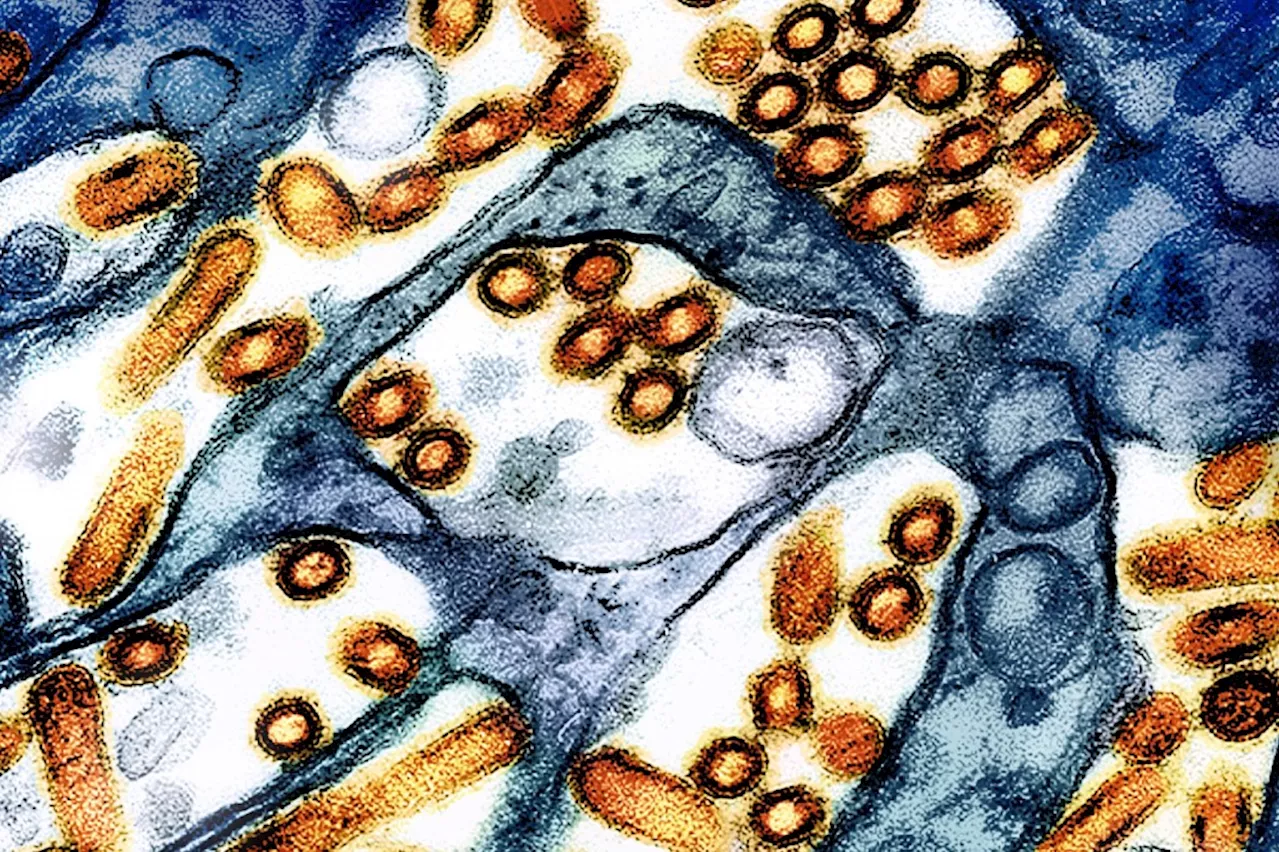
A new strain of bird flu with concerning mutations has been detected in a human patient, prompting health officials to issue warnings about the potential for increased transmission.
A person over 65 with underlying medical conditions was hospitalized with the flu after exposure to a backyard flock of birds and wild birds. Genetic analysis of the virus found changes expected to enhance its ability to infect the upper airways of humans and spread more easily from person to person. These same changes were not seen in the birds the person had been exposed to, indicating that they developed in the person after infection.
Although the overall risk to the public remains low, people who keep chickens and other birds in their backyards are at higher risk for bird flu, as are workers on dairy and poultry farms. People who work with animals, or have been in contact with sick or dead animals or their droppings, should watch for breathing problems and red, infected eyes for 10 days after exposure. If they develop symptoms, they should tell their health care provider about their recent exposure. Do not touch sick or dead animals or their droppings, and do not bring sick wild animals into your home. Do not eat uncooked or undercooked food. Cook poultry, eggs and other animal products to the proper temperature, and prevent cross-contamination between raw and cooked food. Avoid uncooked food products such as unpasteurized raw milk or cheeses from animals that have a suspected or confirmed infection. If you work on poultry or dairy farms, talk to a health care provider about getting your seasonal flu vaccination. It will not prevent infection with avian influenza viruses, but it can reduce the risk of coinfection with avian and flu viruses. Report dead or sick birds or animals to the US Department of Agriculture toll-free at 1-866-536-7593
BIRD FLU HUMAN INFECTION TRANSMISSION HEALTH WARNINGS PUBLIC HEALTH
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
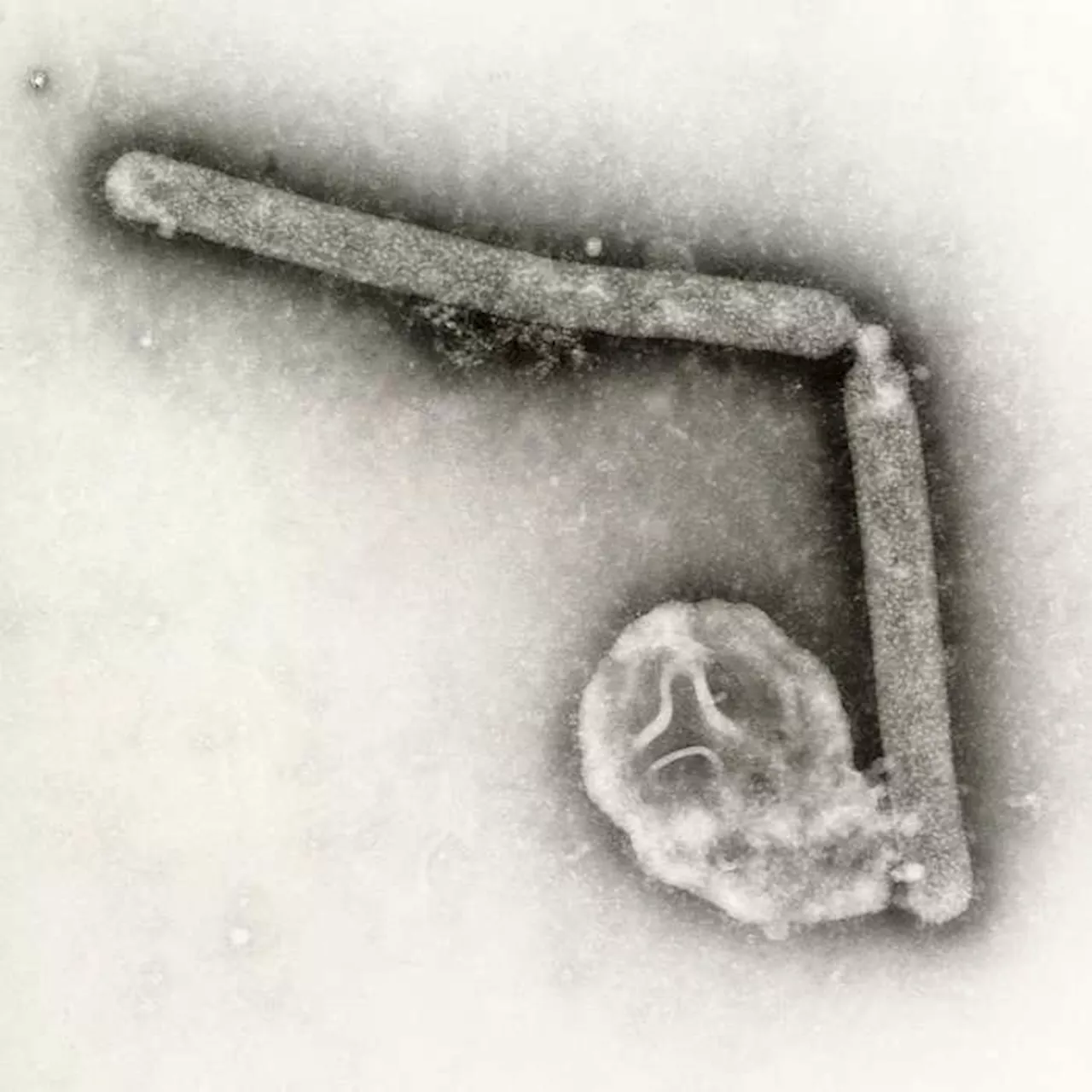 Bird Flu Virus Mutation Raises ConcernsA recent mutation in the bird flu virus has sparked concern among scientists, as it appears to enhance the virus's ability to bind to human respiratory cells. While not a cause for immediate alarm, the finding suggests the virus may be evolving towards greater transmissibility between humans.
Bird Flu Virus Mutation Raises ConcernsA recent mutation in the bird flu virus has sparked concern among scientists, as it appears to enhance the virus's ability to bind to human respiratory cells. While not a cause for immediate alarm, the finding suggests the virus may be evolving towards greater transmissibility between humans.
Read more »
 Surge in seasonal flu in Southern California may lead to potential bird flu mutationFlu activity is spiking across Southern California, which is leading to a concerning number of pediatric hospitalizations. Doctors said the threat of bird flu is making this season particularly concerning.
Surge in seasonal flu in Southern California may lead to potential bird flu mutationFlu activity is spiking across Southern California, which is leading to a concerning number of pediatric hospitalizations. Doctors said the threat of bird flu is making this season particularly concerning.
Read more »
 Bird Flu Mutation Detected in First Severe US CaseThe CDC discovered new mutations in the hemagglutinin gene of the first severe bird flu case in the US, raising concerns but maintaining a low risk to the public.
Bird Flu Mutation Detected in First Severe US CaseThe CDC discovered new mutations in the hemagglutinin gene of the first severe bird flu case in the US, raising concerns but maintaining a low risk to the public.
Read more »
 Bird Flu Mutation: Risk of New Pandemic ExplainedA new mutation and the first severe case of H5N1 bird flu discovered in a human in Louisiana has raised concern among some experts of a pandemic.
Bird Flu Mutation: Risk of New Pandemic ExplainedA new mutation and the first severe case of H5N1 bird flu discovered in a human in Louisiana has raised concern among some experts of a pandemic.
Read more »
 CDC Detects Bird Flu Mutation in Human, Amid New Infections in CatsThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
CDC Detects Bird Flu Mutation in Human, Amid New Infections in CatsThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
Read more »
 A Single Mutation Could Bring Bird Flu a Critical Step Closer to a New PandemicThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
A Single Mutation Could Bring Bird Flu a Critical Step Closer to a New PandemicThe Best in Science News and Amazing Breakthroughs
Read more »