Bullies have increased risk for violent offenses, shows comprehensive study uniturku
]. Bullying was controlled for victimization and vice-versa. These variables were also divided into three categories that indicated involvement in bullying. These were never being a bully or a victim or being a bully or a victim sometimes or frequently. Parental education level, family structure and child psychopathology were also used as covariates. Hazard ratios and 95% CIs were estimated using Cox regression analyses [].
We also carried out some additional analyses. First, the additional analyses assessed whether the OR for violent offenses in adulthood increased as the frequency of bullying perpetration at 8 years of age increased. The associations between more frequent male bullying and the severity of violent offenses were assessed using multinomial logistic regression analyses. The explanatory variable was bullying perpetration and this had three categories: bullying never, sometimes or frequently.
The correlation between bullying and victimization at 8 years of age was moderate, with a tetrachoric correlation coefficient of 0.52 . Table S3 shows the cross-tabulation for the rates and frequencies of bullying and victimization. We found that the agreement about bullying and victimization between the parents and children, the parents and teachers and the children and teachers was rather low for both bullying and victimization .
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Efficacy and safety of unrestricted visiting policy for critically ill patients: a meta-analysis - Critical CareAim To compare the safety and effects of unrestricted visiting policies (UVPs) and restricted visiting policies (RVPs) in intensive care units (ICUs) with respect to outcomes related to delirium, infection, and mortality. Methods MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, Embase, Web of Science, CINAHL, CBMdisc, CNKI, Wanfang, and VIP database records generated from their inception to 22 January 2022 were searched. Randomized controlled trials and quasi-experimental studies were included. The main outcomes investigated were delirium, ICU-acquired infection, ICU mortality, and length of ICU stay. Two reviewers independently screened studies, extracted data, and assessed risks of bias. Random‑effects and fixed-effects meta‑analyses were conducted to obtain pooled estimates, due to heterogeneity. Meta-analyses were performed using RevMan 5.3 software. The results were analyzed using odds ratios (ORs), 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and standardized mean differences (SMDs). Results Eleven studies including a total of 3741 patients that compared UVPs and RVPs in ICUs were included in the analyses. Random effects modeling indicated that UVPs were associated with a reduced incidence of delirium (OR = 0.4, 95% CI 0.25–0.63, I2 = 71%, p = 0.0005). Fixed-effects modeling indicated that UVPs did not increase the incidences of ICU-acquired infections, including ventilator-associated pneumonia (OR = 0.96, 95% CI 0.71–1.30, I2 = 0%, p = 0.49), catheter-associated urinary tract infection (OR 0.97, 95% CI 0.52–1.80, I2 = 0%, p = 0.55), and catheter-related blood stream infection (OR = 1.15, 95% CI 0.72–1.84, I2 = 0%, p = 0.66), or ICU mortality (OR = 1.03, 95% CI 0.83–1.28, I2 = 49%, p = 0.12). Forest plotting indicated that UVPs could reduce the lengths of ICU stays (SMD = − 0.97, 95% CI − 1.61 to 0.32, p = 0.003). Conclusion The current meta-analysis indicates that adopting a UVP may significantly reduce the incidence of delirium in ICU patients, without increasing the risks of ICU-acquired inf
Efficacy and safety of unrestricted visiting policy for critically ill patients: a meta-analysis - Critical CareAim To compare the safety and effects of unrestricted visiting policies (UVPs) and restricted visiting policies (RVPs) in intensive care units (ICUs) with respect to outcomes related to delirium, infection, and mortality. Methods MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, Embase, Web of Science, CINAHL, CBMdisc, CNKI, Wanfang, and VIP database records generated from their inception to 22 January 2022 were searched. Randomized controlled trials and quasi-experimental studies were included. The main outcomes investigated were delirium, ICU-acquired infection, ICU mortality, and length of ICU stay. Two reviewers independently screened studies, extracted data, and assessed risks of bias. Random‑effects and fixed-effects meta‑analyses were conducted to obtain pooled estimates, due to heterogeneity. Meta-analyses were performed using RevMan 5.3 software. The results were analyzed using odds ratios (ORs), 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and standardized mean differences (SMDs). Results Eleven studies including a total of 3741 patients that compared UVPs and RVPs in ICUs were included in the analyses. Random effects modeling indicated that UVPs were associated with a reduced incidence of delirium (OR = 0.4, 95% CI 0.25–0.63, I2 = 71%, p = 0.0005). Fixed-effects modeling indicated that UVPs did not increase the incidences of ICU-acquired infections, including ventilator-associated pneumonia (OR = 0.96, 95% CI 0.71–1.30, I2 = 0%, p = 0.49), catheter-associated urinary tract infection (OR 0.97, 95% CI 0.52–1.80, I2 = 0%, p = 0.55), and catheter-related blood stream infection (OR = 1.15, 95% CI 0.72–1.84, I2 = 0%, p = 0.66), or ICU mortality (OR = 1.03, 95% CI 0.83–1.28, I2 = 49%, p = 0.12). Forest plotting indicated that UVPs could reduce the lengths of ICU stays (SMD = − 0.97, 95% CI − 1.61 to 0.32, p = 0.003). Conclusion The current meta-analysis indicates that adopting a UVP may significantly reduce the incidence of delirium in ICU patients, without increasing the risks of ICU-acquired inf
Read more »
 FDG-PET Predicts Neoadjuvant Therapy Response and Survival in Borderline Resectable/Locally Advanced Pancreatic AdenocarcinomaBackground: Neoadjuvant therapy (NAT) is used in borderline resectable/locally advanced (BR/LA) pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Anatomic imaging (CT/MRI) poorly predicts response, and biochemical (CA 19-9) markers are not useful (nonsecretors/nonelevated) in many patients. Pathologic response highly predicts survival post-NAT, but is only known postoperatively. Because metabolic imaging (FDG-PET) reveals primary tumor viability, this study aimed to evaluate our experience with preoperative FDG-PET in patients with BR/LA PDAC in predicting NAT response and survival. Methods: We reviewed all patients with resected BR/LA PDAC who underwent NAT with FDG-PET within 60 days of resection. Pre- and post-NAT metabolic (FDG-PET) and biochemical (CA 19-9) responses were dichotomized in addition to pathologic responses. We compared post-NAT metabolic and biochemical responses as preoperative predictors of pathologic responses and recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS). Results: We identified 202 eligible patients. Post-NAT, 58% of patients had optimization of CA 19-9 levels. Major metabolic and pathologic responses were present in 51% and 38% of patients, respectively. Median RFS and OS times were 21 and 48.7 months, respectively. Metabolic response was superior to biochemical response in predicting pathologic response (area under the curve, 0.86 vs 0.75; P|.001). Metabolic response was the only univariate preoperative predictor of OS (odds ratio, 0.25; 95% CI, 0.13–0.40), and was highly correlated (P=.001) with pathologic response as opposed to biochemical response alone. After multivariate adjustment, metabolic response was the single largest independent preoperative predictor (P|.001) for pathologic response (odds ratio, 43.2; 95% CI, 16.9–153.2), RFS (hazard ratio, 0.37; 95% CI, 0.2–0.6), and OS (hazard ratio, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.1–0.4). Conclusions: Among patients with post-NAT resected BR/LA PDAC, FDG-PET highly predicts pathologic response and surv
FDG-PET Predicts Neoadjuvant Therapy Response and Survival in Borderline Resectable/Locally Advanced Pancreatic AdenocarcinomaBackground: Neoadjuvant therapy (NAT) is used in borderline resectable/locally advanced (BR/LA) pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Anatomic imaging (CT/MRI) poorly predicts response, and biochemical (CA 19-9) markers are not useful (nonsecretors/nonelevated) in many patients. Pathologic response highly predicts survival post-NAT, but is only known postoperatively. Because metabolic imaging (FDG-PET) reveals primary tumor viability, this study aimed to evaluate our experience with preoperative FDG-PET in patients with BR/LA PDAC in predicting NAT response and survival. Methods: We reviewed all patients with resected BR/LA PDAC who underwent NAT with FDG-PET within 60 days of resection. Pre- and post-NAT metabolic (FDG-PET) and biochemical (CA 19-9) responses were dichotomized in addition to pathologic responses. We compared post-NAT metabolic and biochemical responses as preoperative predictors of pathologic responses and recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS). Results: We identified 202 eligible patients. Post-NAT, 58% of patients had optimization of CA 19-9 levels. Major metabolic and pathologic responses were present in 51% and 38% of patients, respectively. Median RFS and OS times were 21 and 48.7 months, respectively. Metabolic response was superior to biochemical response in predicting pathologic response (area under the curve, 0.86 vs 0.75; P|.001). Metabolic response was the only univariate preoperative predictor of OS (odds ratio, 0.25; 95% CI, 0.13–0.40), and was highly correlated (P=.001) with pathologic response as opposed to biochemical response alone. After multivariate adjustment, metabolic response was the single largest independent preoperative predictor (P|.001) for pathologic response (odds ratio, 43.2; 95% CI, 16.9–153.2), RFS (hazard ratio, 0.37; 95% CI, 0.2–0.6), and OS (hazard ratio, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.1–0.4). Conclusions: Among patients with post-NAT resected BR/LA PDAC, FDG-PET highly predicts pathologic response and surv
Read more »
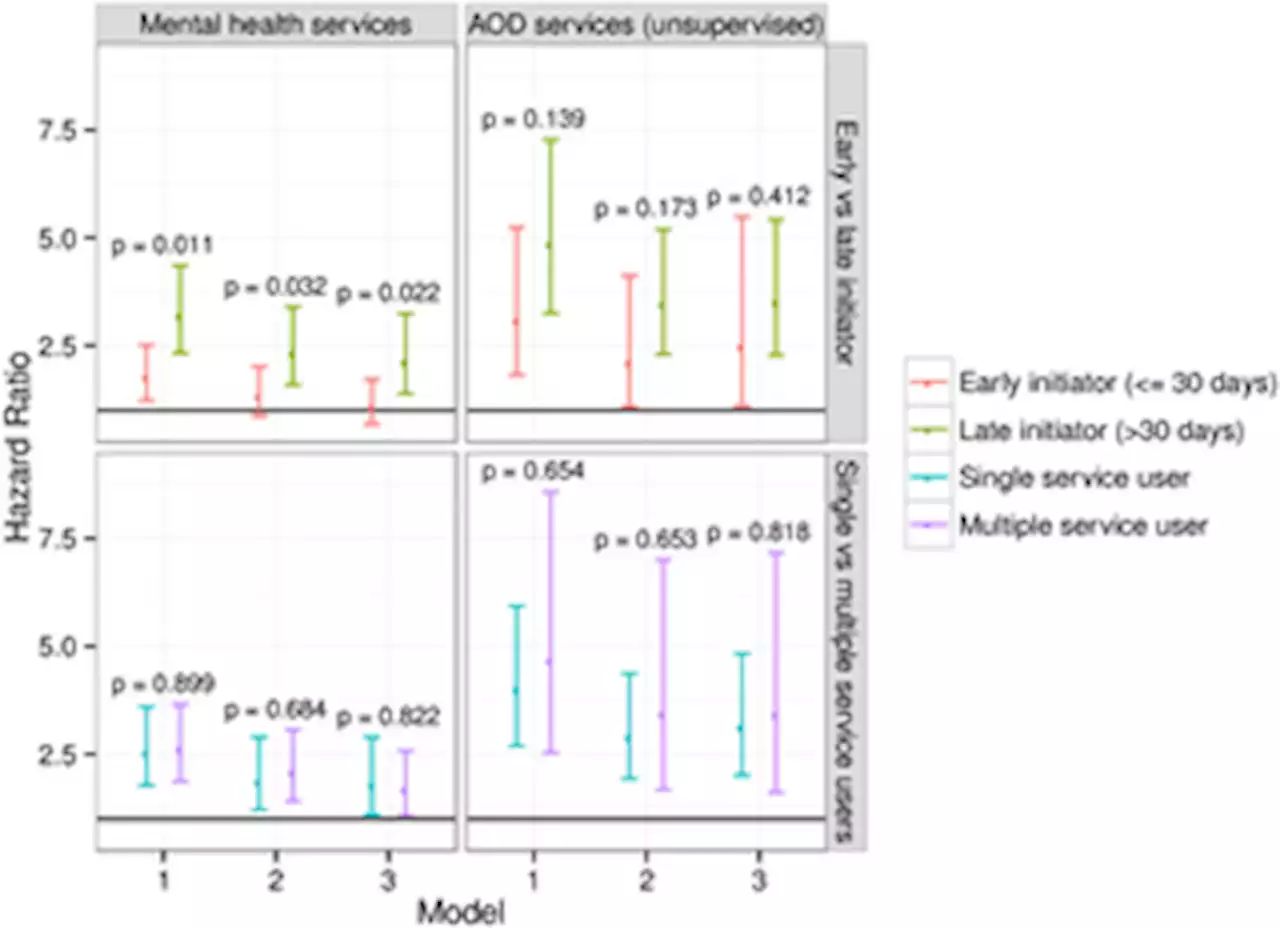 Association between contact with mental health and substance use services and reincarceration after release from prisonObjective People released from prison who experience mental health and substance use problems are at high risk of reincarceration. This study aimed to examine the association between contact with mental health and substance use treatment services, and reincarceration, among adults released from prison. Methods Pre-release survey data from 1,115 adults released from prisons in Queensland, Australia were linked with administrative health and correctional records covering a median of 787 days post-release. We constructed marginal structural Cox proportional hazards models, adjusting for pre-release variables and time-varying indicators of emergent mental health and substance use problems, to examine the association between contact with mental health and substance use treatment services, and reincarceration. Results The adjusted hazard ratio (AHR) for reincarceration associated with mental health service contact was 1.76 (95%CI 1.23,2.51). Among those not on parole following release, the AHR for reincarceration associated with substance use treatment service contact was 3.16 (95%CI 2.09,4.77); we found no evidence for an association among those who were released on parole (AHR=1.07; 95%CI 0.80,1.43). Conclusions Although we cannot eliminate the possibility of residual confounding, our findings suggest that infrequent or unsustained contact with community-based mental health and substance use treatment services is not protective against reincarceration, and may even be iatrogenic. Increased investment in high-quality and timely behavioural health services for people released from prison may simultaneously improve health outcomes, and reduce reincarceration.
Association between contact with mental health and substance use services and reincarceration after release from prisonObjective People released from prison who experience mental health and substance use problems are at high risk of reincarceration. This study aimed to examine the association between contact with mental health and substance use treatment services, and reincarceration, among adults released from prison. Methods Pre-release survey data from 1,115 adults released from prisons in Queensland, Australia were linked with administrative health and correctional records covering a median of 787 days post-release. We constructed marginal structural Cox proportional hazards models, adjusting for pre-release variables and time-varying indicators of emergent mental health and substance use problems, to examine the association between contact with mental health and substance use treatment services, and reincarceration. Results The adjusted hazard ratio (AHR) for reincarceration associated with mental health service contact was 1.76 (95%CI 1.23,2.51). Among those not on parole following release, the AHR for reincarceration associated with substance use treatment service contact was 3.16 (95%CI 2.09,4.77); we found no evidence for an association among those who were released on parole (AHR=1.07; 95%CI 0.80,1.43). Conclusions Although we cannot eliminate the possibility of residual confounding, our findings suggest that infrequent or unsustained contact with community-based mental health and substance use treatment services is not protective against reincarceration, and may even be iatrogenic. Increased investment in high-quality and timely behavioural health services for people released from prison may simultaneously improve health outcomes, and reduce reincarceration.
Read more »
 David Jenkins: British diving coach died in Turkey, coroner saysA Team GB diving coach who worked with Tom Daley died in Turkey aged 31, a coroner's court has heard.
David Jenkins: British diving coach died in Turkey, coroner saysA Team GB diving coach who worked with Tom Daley died in Turkey aged 31, a coroner's court has heard.
Read more »
