Chemists offer a new explanation for how collagen in dinosaur bones may have survived millions of years: An atomic-level interaction prevents its bonds from being broken down by water.
Chemists explain why dinosaur collagen may have survived for millions of years." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 4 September 2024. <www.sciencedaily.com
Researchers have developed a new way to fortify foods with vitamin A, which they hope could help to improve the health of millions of people around the world. In a new study, they showed that ... Scientists have used CT scans to digitally reconstruct the brain, inner ear, and surrounding bones of two well-preserved Daspletosaurus specimens. This massive tyrannosaur ...
Gray wolves are among the largest predators to have survived the extinction at the end of the last ice age. A new study analysing teeth and bones shows that the wolves may have survived by adapting ... There's a whole world behind the scenes at natural history museums that most people never see -- millions upon millions of dinosaur bones, pickled sharks, dried leaves, and every other part of ...What a Submerged Ancient Bridge Discovered in a Spanish Cave Reveals About Early Human Settlement
Molecular Biology Cell Biology Genetics Fossils Evolution Origin Of Life Dinosaurs
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Chemists develop new sustainable reaction for creating unique molecular building blocksPolymers can be thought of like trains: Just as a train is composed of multiple cars, polymers are made up of multiple monomers, and the couplings between the train cars are similar to the chemical bonds that link monomers together.
Chemists develop new sustainable reaction for creating unique molecular building blocksPolymers can be thought of like trains: Just as a train is composed of multiple cars, polymers are made up of multiple monomers, and the couplings between the train cars are similar to the chemical bonds that link monomers together.
Read more »
 Chemists develop new sustainable reaction for creating unique molecular building blocksPolymers can be thought of like trains: Just as a train is composed of multiple cars, polymers are made up of multiple monomers, and the couplings between the train cars are similar to the chemical bonds that link monomers together.
Chemists develop new sustainable reaction for creating unique molecular building blocksPolymers can be thought of like trains: Just as a train is composed of multiple cars, polymers are made up of multiple monomers, and the couplings between the train cars are similar to the chemical bonds that link monomers together.
Read more »
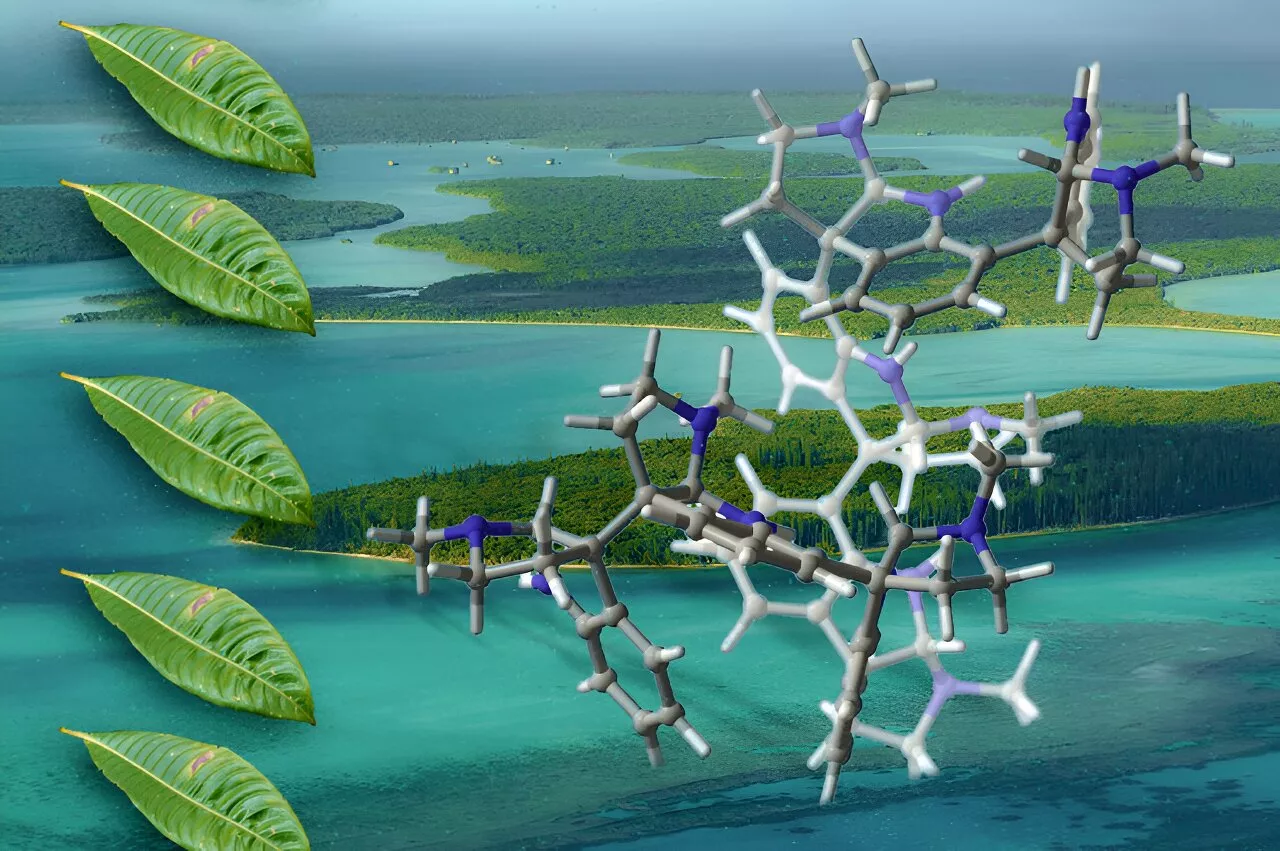 Chemists synthesize plant-derived molecules that hold potential as pharmaceuticalsMIT chemists have developed a new way to synthesize complex molecules that were originally isolated from plants and could hold potential as antibiotics, analgesics, or cancer drugs.
Chemists synthesize plant-derived molecules that hold potential as pharmaceuticalsMIT chemists have developed a new way to synthesize complex molecules that were originally isolated from plants and could hold potential as antibiotics, analgesics, or cancer drugs.
Read more »
 Chemists synthesize plant-derived molecules that hold potential as pharmaceuticalsChemists developed a way to synthesize complex molecules called oligocyclotryptamines, originally found in plants, which could hold potential as antibiotics, analgesics, or anticancer drugs.
Chemists synthesize plant-derived molecules that hold potential as pharmaceuticalsChemists developed a way to synthesize complex molecules called oligocyclotryptamines, originally found in plants, which could hold potential as antibiotics, analgesics, or anticancer drugs.
Read more »
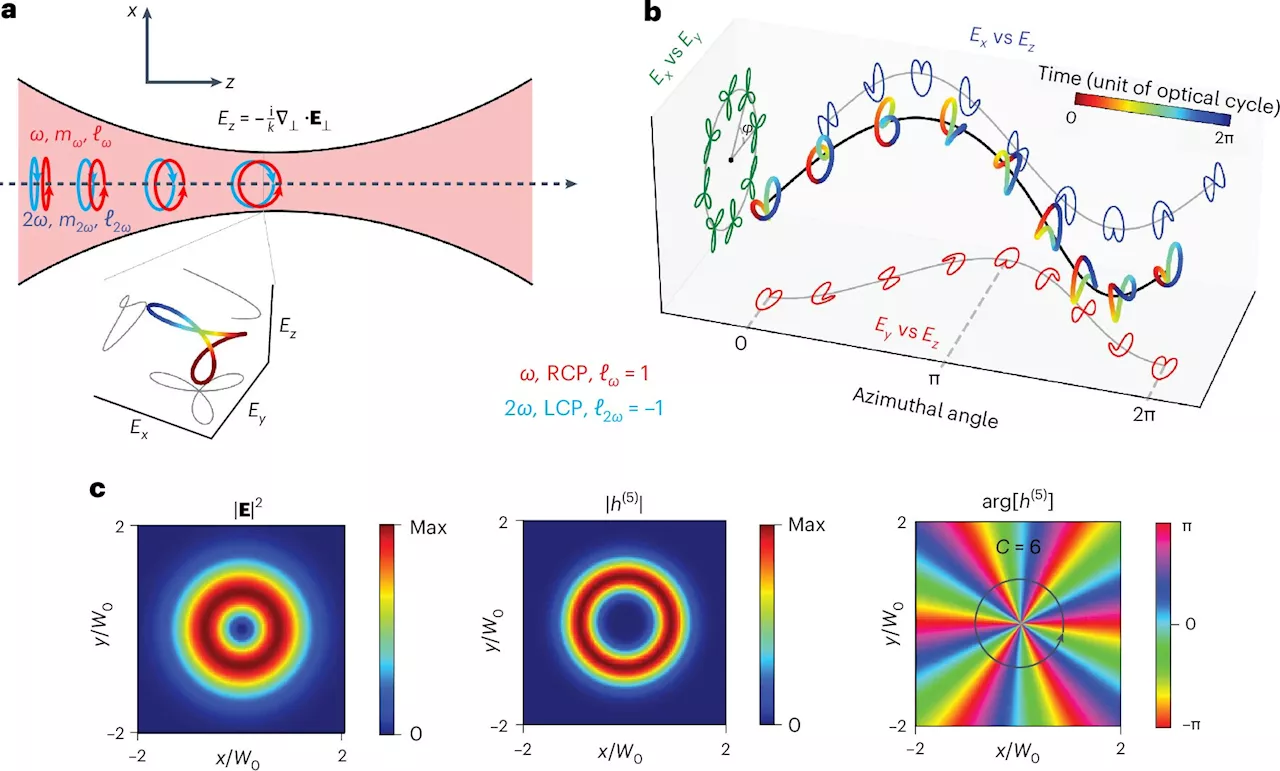 New 'chiral vortex' of light allows chemists to 'see' molecules through the mirrorAn entirely new structure of light is helping to measure chirality in molecules more accurately and robustly than ever before, in a major potential step for the pharmaceutical industry.
New 'chiral vortex' of light allows chemists to 'see' molecules through the mirrorAn entirely new structure of light is helping to measure chirality in molecules more accurately and robustly than ever before, in a major potential step for the pharmaceutical industry.
Read more »
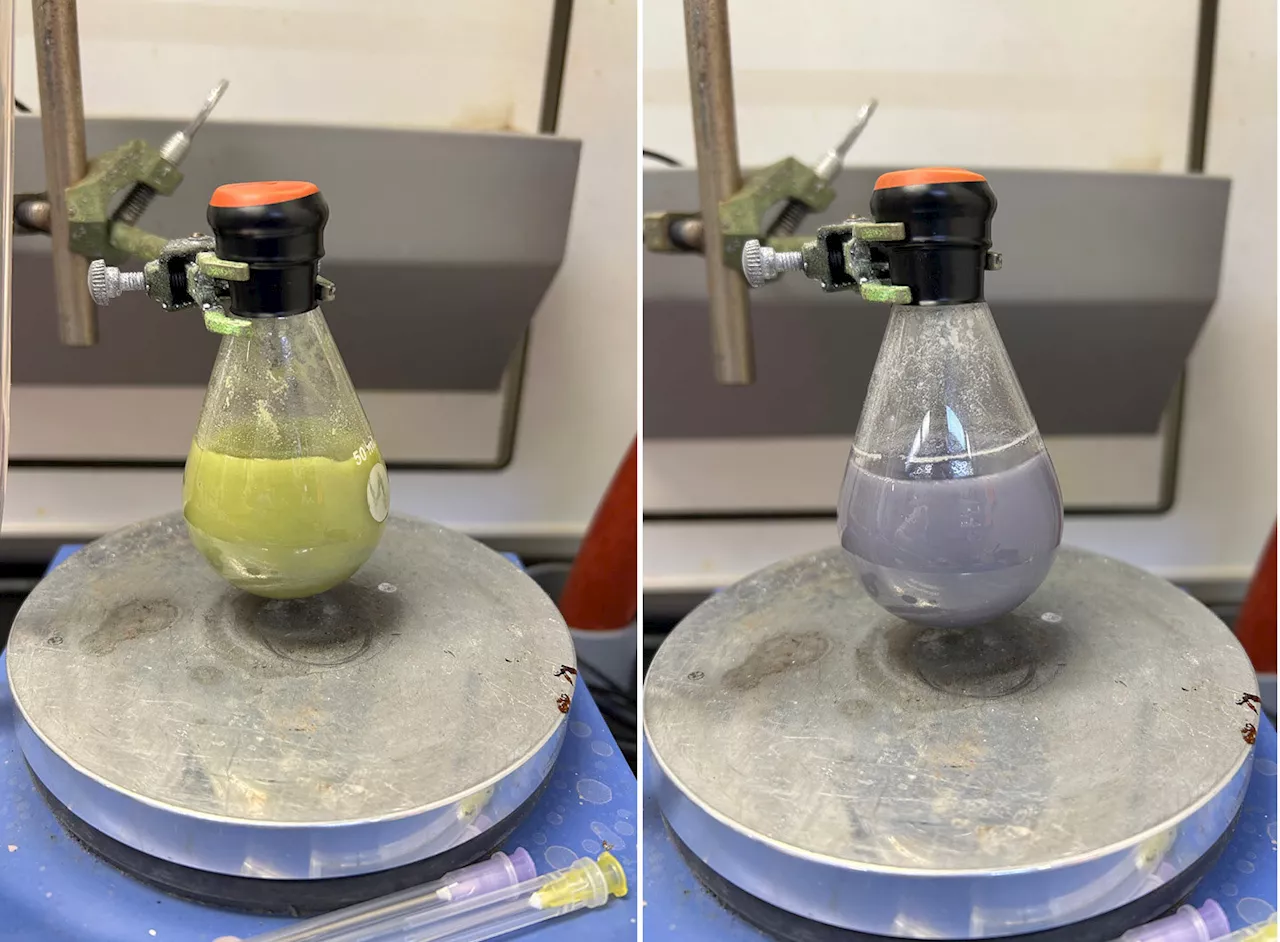 Chemists succeed in upscaling a common reagent for industrial level applicationsThe metallic element samarium, when bound with other elements, is an incredibly useful chemical reagent for synthesizing molecules that can lead to new pharmaceuticals.
Chemists succeed in upscaling a common reagent for industrial level applicationsThe metallic element samarium, when bound with other elements, is an incredibly useful chemical reagent for synthesizing molecules that can lead to new pharmaceuticals.
Read more »
