Synthetic biology presents novel approaches to combat the primary cause of death in hospitals. Scientists have created the first 'living medicine' to cure lung infections. This innovative treatment is aimed at Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a bacteria known for its resistance to many antibiotics and a fre
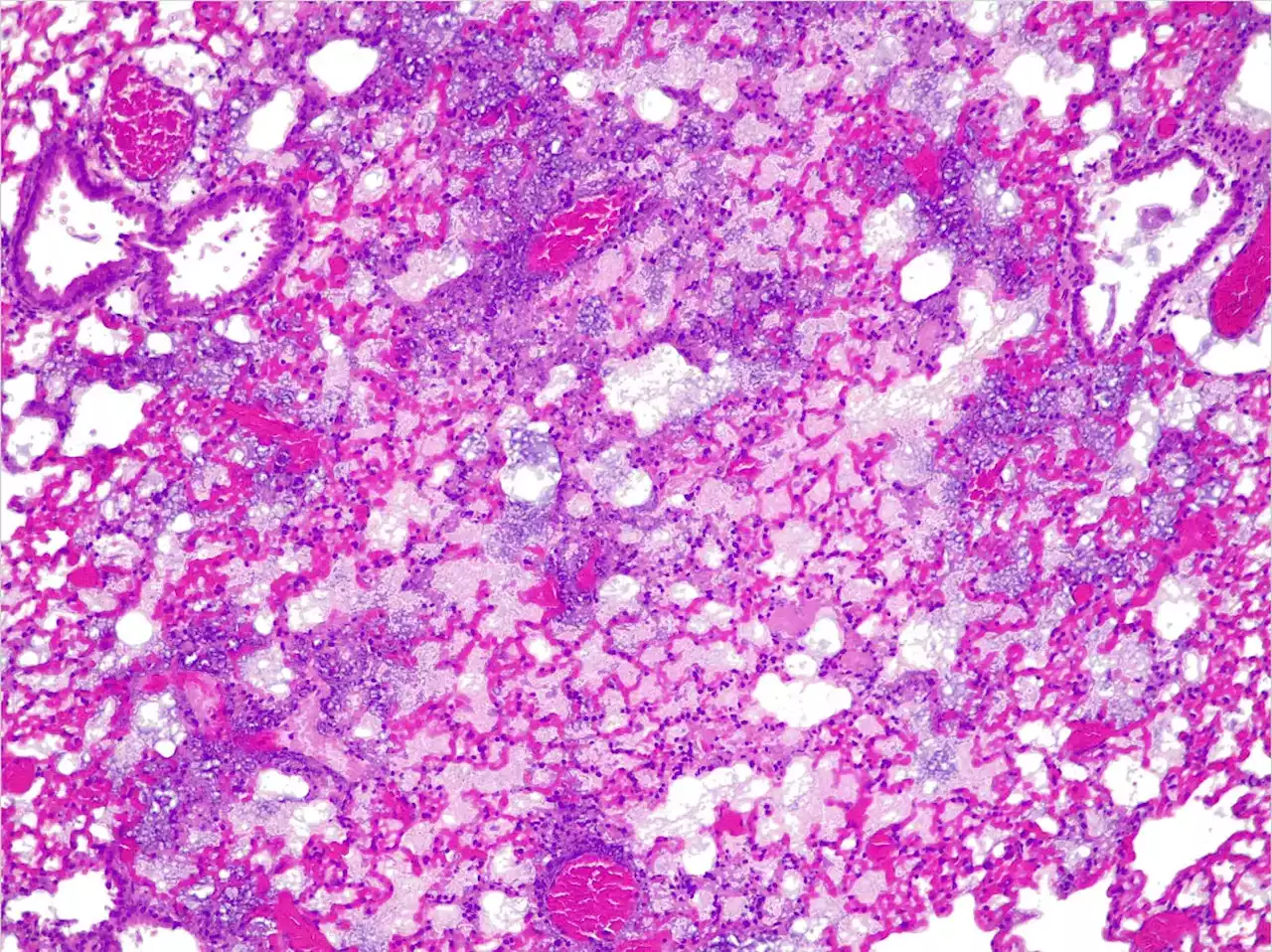
. The mouse was treated with a version ofthat could not produce therapeutic molecules, resulting in severe pneumoniae. This is characterized by massive infiltration of inflammatory cells into the alveolar septa, resulting in loss of air in the alveoli. Credit: Rocco Mazzolini/CRGScientists have created the first “living medicine” to cure lung infections. This innovative treatment is aimed at, a bacteria known for its resistance to many antibiotics and a frequent cause of infections in hospitals.
“We have developed a battering ram that lays siege to antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The treatment punches holes in their cell walls, providing crucial entry points for antibiotics to invade and clear infections at their source. We believe this is a promising new strategy to address the leading cause of mortality in hospitals,” says Dr.
In addition to designing the ‘living medicine’, Dr. Serrano’s research team is also using their expertise in synthetic biology to design new proteins that can be delivered byinfections.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Double lung transplants successfully treat late-stage lung cancer, in a first with new techniqueA new double lung transplant technique was successful for two patients with lung cancer, Northwestern Medicine announced.
Double lung transplants successfully treat late-stage lung cancer, in a first with new techniqueA new double lung transplant technique was successful for two patients with lung cancer, Northwestern Medicine announced.
Read more »
 Scientists restore sight in mice using a new gene-editing techniqueScientists in China have effectively treated retinitis pigmentosa, a leading cause of blindness in humans, in mice.
Scientists restore sight in mice using a new gene-editing techniqueScientists in China have effectively treated retinitis pigmentosa, a leading cause of blindness in humans, in mice.
Read more »
 Scientists Identify New Schizophrenia Risk Genes in First-of-Its-Kind StudyTwo newly discovered genes have been linked to schizophrenia while a previously known gene associated with schizophrenia risk has also been linked to autism in a massive new study.
Scientists Identify New Schizophrenia Risk Genes in First-of-Its-Kind StudyTwo newly discovered genes have been linked to schizophrenia while a previously known gene associated with schizophrenia risk has also been linked to autism in a massive new study.
Read more »
 Chemo Doesn't Improve Lung Adenocarcinoma Survival in MostOnly never-smokers with high PDL-1 expression lived longer when chemotherapy was added to upfront PD-(L)1 blockers. The study was published as a preprint and has not yet been peer reviewed.
Chemo Doesn't Improve Lung Adenocarcinoma Survival in MostOnly never-smokers with high PDL-1 expression lived longer when chemotherapy was added to upfront PD-(L)1 blockers. The study was published as a preprint and has not yet been peer reviewed.
Read more »
 Merck’s combination therapy in lung cancer fails a Phase 2 clinical trialMerck & Co. Inc. said late Thursday that its combination therapy of vibostolimab and Keytruda did not outperform chemotherapy in a Phase 2 clinical trial of...
Merck’s combination therapy in lung cancer fails a Phase 2 clinical trialMerck & Co. Inc. said late Thursday that its combination therapy of vibostolimab and Keytruda did not outperform chemotherapy in a Phase 2 clinical trial of...
Read more »
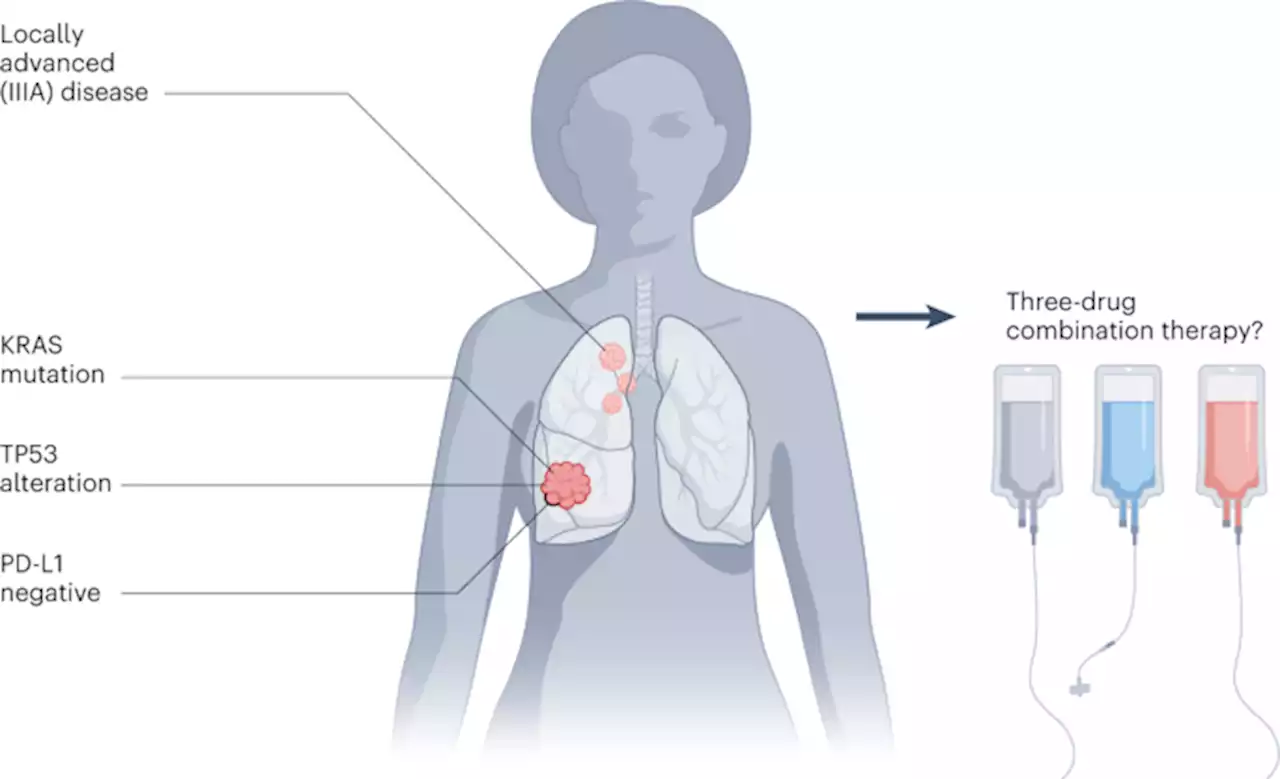 Advancing neoadjuvant immunotherapy for lung cancer - Nature MedicineThe NEOSTAR trial is a key step on route to better outcomes; but the best approach is likely to be an individualized one, reflecting the many factors that influence treatment response.
Advancing neoadjuvant immunotherapy for lung cancer - Nature MedicineThe NEOSTAR trial is a key step on route to better outcomes; but the best approach is likely to be an individualized one, reflecting the many factors that influence treatment response.
Read more »