I am a scientist, businessman, author, and philanthropist. For nearly two decades, I was a professor at Harvard Medical School and Harvard School of Public Health where I founded two academic research departments, the Division of Biochemical Pharmacology and the Division of Human Retrovirology.
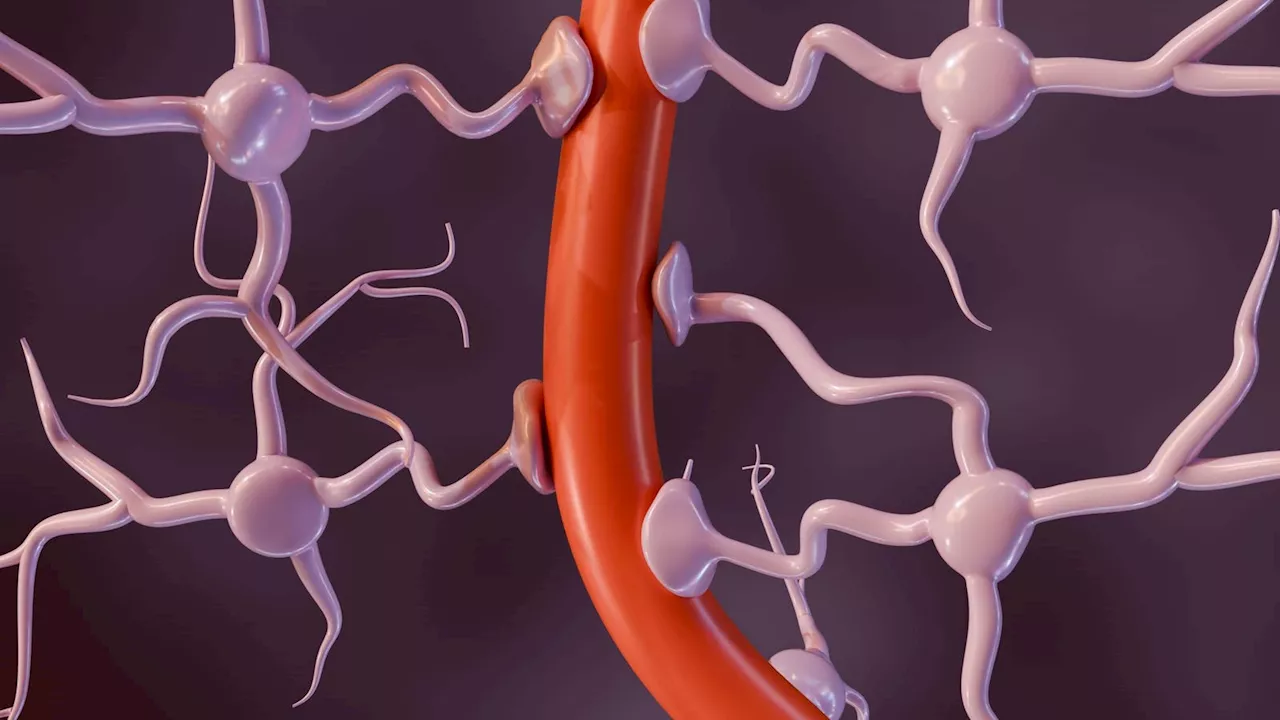
Despite being the most prevalent neurodegenerative disease globally, Alzheimer’s disease has been notoriously challenging to prevent, let alone cure. The biggest hurdle for delivering drugs into the brain is the blood-brain barrier . These tiny blood vessels form tight junctions between brain cells to regulate the movement of molecules from the blood into the brain.
A growing body of evidence now shows that insulin resistance may also be implicated in Alzheimer’s disease. In post-mortem exams of human and animal brains with Alzheimer’s disease, changes in the brain’s insulin-binding receptors seem to correlate with learning and memory deficits. Other reports suggest that impaired insulin signaling may be associated with the accumulation of beta-amyloid and tau neurofibrillary tangles, which are characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease.
If insulin-binding receptors are impaired in Alzheimer’s, it is possible that drugs that target those receptors may be able to slow, or prevent, cognitive decline. The first question researchers had to answer, however, was where in the brain are these receptors located. To answer this question, Leclrec et. al began their study by examining brain tissue samples from healthy individuals without dementia. They were surprised to find that there were no insulin-binding receptors in the brain itself.
When they examined brain samples from individuals with Alzheimer’s disease, however, the number of insulin-binding receptors found in the blood-brain barrier was considerably reduced. Leclerc et. al also observed this trend in mice models with genetic mutations associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Not only were there fewer insulin-binding receptors but the activation of these receptors was also blunted.
This presents a promising treatment approach for Alzheimer’s disease. Without having to cross the blood-brain barrier, drugs that target insulin-binding receptors within the blood vessels directly may be able to influence brain activity. However, it is still not well understood how insulin resistance contributes to cognitive decline, nor how stimulating these receptors would improve symptoms.
Aging Blood-Brain Barrier BBB Heart Disese Brain
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Mandarin Middle School school police officer arrested for battery at schoolDuring an investigation, Jacksonville Sheriff T.K. Waters said JSO told Dollar General stores to warn their employees about the string of armed robberies.
Mandarin Middle School school police officer arrested for battery at schoolDuring an investigation, Jacksonville Sheriff T.K. Waters said JSO told Dollar General stores to warn their employees about the string of armed robberies.
Read more »
 Harvard-Westlake baseball shut down by Corona pitching in CIF-SS Division 1 championshipHarvard-Westlake generates just two hits and no runs against Corona ace Ethan Schiefelbein in the Division 1 final.
Harvard-Westlake baseball shut down by Corona pitching in CIF-SS Division 1 championshipHarvard-Westlake generates just two hits and no runs against Corona ace Ethan Schiefelbein in the Division 1 final.
Read more »
 Harvard-Westlake baseball holds off San Dimas to move on to Division 1 semifinalsHarvard-Westlake’s Duncan Marsten throws a complete game and allows only five hits to a relentless San Dimas lineup that falls short in the CIF-SS quarterfinals.
Harvard-Westlake baseball holds off San Dimas to move on to Division 1 semifinalsHarvard-Westlake’s Duncan Marsten throws a complete game and allows only five hits to a relentless San Dimas lineup that falls short in the CIF-SS quarterfinals.
Read more »
 2024 NFL division predictions: Winners for each AFC and NFC divisionNow that the full 2024 NFL schedule is out, check out predictions for winners of all eight divisons from our NFL staff.
2024 NFL division predictions: Winners for each AFC and NFC divisionNow that the full 2024 NFL schedule is out, check out predictions for winners of all eight divisons from our NFL staff.
Read more »
 David Velasquez, Harvard Medical and Business School Graduate, on His Family StoryDavid Velasquez will be the first person to graduate from Harvard Business School, Kennedy School, and Medical School. His family immigrated from Nicaragua, and spoke no English.
David Velasquez, Harvard Medical and Business School Graduate, on His Family StoryDavid Velasquez will be the first person to graduate from Harvard Business School, Kennedy School, and Medical School. His family immigrated from Nicaragua, and spoke no English.
Read more »
 Former Disney star Bridgit Mendler officially graduates Harvard Law SchoolFormer Disney channel star Bridgit Mendler is one step closer to becoming a lawyer following her 2024 graduation from Harvard Law school. What, like it's hard?
Former Disney star Bridgit Mendler officially graduates Harvard Law SchoolFormer Disney channel star Bridgit Mendler is one step closer to becoming a lawyer following her 2024 graduation from Harvard Law school. What, like it's hard?
Read more »