Science, Space and Technology News 2024
Led by Boston College physicist Qiong Ma, an international team working with single-atom thick crystals found TaIrTe4’s transition between the two distinct topological states of insulation and conduction. The material exhibited zero electrical conductivity within its interior, while its boundaries remain conductive. The team’s investigation determined that the two topological states stem from disparate origins.
The findings introduce a novel effect that the team calls the dual topological insulator or the dual quantum spin Hall insulator, Ma said.Exceptionally thin, two-dimensional layers of a crystalline material called TaIrTe4, created from tantalum, iridium, and tellurium, were the focus of the team of scientists from BC,, Texas A&M, the University of Tennessee, Singapore’s Nanyang Technological University, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Japan’s National Institute for Materials Science.
Ma said the project’s primary objective was to test the theoretical prediction that suggests the thinnest TaIrTe4 layer acts as a two-dimensional topological insulator – also known as a quantum spin Hall insulator – a novel material where its interior is insulating and electricity flows along its boundaries without any energy loss. This unique combination makes these materials a focus of researchers trying to develop future generations of energy-efficient electronic devices.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
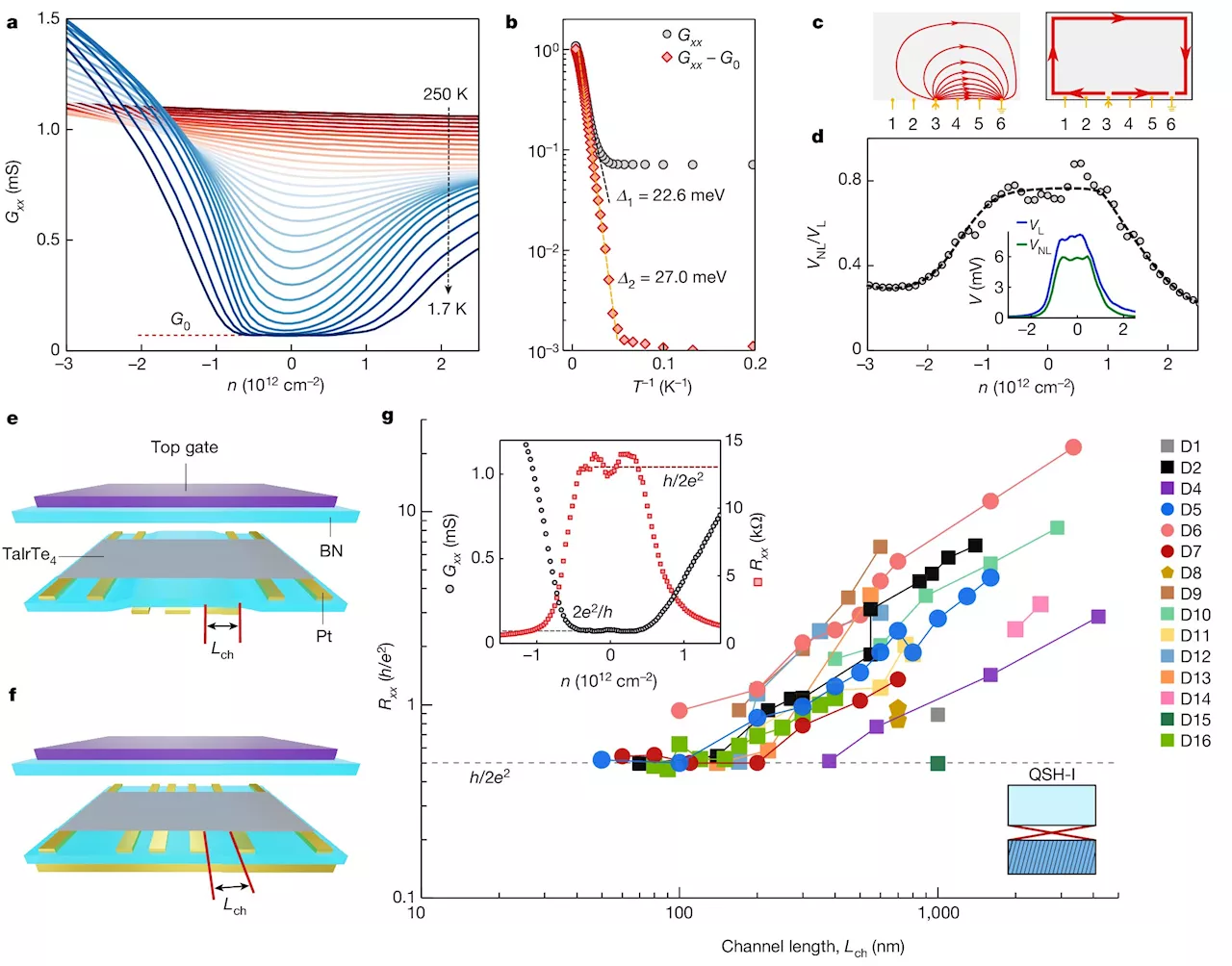 Researchers discover dual topological phases in an intrinsic monolayer crystalDual topological phases have been discovered in an intrinsic monolayer crystal, a finding that reveals new and unique rule-bending properties in a quantum material, an international team of scientists led by Boston College physicists reported recently in the online version of the journal Nature.
Researchers discover dual topological phases in an intrinsic monolayer crystalDual topological phases have been discovered in an intrinsic monolayer crystal, a finding that reveals new and unique rule-bending properties in a quantum material, an international team of scientists led by Boston College physicists reported recently in the online version of the journal Nature.
Read more »
 Unlocking exotic physics: Exploring graphene's topological bands in super-moiré structuresIn a new study, scientists from Singapore and Spain have presented a new avenue for exploring exotic physics in graphene. They focus on electronic interactions in graphene when it is sandwiched in a three-layer structure which provides a platform to exploit unique electronic band configurations.
Unlocking exotic physics: Exploring graphene's topological bands in super-moiré structuresIn a new study, scientists from Singapore and Spain have presented a new avenue for exploring exotic physics in graphene. They focus on electronic interactions in graphene when it is sandwiched in a three-layer structure which provides a platform to exploit unique electronic band configurations.
Read more »
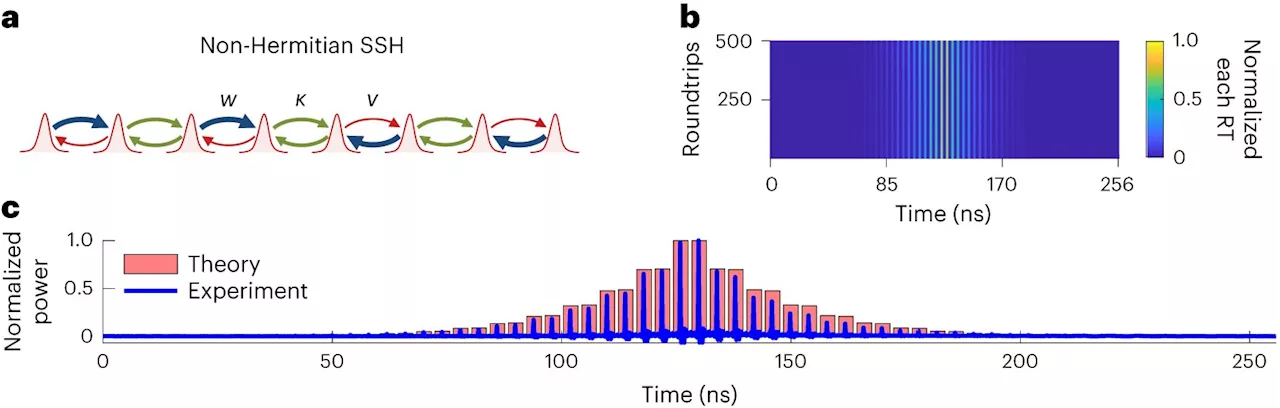 Using mode-locked lasers to realize and study non-Hermitian topological physicsMode-locked lasers are advanced lasers that produce very short pulses of light, with durations ranging from femtoseconds to picoseconds. These lasers are widely used to study ultrafast and nonlinear optical phenomena, but they have also proved useful for various technological applications.
Using mode-locked lasers to realize and study non-Hermitian topological physicsMode-locked lasers are advanced lasers that produce very short pulses of light, with durations ranging from femtoseconds to picoseconds. These lasers are widely used to study ultrafast and nonlinear optical phenomena, but they have also proved useful for various technological applications.
Read more »
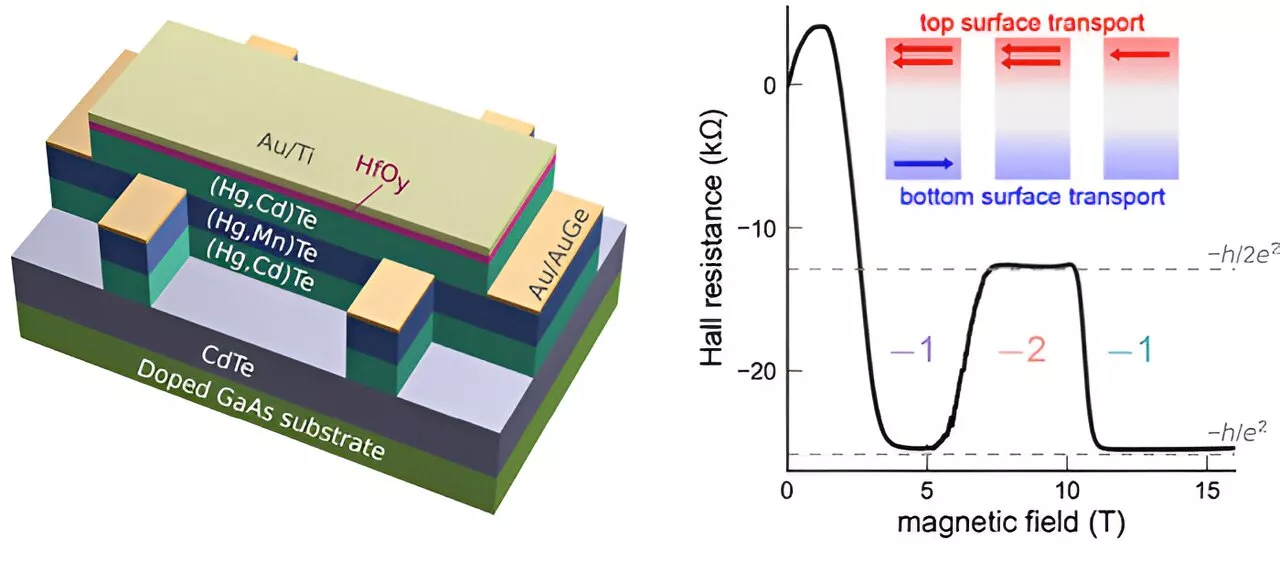 Physicists demonstrate parity anomaly in a topological insulatorExperimental and theoretical physicists from the Würzburg Institute for Topological Insulators have observed a re-entrant quantum Hall effect in a mercury telluride device and have identified it as a signature of parity anomaly.
Physicists demonstrate parity anomaly in a topological insulatorExperimental and theoretical physicists from the Würzburg Institute for Topological Insulators have observed a re-entrant quantum Hall effect in a mercury telluride device and have identified it as a signature of parity anomaly.
Read more »
 New topological metamaterial amplifies sound waves exponentiallyResearchers at AMOLF, in collaboration with partners from Germany, Switzerland, and Austria, have realized a new type of metamaterial through which sound waves flow in an unprecedented fashion. It provides a novel form of amplification of mechanical vibrations, which has the potential to improve sensor technology and information processing devices.
New topological metamaterial amplifies sound waves exponentiallyResearchers at AMOLF, in collaboration with partners from Germany, Switzerland, and Austria, have realized a new type of metamaterial through which sound waves flow in an unprecedented fashion. It provides a novel form of amplification of mechanical vibrations, which has the potential to improve sensor technology and information processing devices.
Read more »
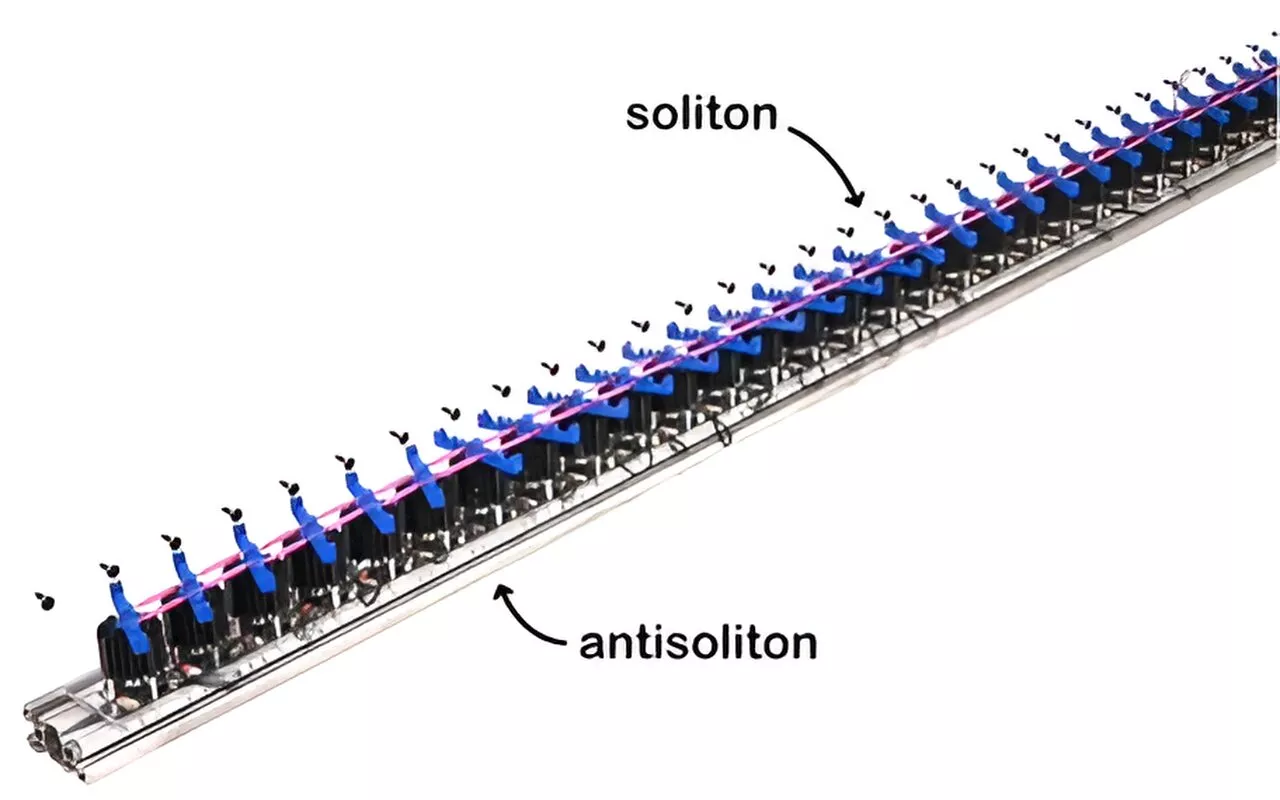 An endless domino effect: Non-reciprocal topological solitons in active metamaterialsTopological solitons can be found in many places and at many different length scales. For example, they take the form of kinks in coiled telephone cords and large molecules such as proteins. At a very different scale, a black hole can be understood as a topological soliton in the fabric of spacetime.
An endless domino effect: Non-reciprocal topological solitons in active metamaterialsTopological solitons can be found in many places and at many different length scales. For example, they take the form of kinks in coiled telephone cords and large molecules such as proteins. At a very different scale, a black hole can be understood as a topological soliton in the fabric of spacetime.
Read more »
