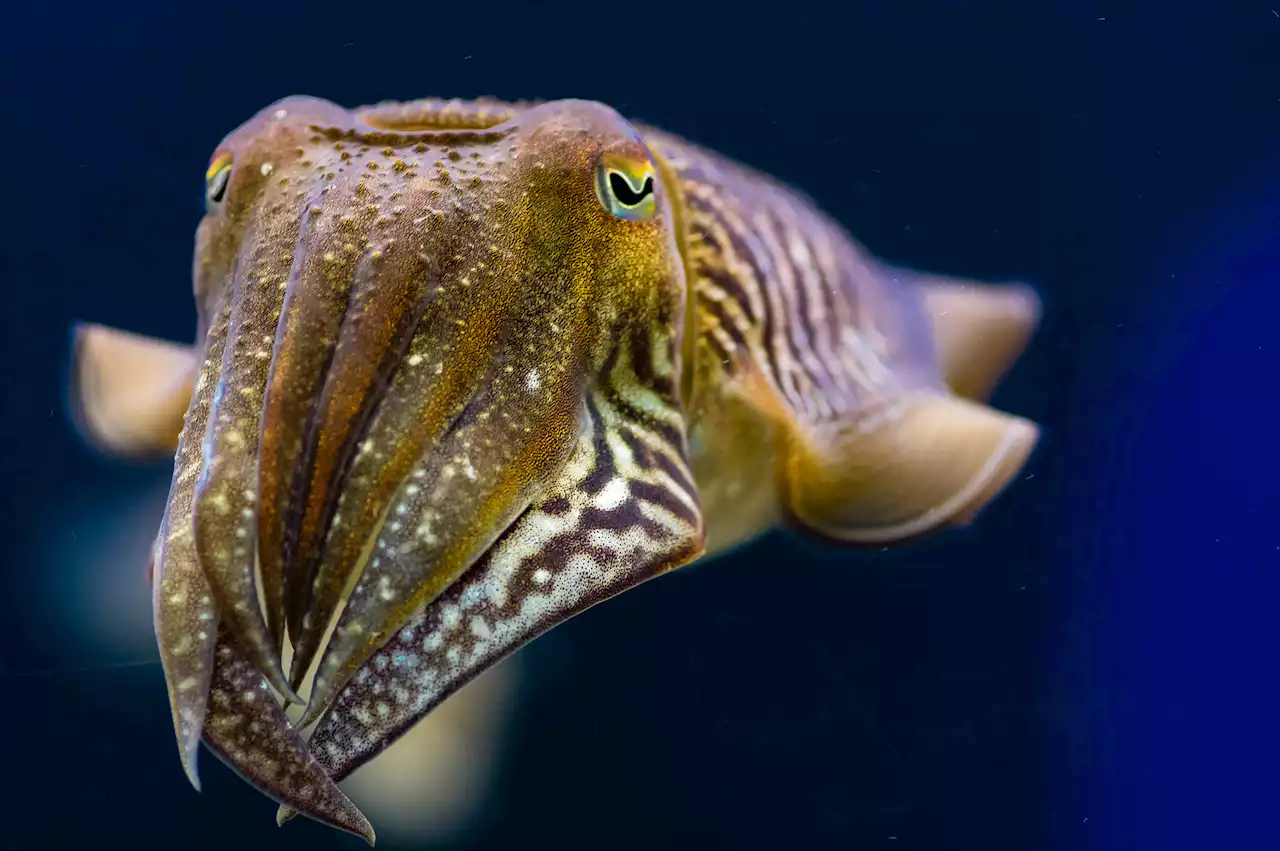
Scientists put Cuttlefish through a marshmallow chest to see how intelligent they are and the results are shocking.
Scientists have discovered something intriguing about cuttlefish after putting them through a “marshmallow test.” The test, which is designed for children, showed that the cuttlefish have the ability to exert self-control for several seconds, whereas several other creatures can exert it for several minutes.
This discovery, the researchers say, is an example of advanced self-control and shows that the creatures perform better in cognitive tasks. It has also been hypothesized that these positive results could show a response to specific socio-ecological pressures. This ability to learn and adapt could be part of what helps the cuttlefish survive in the dangerous world that it lives within. The new marshmallow test that the cuttlefish were given saw the cuttlefish put in a small area with crab meat. They found that the cuttlefish could refrain from eating the crab meat because they learned that something better was coming at dinner time.The test is very simple, and because it can be adjusted so simply, it’s easy to adjust it for multiple types of animals.
However, it’s difficult to tell whether the cuttlefish passing the marshmallow test is because of it exerting self-control or if it was just a change in their foraging behavior. Perhaps more research into cuttlefish and other animals could help us better understand whether or not it’s self-control. Previously scientists madeThey also found that it could adapt to changes in test parts that gave the cuttlefish some kind of reward.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
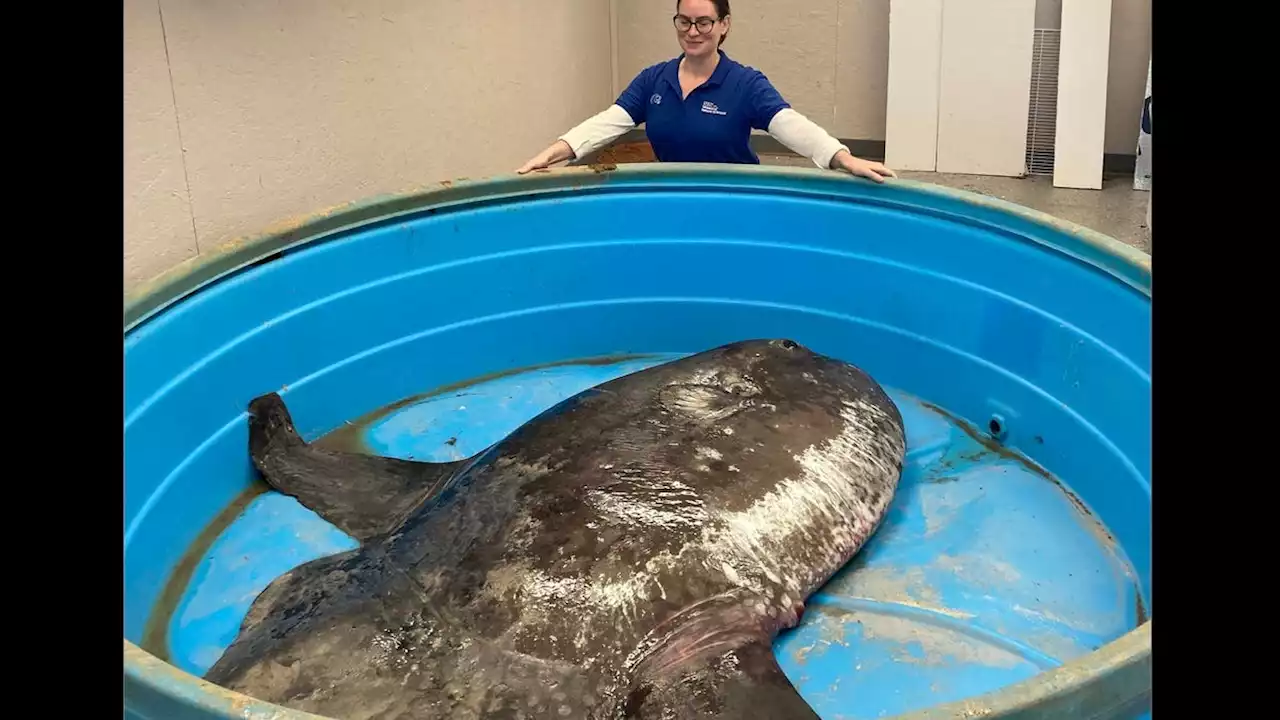 450-pound sunfish discovered on North Carolina beach; scientists are overjoyedA massive sunfish was discovered Wednesday on a North Carolina beach and was so heavy that scientists required a horse scale to obtain its weight.
450-pound sunfish discovered on North Carolina beach; scientists are overjoyedA massive sunfish was discovered Wednesday on a North Carolina beach and was so heavy that scientists required a horse scale to obtain its weight.
Read more »
 Scientists just found mountains of sugar hidden beneath the oceanSeagrass ecosystems hold colossal reserves of sugar we never knew existed before, with 32 billion cans of Coca-Cola's worth of it hiding in the seabed.
Scientists just found mountains of sugar hidden beneath the oceanSeagrass ecosystems hold colossal reserves of sugar we never knew existed before, with 32 billion cans of Coca-Cola's worth of it hiding in the seabed.
Read more »
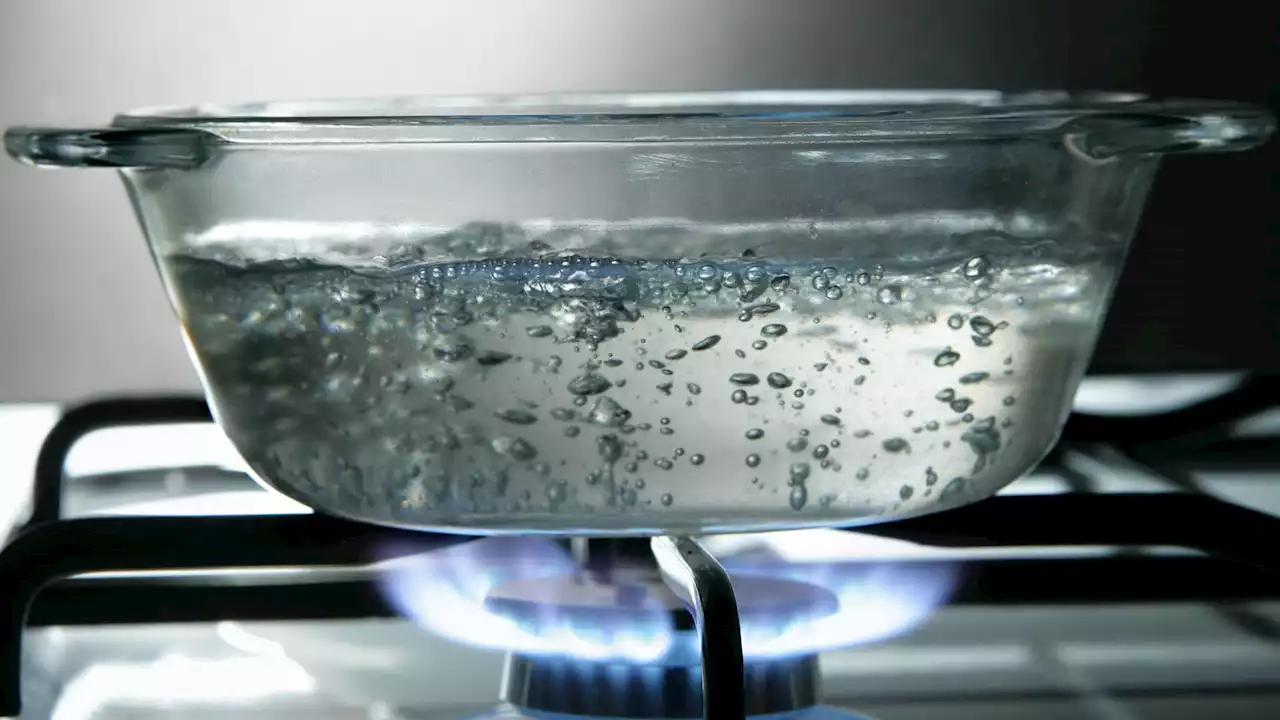 MIT scientists have found a way to boil water more quickly and efficientlyMIT scientists have found a way to improve at the same time the two key parameters that are conducive to the boiling process, the heat transfer coefficient (HTC) and the critical heat flux (CHF).
MIT scientists have found a way to boil water more quickly and efficientlyMIT scientists have found a way to improve at the same time the two key parameters that are conducive to the boiling process, the heat transfer coefficient (HTC) and the critical heat flux (CHF).
Read more »
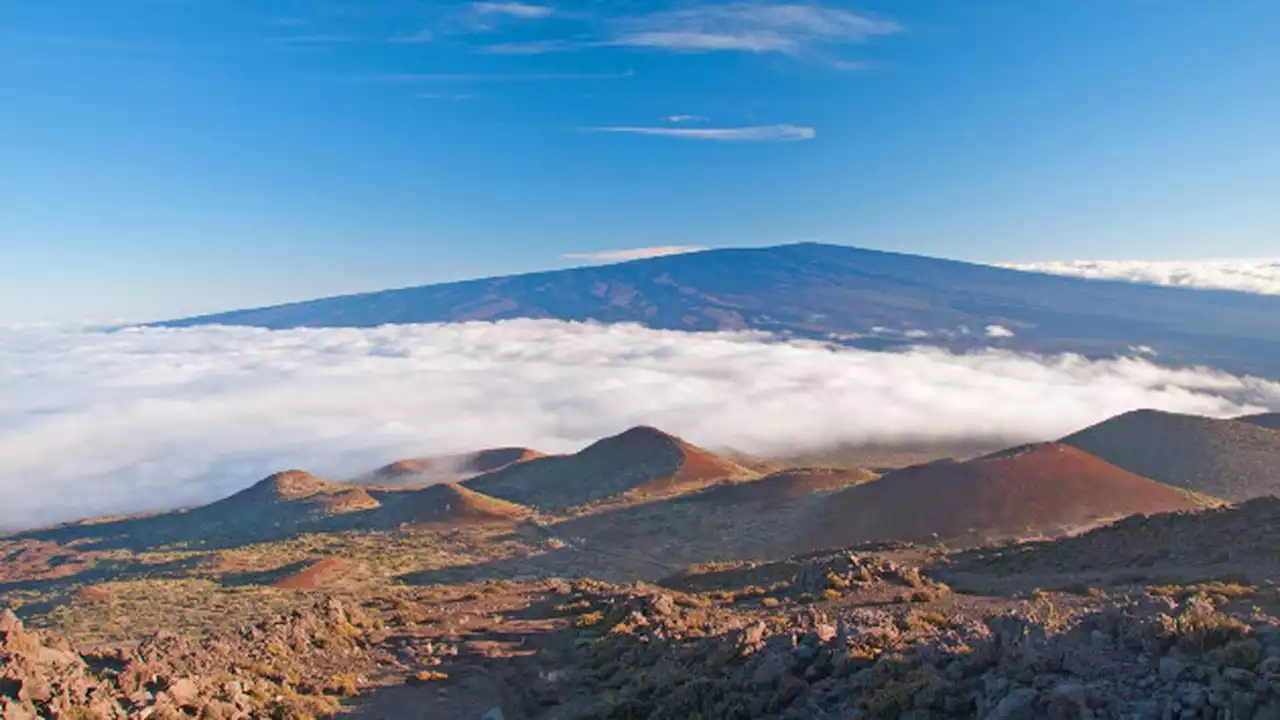 Scientists observe 2 new lava flows on Mauna Loa, the world's largest active volcanoNEW YORK — Scientists have observed two new lava flows out of the Mauna Loa volcano on Hawaii's Big Island -- the largest active volcano in the world.
Scientists observe 2 new lava flows on Mauna Loa, the world's largest active volcanoNEW YORK — Scientists have observed two new lava flows out of the Mauna Loa volcano on Hawaii's Big Island -- the largest active volcano in the world.
Read more »
 In the hunt for a male contraceptive, scientists look to stop sperm in their tracksFor decades birth control research focused on women. Now there's a new push to develop gels, pills or other products that could keep men from getting their partners pregnant.
In the hunt for a male contraceptive, scientists look to stop sperm in their tracksFor decades birth control research focused on women. Now there's a new push to develop gels, pills or other products that could keep men from getting their partners pregnant.
Read more »
 Resurrecting Billon-Year-Old Enzymes – Scientists Reveal New Key Information About PhotosynthesisBack to the future of photosynthesis. Rubisco, the central biocatalyst in photosynthesis, is the most prevalent enzyme on the planet. A group of Max Planck Institute researchers has uncovered one of the key early photosynthesis adaptations by reconstructing billion-year-old enzymes. Their findings
Resurrecting Billon-Year-Old Enzymes – Scientists Reveal New Key Information About PhotosynthesisBack to the future of photosynthesis. Rubisco, the central biocatalyst in photosynthesis, is the most prevalent enzyme on the planet. A group of Max Planck Institute researchers has uncovered one of the key early photosynthesis adaptations by reconstructing billion-year-old enzymes. Their findings
Read more »
