Researchers utilized a large-scale unlabeled dataset from the U.K. Biobank to train deep-learning models for accurately monitoring physical activity through wearables, demonstrating enhanced accuracy and generalizability across diverse environments and devices.
By Dr. Chinta SidharthanApr 21 2024Reviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc. In a recent study published in the journal NPJ Digital Medicine , researchers used the large-scale accelerometer dataset from the United Kingdom Biobank consisting of unlabeled data for 700,000 person days to build models to monitor physical activity levels with more accuracy and generalizability.
While fields such as natural language processing and computer vision have advanced significantly due to the availability of surplus data to train these learning models, the dearth of large-scale datasets that can be used to train algorithms has constrained the progress in developing models that reliably and accurately recognize human activity.
The researchers used a self-supervised learning approach, which has successfully been used for examples such as generative pre-trained transformers or GPT. Recent studies have used numerous self-supervised learning approaches such as masked reconstruction, multi-task self-supervision, bootstrapping, and contrastive learning to examine the analysis of data from wearable sensors. The present study applied the multi-task self-supervision method to the large U.K.
Results The results showed that when the models trained in this study were tested on eight benchmark datasets, they outperformed the baselines with a median relative improvement of 24.4%. Furthermore, the model could be generalized across a wide range of motion sensor devices, living environments, cohorts, and external datasets.
Healthcare Language Medicine Sleep
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Strictly's new series to face big change - and a surprising new royal locationWhy this year will be particularly special for Strictly Come Dancing
Strictly's new series to face big change - and a surprising new royal locationWhy this year will be particularly special for Strictly Come Dancing
Read more »
 Grounded adds four new Xbox achievements and New Game+ with today's big updateGrounded adds four new Xbox achievements with today's huge Fully Yoked update, which also adds New Game+ and a whole load of new content, features, and updates.
Grounded adds four new Xbox achievements and New Game+ with today's big updateGrounded adds four new Xbox achievements with today's huge Fully Yoked update, which also adds New Game+ and a whole load of new content, features, and updates.
Read more »
 Researchers create new platform to identify proteins for targeted treatment of diseaseResearchers at the University of Toronto and Sinai Health have created a new platform to identify proteins that can be co-opted to control the stability of other proteins -; a new but largely unrealized approach to the treatment of disease.
Researchers create new platform to identify proteins for targeted treatment of diseaseResearchers at the University of Toronto and Sinai Health have created a new platform to identify proteins that can be co-opted to control the stability of other proteins -; a new but largely unrealized approach to the treatment of disease.
Read more »
 UQ researchers use new dosing technology to enhance ICU antibiotic treatmentUniversity of Queensland researchers have used dosing software to accelerate the effects of antibiotics in patients being treated for sepsis in Intensive Care Units.
UQ researchers use new dosing technology to enhance ICU antibiotic treatmentUniversity of Queensland researchers have used dosing software to accelerate the effects of antibiotics in patients being treated for sepsis in Intensive Care Units.
Read more »
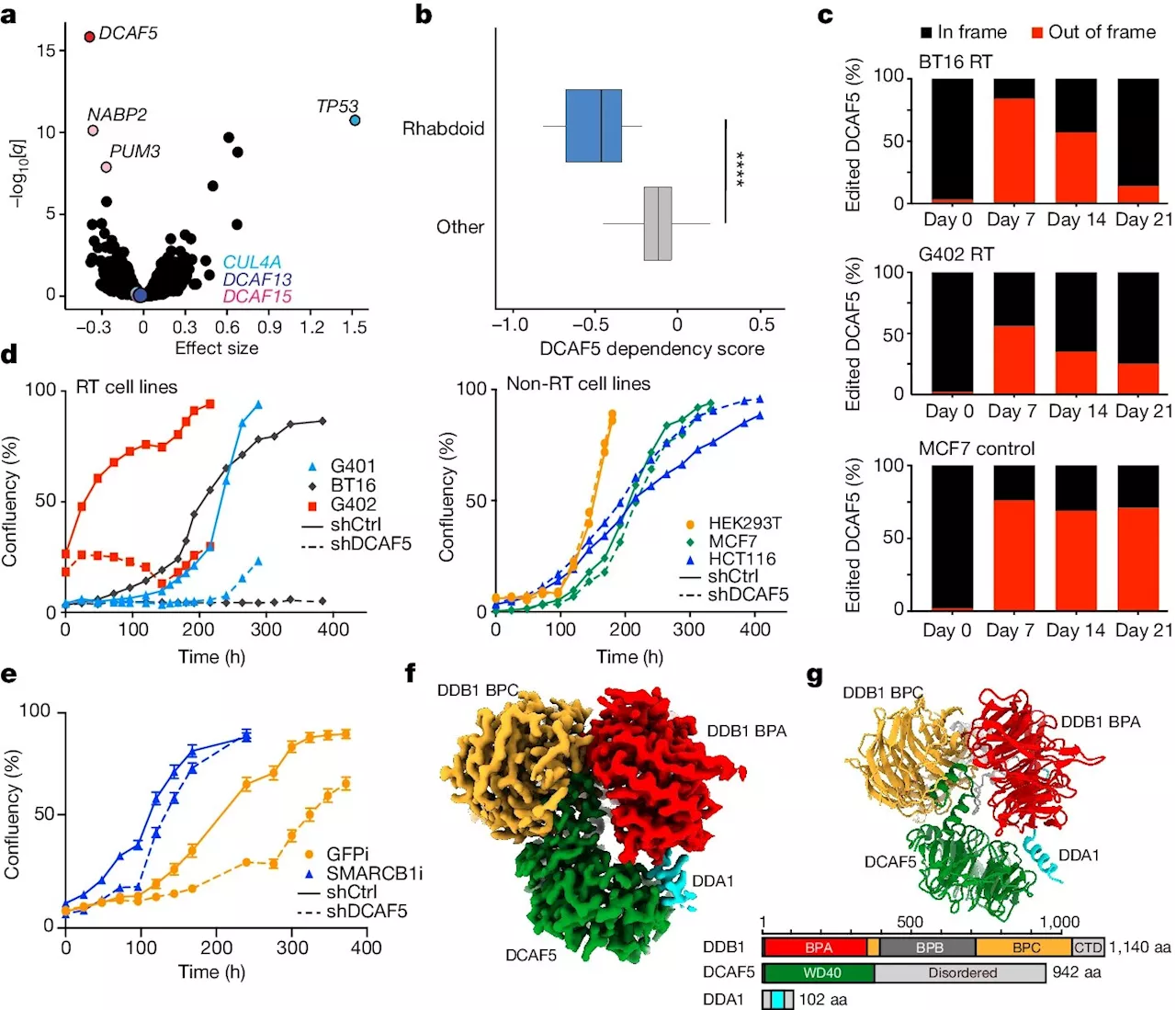 Researchers turn back the clock on cancer cells to offer new treatment paradigmSt. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists reversed an aggressive cancer, reverting malignant cells towards a more normal state. Rhabdoid tumors are an aggressive cancer which is missing a key tumor suppressor protein.
Researchers turn back the clock on cancer cells to offer new treatment paradigmSt. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists reversed an aggressive cancer, reverting malignant cells towards a more normal state. Rhabdoid tumors are an aggressive cancer which is missing a key tumor suppressor protein.
Read more »
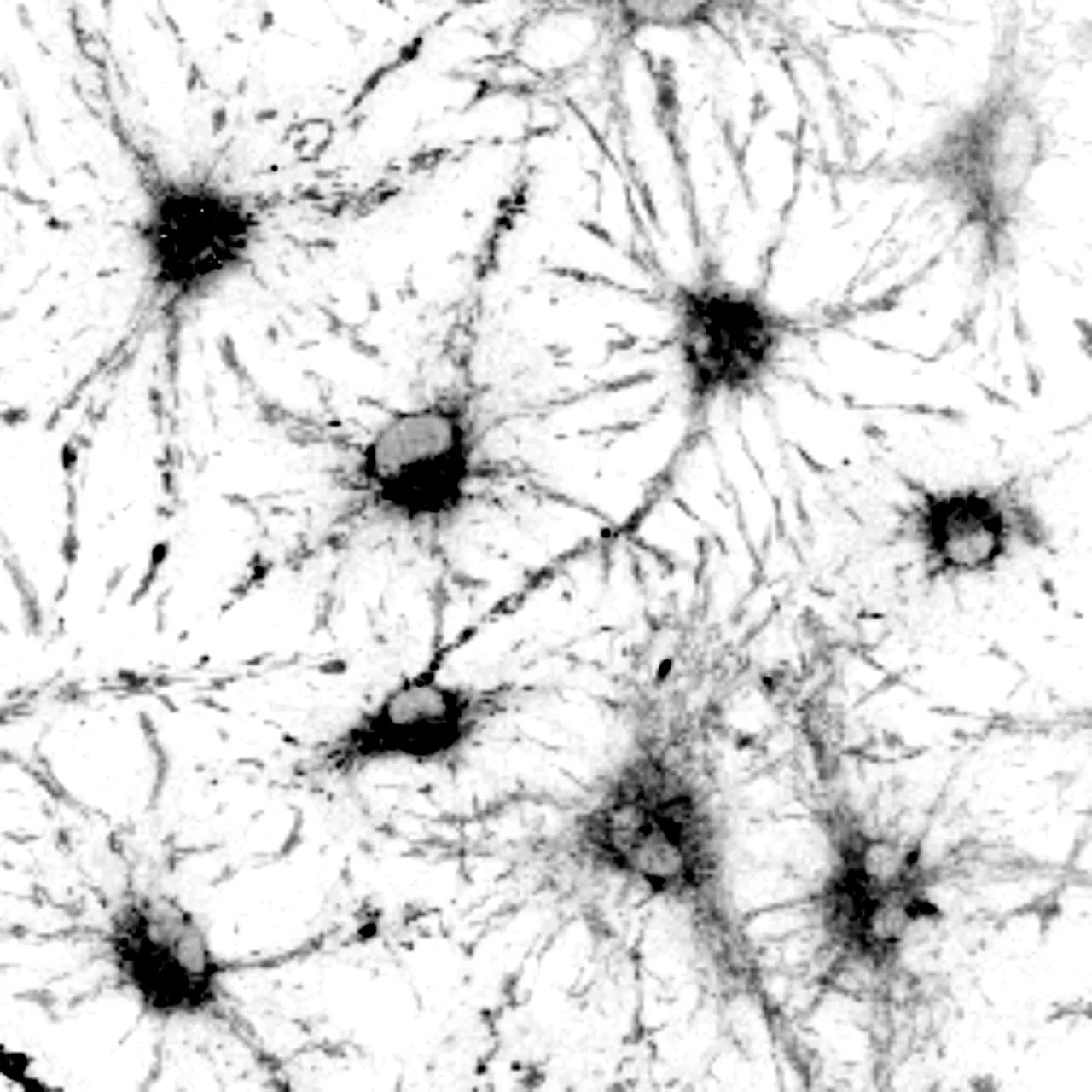 New tool provides researchers with improved understanding of stem cell aging in the brainResearchers can use the light naturally thrown off by biological specimens to better study the different states of stem cells in the nervous system, thanks to a tool developed at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, brightening their chances for studying the way stem cells age.
New tool provides researchers with improved understanding of stem cell aging in the brainResearchers can use the light naturally thrown off by biological specimens to better study the different states of stem cells in the nervous system, thanks to a tool developed at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, brightening their chances for studying the way stem cells age.
Read more »
