Astronomers have detected the rotation of a galaxy dating back to just 550 million years after the big bang—when the universe was 4% of its current age.
Astronomers have detected the rotation of a galaxy dating back to just 550 million years after the big bang, when the universe was 4% of its current age. The rotation suggests this baby galaxy was not an amorphous blob but rather an organized disk, just like the Milky Way and similar galaxies that have had more than 13 billion years to mature. It’s yet more evidence that galaxies grow and evolve faster than theorists had expected.
The stars in this trendsetting galaxy were also mature, indicating they formed 300 million years earlier, when the universe was just 250 million years old. That’s good news for the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope—launched last year and. If these first galaxies gave birth to lots of stars in a burst early on, they will likely be “luminous enough for Webb to see,” says Richard Ellis, an astronomer at University College London and co-author of the new study.
They decided to take a longer and closer look with ALMA. Such telescope arrays have an ability to “zoom in” by spreading the dishes further apart and combining their signals through a process known as interferometry. The team observed JD1 when the dishes were spread over an area 2.5 kilometers across, giving the sharpness of vision of a single dish of that size.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Astronomers search for light that holds answer to how earliest galaxies formedFeatures of some of the earliest galaxies in the universe are coming into sharper focus.
Astronomers search for light that holds answer to how earliest galaxies formedFeatures of some of the earliest galaxies in the universe are coming into sharper focus.
Read more »
 Here’s how the first images from the James Webb Space Telescope stack up to Hubble’s epic shotsFrom deep views of the Universe to detritus of dead stars.
Here’s how the first images from the James Webb Space Telescope stack up to Hubble’s epic shotsFrom deep views of the Universe to detritus of dead stars.
Read more »
 Astronomers Have Detected a Rotating Galaxy From The Early Days of The UniverseA team of astronomers have used the ALMA telescope to find a slowly-rotating galaxy in the early Universe. That galaxy is the youngest ever found with a measured rotation, and it's much slower than present-day galaxies.
Astronomers Have Detected a Rotating Galaxy From The Early Days of The UniverseA team of astronomers have used the ALMA telescope to find a slowly-rotating galaxy in the early Universe. That galaxy is the youngest ever found with a measured rotation, and it's much slower than present-day galaxies.
Read more »
 The Earliest Galaxies Rotated Slowly, Revving up Over Billions of YearsA team of astronomers have used the ALMA telescope to find a slowly-rotating galaxy in the early universe.
The Earliest Galaxies Rotated Slowly, Revving up Over Billions of YearsA team of astronomers have used the ALMA telescope to find a slowly-rotating galaxy in the early universe.
Read more »
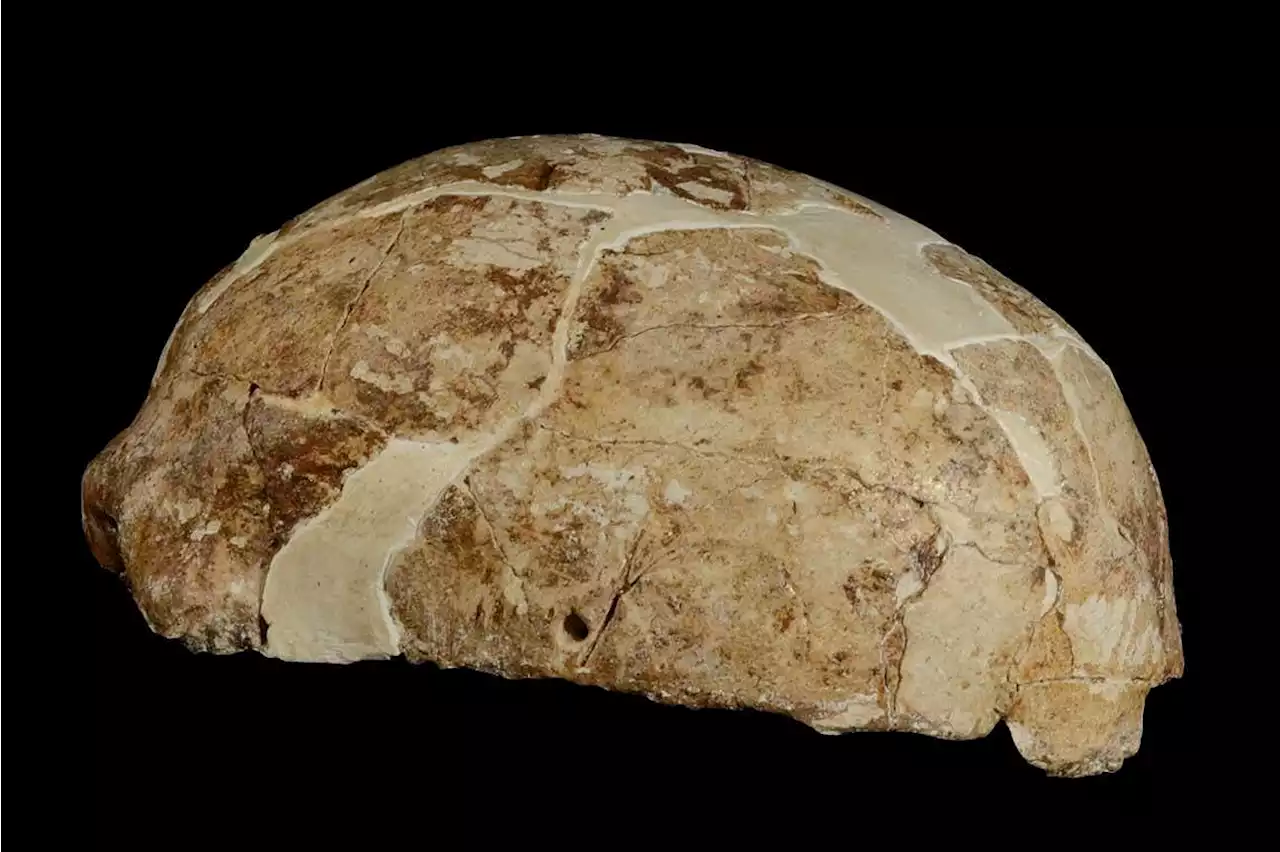 Ancient DNA adds to evidence for Native Americans' east Asian ancestryGenetic analysis of a woman’s skull from 14,000 years ago found in south-west China suggests she was related to an ancient population that migrated to North America from east Asia
Ancient DNA adds to evidence for Native Americans' east Asian ancestryGenetic analysis of a woman’s skull from 14,000 years ago found in south-west China suggests she was related to an ancient population that migrated to North America from east Asia
Read more »
 Sea Star Embryos Spin Into a Formation That's Just Like a Living CrystalTiny gelatinous blobs spin perfect pirouettes in the water – their movement whipping up a force that attracts their neighbors. As enough of them gather together, this synchronized dance aligns them into precise six-sided, ordered, repeating pattern
Sea Star Embryos Spin Into a Formation That's Just Like a Living CrystalTiny gelatinous blobs spin perfect pirouettes in the water – their movement whipping up a force that attracts their neighbors. As enough of them gather together, this synchronized dance aligns them into precise six-sided, ordered, repeating pattern
Read more »