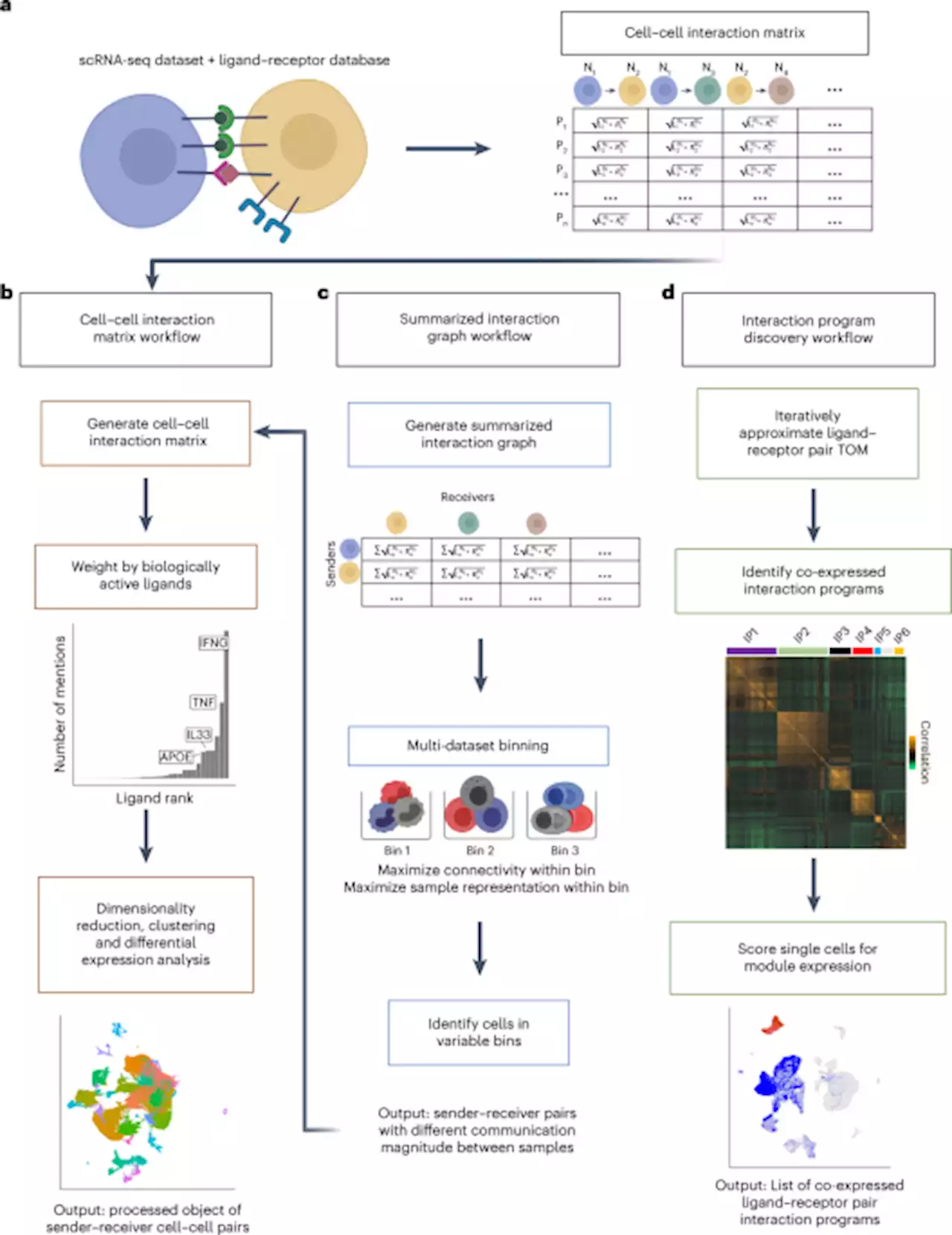
Comparative analysis of cell–cell communication at single-cell resolution
, which indicates that these circuits may induce downstream Notch signaling. In sum, these data illustrate how the single-cell resolution of Scriabin’s CCC analysis workflow can perform integrated longitudinal analyses, nominating hypotheses for experimental validation.Most existing CCC methodologies aggregate ligand and receptor expression values at the level of the cell type or cluster, potentially obscuring biologically valuable information.
A major challenge of single-cell-resolved CCC analysis is data inflation: because CCC analysis fundamentally involves performing pairwise calculations on cells or cell groups, it is frequently computationally prohibitive to analyze every sender–receiver cell pair. Some existing tools, such as NICHES, support single-cell resolution CCC analysis but involve subsampling strategies when applied at scale.
We observe that aggregation obscures potentially biologically meaningful subsets of T cells in SCC as well as in RRs in leprosy granulomas. Owing to the degree of transcriptional perturbation in T cells during RRs, subclustering is not always a tenable approach to increasing the resolution of CCC analyses because it, in turn, can preclude analysis at a per-sample level.
As the throughput of scRNA-seq workflows continues to increase, it will be important that single-cell-resolution CCC methods are scalable to any dataset size. We introduce two complementary workflows to address this challenge.
As an alternative, we also introduce a second single-cell-resolution CCC workflow that is scalable to datasets of any size. The interaction program discovery workflow of Scriabin accomplishes this by focusing first on common patterns of ligand–receptor pair co-expression rather than individual cell–cell pairs. Individual cells can be scored for expression of these interaction programs post hoc, enabling downstream comparative analyses with a comprehensive view of CCC structure.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 The promise of phages - Nature BiotechnologyThe promise of phages Phage therapy is an exciting alternative to antibiotics. Why now?
The promise of phages - Nature BiotechnologyThe promise of phages Phage therapy is an exciting alternative to antibiotics. Why now?
Read more »
 New precision-breeding law unlocks gene editing in England - Nature BiotechnologyNature Biotechnology - New precision-breeding law unlocks gene editing in England
New precision-breeding law unlocks gene editing in England - Nature BiotechnologyNature Biotechnology - New precision-breeding law unlocks gene editing in England
Read more »
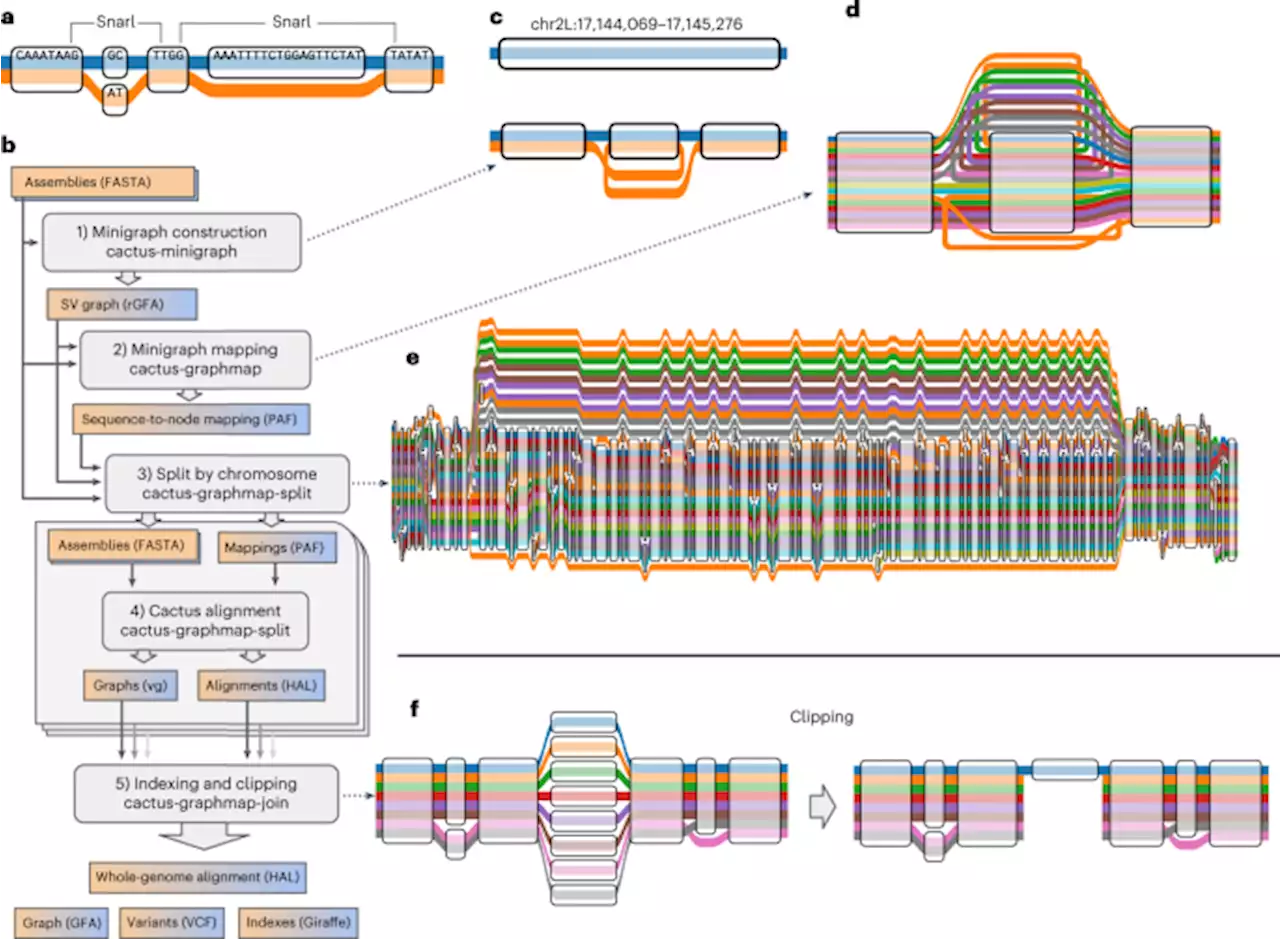 Pangenome graph construction from genome alignments with Minigraph-Cactus - Nature BiotechnologyConstructing genome graphs directly from genome assemblies overcomes single-reference bias.
Pangenome graph construction from genome alignments with Minigraph-Cactus - Nature BiotechnologyConstructing genome graphs directly from genome assemblies overcomes single-reference bias.
Read more »
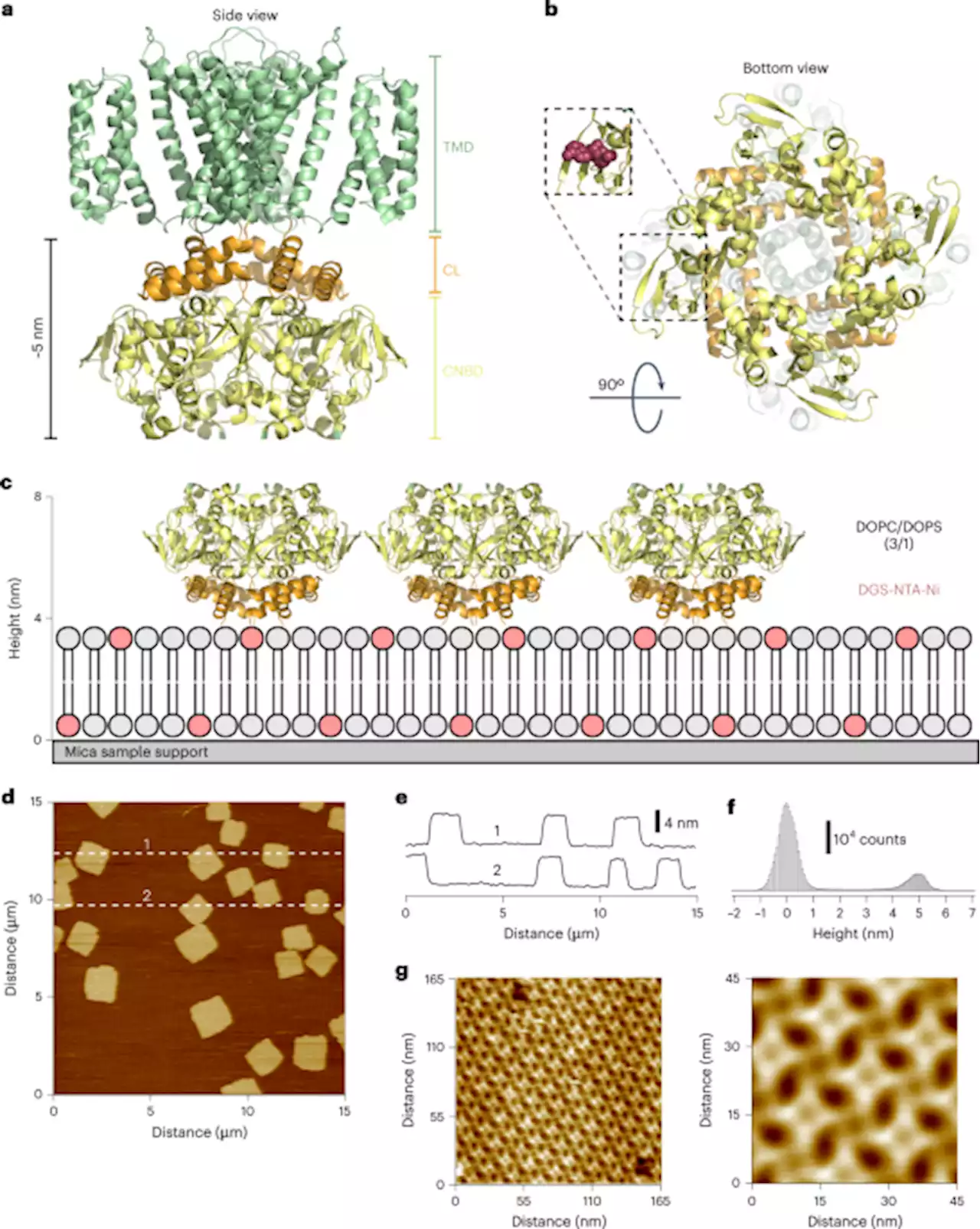 Discrimination between cyclic nucleotides in a cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel - Nature Structural & Molecular BiologyUsing atomic force microscopy, Pan et al. show that cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel SthK, which can be differentially activated by cAMP and cGMP, binds both cyclic nucleotides but only cAMP can access a deep-bound state that could be essential for cAMP-dependent channel activation.
Discrimination between cyclic nucleotides in a cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel - Nature Structural & Molecular BiologyUsing atomic force microscopy, Pan et al. show that cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel SthK, which can be differentially activated by cAMP and cGMP, binds both cyclic nucleotides but only cAMP can access a deep-bound state that could be essential for cAMP-dependent channel activation.
Read more »
 What Cargo Cult Rituals Show Us About Human NatureWhat a surprising cultural practice in Melanesia suggests about humanity—and why rituals are a social technology, writes xygalatas
What Cargo Cult Rituals Show Us About Human NatureWhat a surprising cultural practice in Melanesia suggests about humanity—and why rituals are a social technology, writes xygalatas
Read more »
 ‘Wild Scandinavia: Life on the Edge’ Review: Nordic Nature on PBSReview: With breathtaking cinematography, PBS's 'Wild Scandinavia: Life on the Edge' explores environments including the fiords of Norway and the open sea, as well as the creatures—and people—that inhabit them
‘Wild Scandinavia: Life on the Edge’ Review: Nordic Nature on PBSReview: With breathtaking cinematography, PBS's 'Wild Scandinavia: Life on the Edge' explores environments including the fiords of Norway and the open sea, as well as the creatures—and people—that inhabit them
Read more »