New research highlights the significant link between alcohol consumption and increased cancer risk. The report suggests that over 5% of all cancer cases are attributed to alcohol, making it the third biggest modifiable risk factor after obesity and smoking.
It's long been known that no amount of alcohol is good for the body — and now new research spotlights the potential harm it can cause. More than 5% of all cancer cases are caused by drinking alcohol, according to the Cancer Progress Report 2024 from the American Association for Cancer Research . Among the modifiable risk factors for cancer, alcohol is the third biggest, behind obesity and cigarette smoking .
For men, it is two drinks or fewer per day, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . 'We've long known that alcohol impacts any number of organs, starting with the brain and working its way down to the colorectal system.' 'Drinking alcohol in moderation may increase your overall risks of death and chronic disease,' the agency stated on its website. 'Even low levels of alcohol use can raise the risk of certain cancers.
Alcohol Cancer Risk Health Research
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Alcohol Consumption Linked To A Significant Percentage Of US CancersA new report from the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) reveals that while the US has seen a dramatic decline in cancer deaths, alcohol consumption is a major contributing factor to cancer risk. The report highlights the need for greater awareness about this lesser-known risk factor.
Alcohol Consumption Linked To A Significant Percentage Of US CancersA new report from the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) reveals that while the US has seen a dramatic decline in cancer deaths, alcohol consumption is a major contributing factor to cancer risk. The report highlights the need for greater awareness about this lesser-known risk factor.
Read more »
 Alcohol Consumption: A Hidden Risk Factor Contributing To CancerA new report by the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) highlights the significant decline in U.S. cancer death rates, but also sheds light on a lesser-known risk factor: alcohol consumption. While advancements in treatment and early detection have contributed to the 33% reduction in cancer deaths between 1991 and 2021, excessive alcohol use is linked to 5.4% of U.S. cancer cases in 2019.
Alcohol Consumption: A Hidden Risk Factor Contributing To CancerA new report by the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) highlights the significant decline in U.S. cancer death rates, but also sheds light on a lesser-known risk factor: alcohol consumption. While advancements in treatment and early detection have contributed to the 33% reduction in cancer deaths between 1991 and 2021, excessive alcohol use is linked to 5.4% of U.S. cancer cases in 2019.
Read more »
 China's Consumption Slump Linked to Real Estate Crisis and Local Government DebtAnalysts are pointing to the connection between China's struggling real estate market and local government finances as a key factor behind the country's persistent consumption slowdown. Falling property values and reduced land sales by developers are significantly impacting local government revenue, particularly at the district and county level.
China's Consumption Slump Linked to Real Estate Crisis and Local Government DebtAnalysts are pointing to the connection between China's struggling real estate market and local government finances as a key factor behind the country's persistent consumption slowdown. Falling property values and reduced land sales by developers are significantly impacting local government revenue, particularly at the district and county level.
Read more »
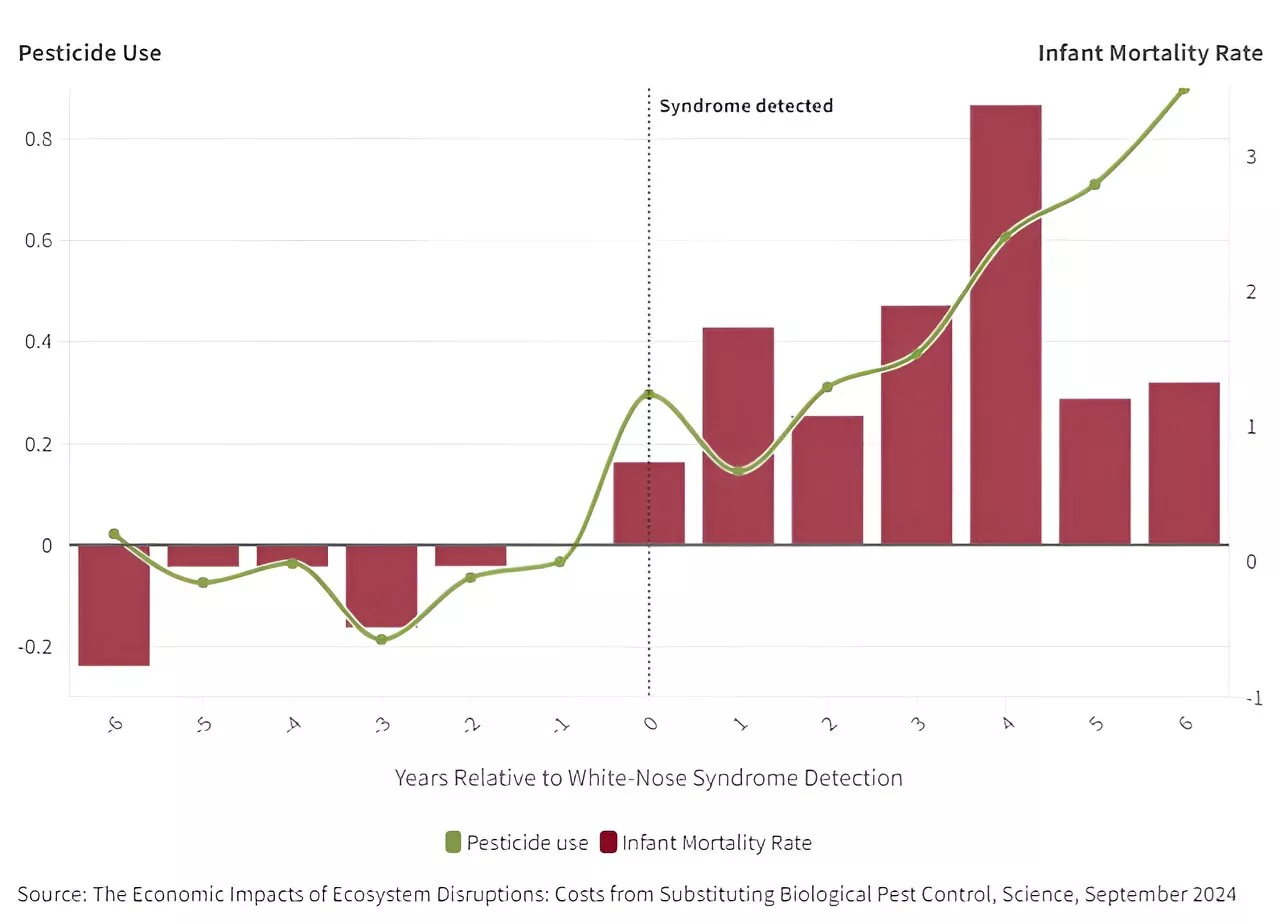 Bat population collapse linked to increased pesticide use and more than 1,000 infant deathsBats are considered a natural pesticide, widely relied on by farmers as an alternative to chemical pesticides to protect their crops from insects.
Bat population collapse linked to increased pesticide use and more than 1,000 infant deathsBats are considered a natural pesticide, widely relied on by farmers as an alternative to chemical pesticides to protect their crops from insects.
Read more »
 Food Insecurity During Pregnancy Linked To Increased Health RisksNew research from Newcastle University has found that pregnant women experiencing food insecurity are up to four times more likely to have poor mental health, as well as increased risks of obesity, diabetes, and dental problems.
Food Insecurity During Pregnancy Linked To Increased Health RisksNew research from Newcastle University has found that pregnant women experiencing food insecurity are up to four times more likely to have poor mental health, as well as increased risks of obesity, diabetes, and dental problems.
Read more »
 Diabetic Neuropathy and Retinopathy Linked to Increased Risk for PeriodontitisThe coexistence of neuropathy and retinopathy increased the risk for moderate/severe periodontitis, and dyslipidemia had an additive effect.
Diabetic Neuropathy and Retinopathy Linked to Increased Risk for PeriodontitisThe coexistence of neuropathy and retinopathy increased the risk for moderate/severe periodontitis, and dyslipidemia had an additive effect.
Read more »
