Gamma delta T cells can fight aggressive breast cancer UniFreiburg
There are no targeted therapies for patients with triple-negative breast cancer .
. γδ T cells are commonly observed to infiltrate solid tumors and have an extensive repertoire of tumor-sensing mechanisms, recognizing stress-induced molecules and phosphoantigens on transformed cells. Herein, we show that patient-derived triple-negative s, however, were refractory to γδ T-cell immunotherapy. We unraveled concerted differentiation and immune escape mechanisms: xenografted
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Woman loses breast after being told she was 'too young to have cancer'Woman, 23, undergoes life-changing surgery after being told she was 'too young to have cancer'
Woman loses breast after being told she was 'too young to have cancer'Woman, 23, undergoes life-changing surgery after being told she was 'too young to have cancer'
Read more »
 Classifying cancer cells to predict metastatic potentialCancer cells that initiate metastasis, or the spread of the disease from its primary location, are different from cancer cells that stay in the original tumor. Distinguishing metastasis-initiating cell types can determine the severity of cancer and help medical practitioners decide on a course of treatment.
Classifying cancer cells to predict metastatic potentialCancer cells that initiate metastasis, or the spread of the disease from its primary location, are different from cancer cells that stay in the original tumor. Distinguishing metastasis-initiating cell types can determine the severity of cancer and help medical practitioners decide on a course of treatment.
Read more »
 Medela Harmony Flex Manual Breast PumpOur testers review the Medela Harmony Flex Manual Breast Pump so you can see if it's right for you and your needs
Medela Harmony Flex Manual Breast PumpOur testers review the Medela Harmony Flex Manual Breast Pump so you can see if it's right for you and your needs
Read more »
 MicroRNAs as the critical regulators of autophagy-mediated cisplatin response in tumor cells - Cancer Cell InternationalChemotherapy is one of the most common therapeutic methods in advanced and metastatic tumors. Cisplatin (CDDP) is considered as one of the main first-line chemotherapy drugs in solid tumors. However, there is a high rate of CDDP resistance in cancer patients. Multi-drug resistance (MDR) as one of the main therapeutic challenges in cancer patients is associated with various cellular processes such as drug efflux, DNA repair, and autophagy. Autophagy is a cellular mechanism that protects the tumor cells toward the chemotherapeutic drugs. Therefore, autophagy regulatory factors can increase or decrease the chemotherapy response in tumor cells. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have a pivotal role in regulation of autophagy in normal and tumor cells. Therefore, in the present review, we discussed the role of miRNAs in CDDP response through the regulation of autophagy. It has been reported that miRNAs mainly increased the CDDP sensitivity in tumor cells by inhibition of autophagy. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and autophagy-related genes (ATGs) were the main targets of miRNAs in the regulation of autophagy-mediated CDDP response in tumor cells. This review can be an effective step to introduce the miRNAs as efficient therapeutic options to increase autophagy-mediated CDDP sensitivity in tumor cells.
MicroRNAs as the critical regulators of autophagy-mediated cisplatin response in tumor cells - Cancer Cell InternationalChemotherapy is one of the most common therapeutic methods in advanced and metastatic tumors. Cisplatin (CDDP) is considered as one of the main first-line chemotherapy drugs in solid tumors. However, there is a high rate of CDDP resistance in cancer patients. Multi-drug resistance (MDR) as one of the main therapeutic challenges in cancer patients is associated with various cellular processes such as drug efflux, DNA repair, and autophagy. Autophagy is a cellular mechanism that protects the tumor cells toward the chemotherapeutic drugs. Therefore, autophagy regulatory factors can increase or decrease the chemotherapy response in tumor cells. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have a pivotal role in regulation of autophagy in normal and tumor cells. Therefore, in the present review, we discussed the role of miRNAs in CDDP response through the regulation of autophagy. It has been reported that miRNAs mainly increased the CDDP sensitivity in tumor cells by inhibition of autophagy. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and autophagy-related genes (ATGs) were the main targets of miRNAs in the regulation of autophagy-mediated CDDP response in tumor cells. This review can be an effective step to introduce the miRNAs as efficient therapeutic options to increase autophagy-mediated CDDP sensitivity in tumor cells.
Read more »
 Mum loses breast and left fighting for life after ‘botched’ surgery in TurkeyGRAPHIC IMAGE WARNING: Sara Platt, who forked out £14,000 for a tummy tuck, breast implants and three other procedures in Antalya earlier this year, has spoken out about her ordeal.
Mum loses breast and left fighting for life after ‘botched’ surgery in TurkeyGRAPHIC IMAGE WARNING: Sara Platt, who forked out £14,000 for a tummy tuck, breast implants and three other procedures in Antalya earlier this year, has spoken out about her ordeal.
Read more »
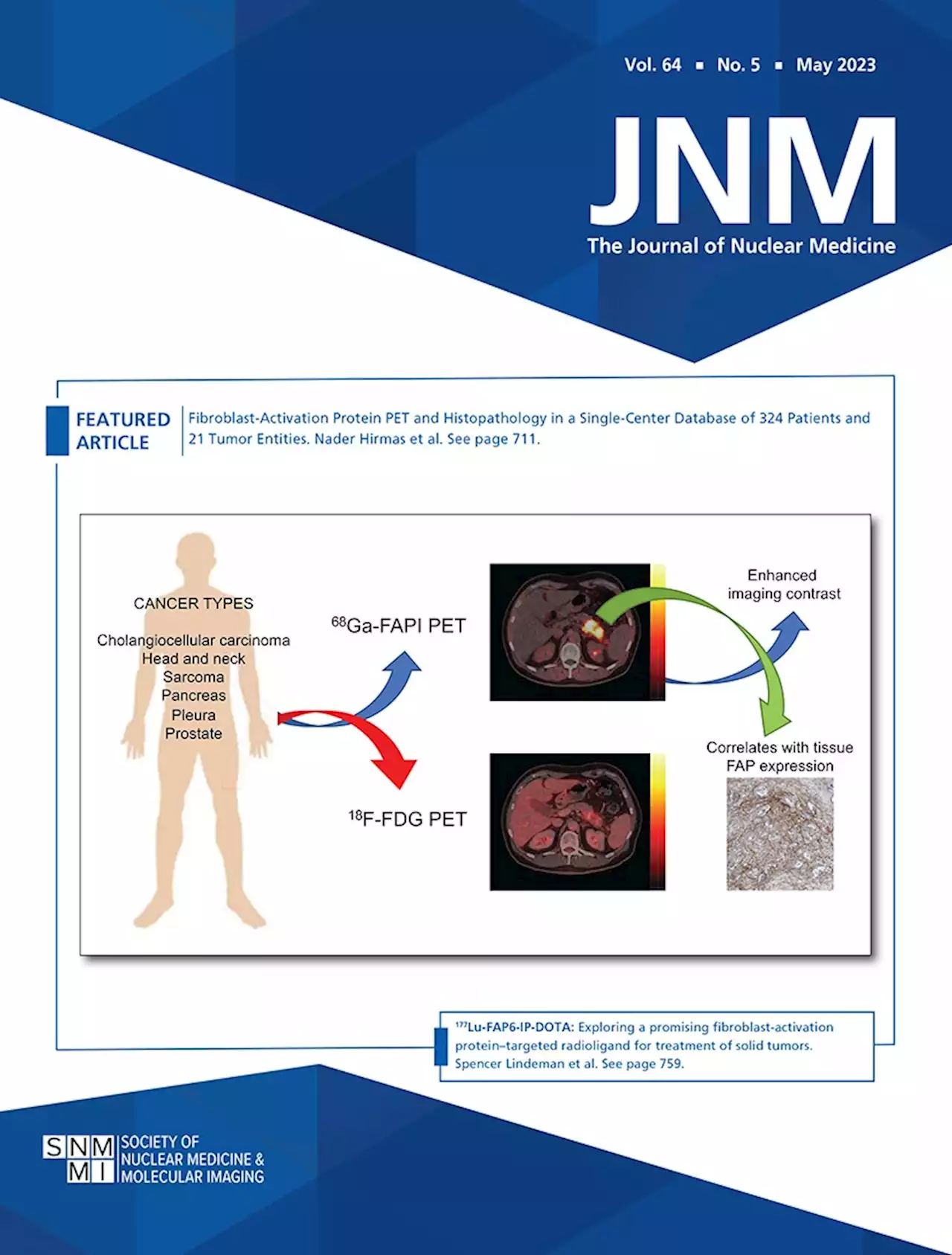 Fibroblast-Activation Protein PET and Histopathology in a Single-Center Database of 324 Patients and 21 Tumor EntitiesWe present an overview of our prospective fibroblast-activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) registry study across a 3-y period, with head-to-head comparison of tumor uptake in 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET, as well as FAP immunohistochemistry. Methods: This is an interim analysis of the ongoing 68Ga-FAPI PET prospective observational trial at our department. Patients who underwent clinical imaging with 68Ga-FAPI PET between October 2018 and October 2021 were included. Tracer uptake was quantified by SUVmax for tumor lesions and by SUVmean for normal organs. PET tumor volume (40% isocontour) and tumor-to-background ratios were calculated. Correlation between SUVmax and FAP staining in tissue samples was analyzed. Results: In total, 324 patients with 21 different tumor entities underwent 68Ga-FAPI imaging; 237 patients additionally received 18F-FDG PET. The most common tumor entities were sarcoma (131/324, 40%), pancreatic cancer (67/324, 21%), and primary tumors of the brain (22/324, 7%). The mean primary tumor SUVmax was significantly higher for 68Ga-FAPI than 18F-FDG among pancreatic cancer (13.2 vs. 6.1, P | 0.001) and sarcoma (14.3 vs. 9.4, P | 0.001), and the same was true for mean SUVmax in metastatic lesions of pancreatic cancer (9.4 vs. 5.5, P | 0.001). Mean primary tumor maximum tumor-to-background ratio was significantly higher for 68Ga-FAPI than 18F-FDG across several tumor entities, most prominently pancreatic cancer (14.7 vs. 3.0, P | 0.001) and sarcoma (17.3 vs. 4.7, P | 0.001). Compared with 18F-FDG, 68Ga-FAPI showed superior detection for locoregional disease in sarcoma (52 vs. 48 total regions detected) and for distant metastatic disease in both sarcoma (137 vs. 131) and pancreatic cancer (65 vs. 57), respectively. Among 61 histopathology samples, there was a positive correlation between 68Ga-FAPI SUVmax and overall FAP immunohistochemistry score ( r=0.352, P=0.005). Conclusion: 68Ga-FAPI demonstrates higher absolute uptake in pancreatic cancer and sarcoma,
Fibroblast-Activation Protein PET and Histopathology in a Single-Center Database of 324 Patients and 21 Tumor EntitiesWe present an overview of our prospective fibroblast-activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) registry study across a 3-y period, with head-to-head comparison of tumor uptake in 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET, as well as FAP immunohistochemistry. Methods: This is an interim analysis of the ongoing 68Ga-FAPI PET prospective observational trial at our department. Patients who underwent clinical imaging with 68Ga-FAPI PET between October 2018 and October 2021 were included. Tracer uptake was quantified by SUVmax for tumor lesions and by SUVmean for normal organs. PET tumor volume (40% isocontour) and tumor-to-background ratios were calculated. Correlation between SUVmax and FAP staining in tissue samples was analyzed. Results: In total, 324 patients with 21 different tumor entities underwent 68Ga-FAPI imaging; 237 patients additionally received 18F-FDG PET. The most common tumor entities were sarcoma (131/324, 40%), pancreatic cancer (67/324, 21%), and primary tumors of the brain (22/324, 7%). The mean primary tumor SUVmax was significantly higher for 68Ga-FAPI than 18F-FDG among pancreatic cancer (13.2 vs. 6.1, P | 0.001) and sarcoma (14.3 vs. 9.4, P | 0.001), and the same was true for mean SUVmax in metastatic lesions of pancreatic cancer (9.4 vs. 5.5, P | 0.001). Mean primary tumor maximum tumor-to-background ratio was significantly higher for 68Ga-FAPI than 18F-FDG across several tumor entities, most prominently pancreatic cancer (14.7 vs. 3.0, P | 0.001) and sarcoma (17.3 vs. 4.7, P | 0.001). Compared with 18F-FDG, 68Ga-FAPI showed superior detection for locoregional disease in sarcoma (52 vs. 48 total regions detected) and for distant metastatic disease in both sarcoma (137 vs. 131) and pancreatic cancer (65 vs. 57), respectively. Among 61 histopathology samples, there was a positive correlation between 68Ga-FAPI SUVmax and overall FAP immunohistochemistry score ( r=0.352, P=0.005). Conclusion: 68Ga-FAPI demonstrates higher absolute uptake in pancreatic cancer and sarcoma,
Read more »
