A small study says zero-calorie sweetener erythritol may increase the risk of blood clots and heart disease. A cardiologist weighs in.
erythritol versus sugar and landed on grim results—specifically, that erythritol increased the risk of blood clots and heart disease.
Erythritol's safety has been an ongoing debate among doctors and consumers. It’s previously been linked to a higher risk of stroke and heart attacks, but according to the, had an extremely limited sample size—only 20 people. Some participants were given water sweetened with 30 grams of erythritol, while others drank water sweetened with 30 grams of regular sugar. Thirty minutes afterward, everyone had their blood drawn.
But, Dr. Bart adds: “The results should be taken with the caveat that the total number of people studied is small." However, this isn't the first study to link erythritol with problematic effects."The same group published a population-based study last year linking higher levels of erythritol to cardiovascular events in 4,000 people,” she notes.
In general, “sugar and sugar substitutes should be limited and avoided where possible,” Dr. Bart says. “Sugar substitutes themselves have been linked to obesity, diabetes, and other health conditions. Plus, they are artificial and can be pro-inflammatory.”
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 New Study Links Controversial Gut Organism to Reduced Body FatScience, Space and Technology News 2024
New Study Links Controversial Gut Organism to Reduced Body FatScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
 New Study Links Anxiety in Young Women to Brain Chemical ImbalanceScience, Space and Technology News 2024
New Study Links Anxiety in Young Women to Brain Chemical ImbalanceScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
SMU study links well blowouts in Permian with wastewater injectionA new study by Southern Methodist University links abandoned well blowouts in Permian with wastewater injection
Read more »
 Popular Dementia Treatment Could Be Doing More Harm Than Good, According to New StudyScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Popular Dementia Treatment Could Be Doing More Harm Than Good, According to New StudyScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
 Groundbreaking Study Links Keto Diet to Reduced Memory LossScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Groundbreaking Study Links Keto Diet to Reduced Memory LossScience, Space and Technology News 2024
Read more »
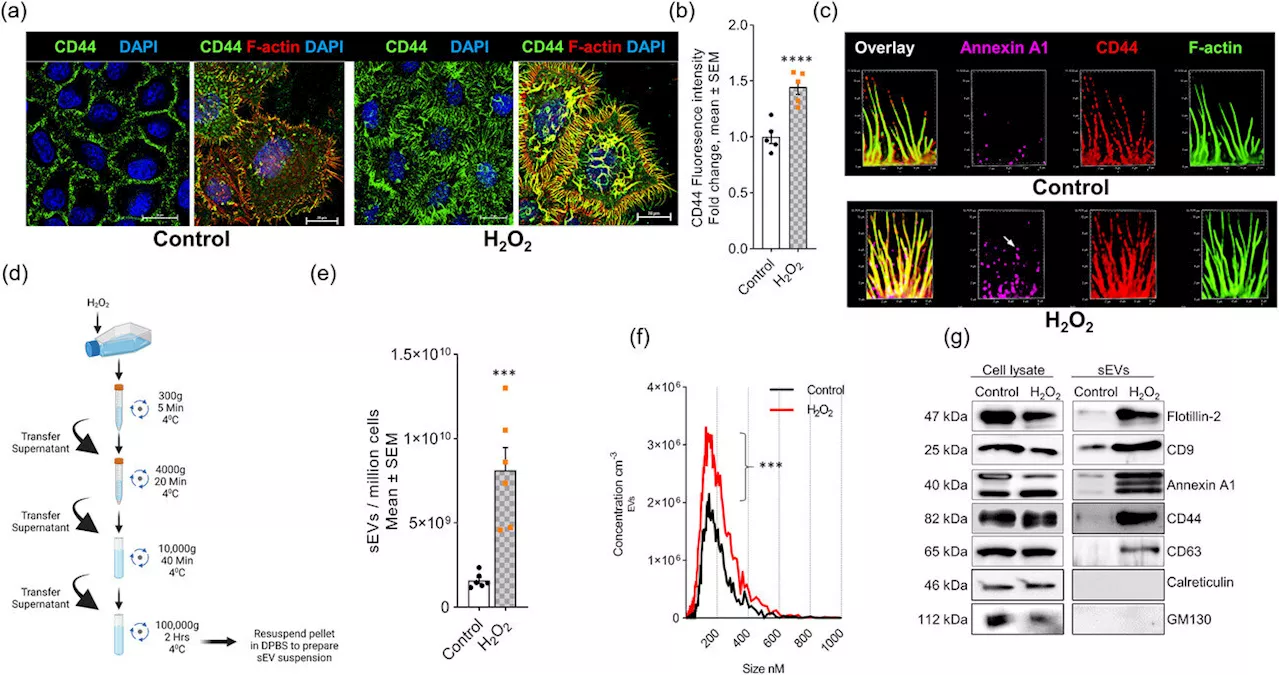 Study links nanoparticles to oxidative stress and neuron deathResearchers at the University of Kentucky have a better understanding of the regulation of extracellular vesicles by oxidative stress and how these vesicles spread oxidative stress and may damage neurons. Extracellular vesicles are nanoparticles released by all cell types that help transport information between cells.
Study links nanoparticles to oxidative stress and neuron deathResearchers at the University of Kentucky have a better understanding of the regulation of extracellular vesicles by oxidative stress and how these vesicles spread oxidative stress and may damage neurons. Extracellular vesicles are nanoparticles released by all cell types that help transport information between cells.
Read more »
