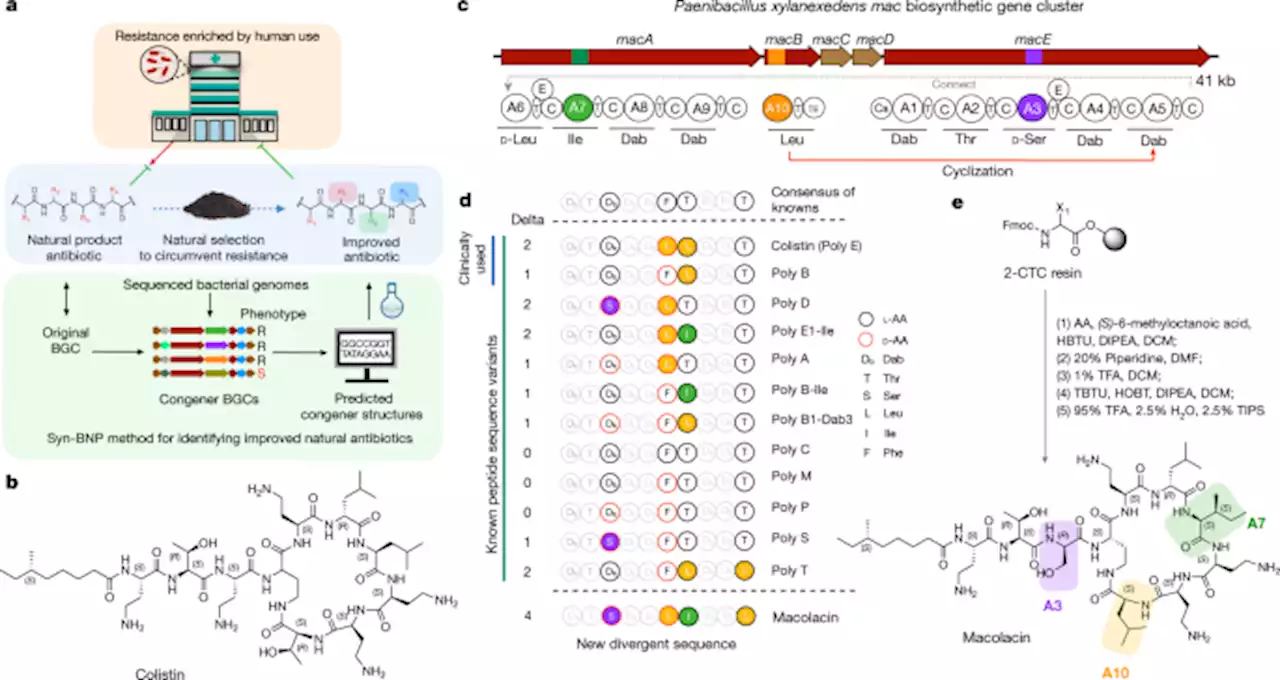
Nature research paper: A naturally inspired antibiotic to target multidrug-resistant pathogens
. The bacterial natural product colistin is considered the last line of defence against a number of Gram-negative pathogens. The recent global spread of the plasmid-borne mobilized colistin-resistance gene. Bacteria-derived antibiotics often appear in nature as collections of similar structures that are encoded by evolutionarily related biosynthetic gene clusters.
. In a mouse neutropenic infection model, a biphenyl analogue of macolacin proved to be effective against extensively drug-resistantwith colistin-resistance, thus providing a naturally inspired and easily produced therapeutic lead for overcoming colistin-resistant pathogens.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
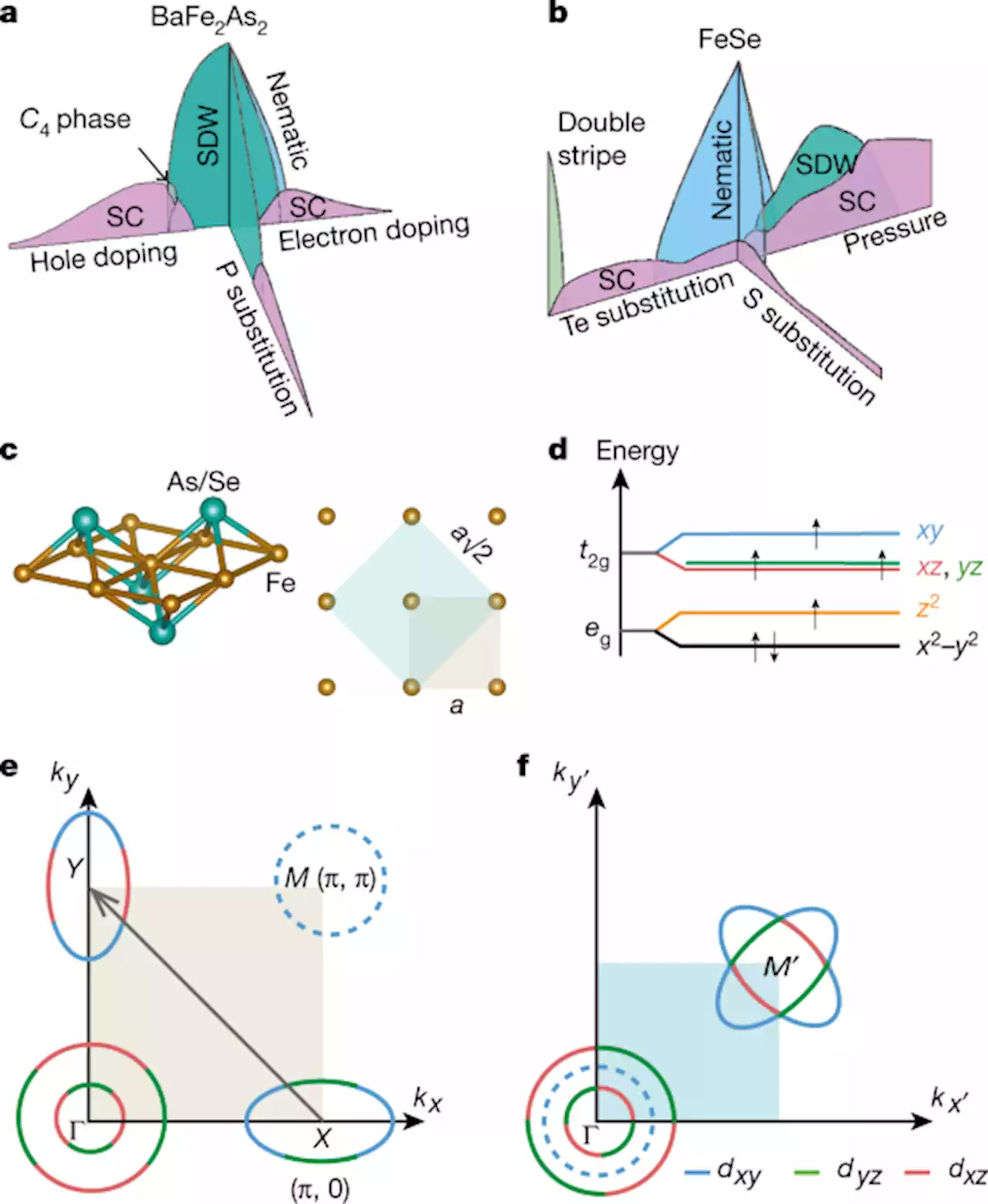 Iron pnictides and chalcogenides: a new paradigm for superconductivity - NatureThe progress and the outstanding issues in understanding the correlated phases in the unconventional iron-based superconductors is reviewed.
Iron pnictides and chalcogenides: a new paradigm for superconductivity - NatureThe progress and the outstanding issues in understanding the correlated phases in the unconventional iron-based superconductors is reviewed.
Read more »
 Crystallization of bosonic quantum Hall states in a rotating quantum gas - NatureSpontaneous crystallization of atoms occurs in a rotating ultracold Bose–Einstein condensate occupying the lowest Landau level, behaviour that is related to a quantum hydrodynamic instability driven by shear forces.
Crystallization of bosonic quantum Hall states in a rotating quantum gas - NatureSpontaneous crystallization of atoms occurs in a rotating ultracold Bose–Einstein condensate occupying the lowest Landau level, behaviour that is related to a quantum hydrodynamic instability driven by shear forces.
Read more »
 A 16-parts-per-trillion measurement of the antiproton-to-proton charge–mass ratio - NatureMultiple high-precision measurement campaigns at CERN of the antiproton-to-proton charge-to-mass ratio—to a precision of 16 parts per trillion—in a cryogenic multi-Penning trap offer no evidence of charge–parity–time violation, and set stringent limits on the clock-weak-equivalence principle.
A 16-parts-per-trillion measurement of the antiproton-to-proton charge–mass ratio - NatureMultiple high-precision measurement campaigns at CERN of the antiproton-to-proton charge-to-mass ratio—to a precision of 16 parts per trillion—in a cryogenic multi-Penning trap offer no evidence of charge–parity–time violation, and set stringent limits on the clock-weak-equivalence principle.
Read more »
 An early transition to magnetic supercriticality in star formation - NatureAn analysis of Zeeman measurements reveals that the reduction of magnetic flux relative to mass, which is necessary for star formation, seems to have occurred earlier than previously thought.
An early transition to magnetic supercriticality in star formation - NatureAn analysis of Zeeman measurements reveals that the reduction of magnetic flux relative to mass, which is necessary for star formation, seems to have occurred earlier than previously thought.
Read more »
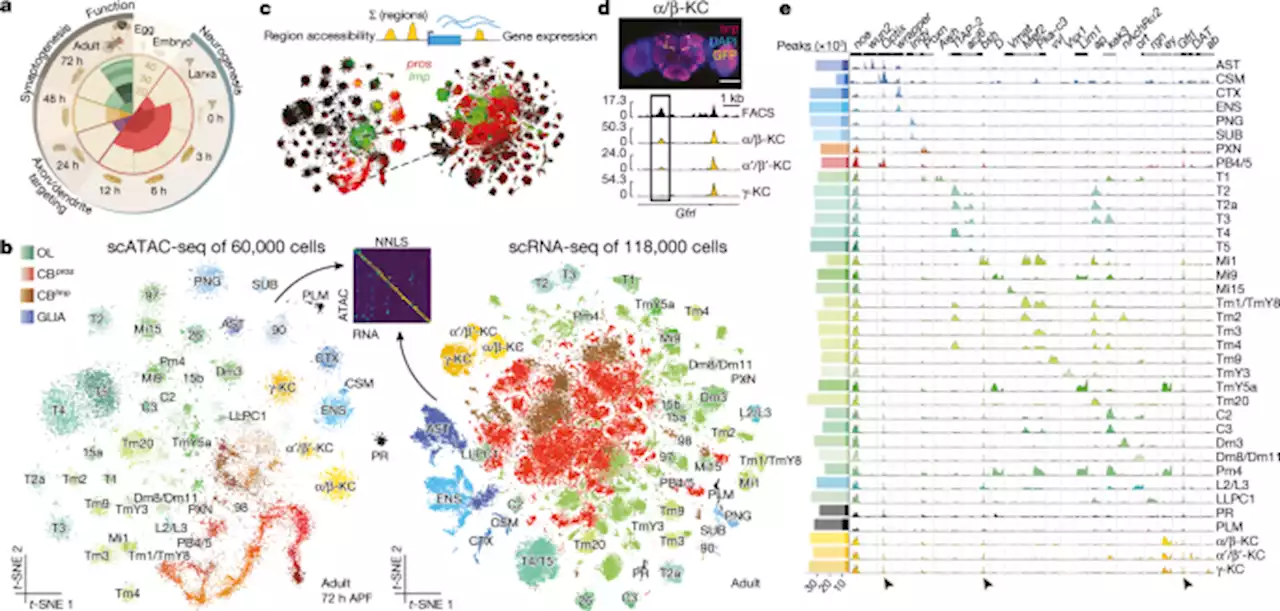 Decoding gene regulation in the fly brain - NatureA chromatin accessibility atlas of 240,919 cells in the adult and developing Drosophila brain reveals 95,000 enhancers, which are integrated in cell-type specific enhancer gene regulatory networks and decoded into combinations of functional transcription factor binding sites using deep learning.
Decoding gene regulation in the fly brain - NatureA chromatin accessibility atlas of 240,919 cells in the adult and developing Drosophila brain reveals 95,000 enhancers, which are integrated in cell-type specific enhancer gene regulatory networks and decoded into combinations of functional transcription factor binding sites using deep learning.
Read more »
 Emergence of methicillin resistance predates the clinical use of antibiotics - NatureMethicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus appeared in European hedgehogs in the pre-antibiotic era as a co-evolutionary adaptation to antibiotic-producing dermatophytes and have spread within the local hedgehog populations and between hedgehogs and secondary hosts.
Emergence of methicillin resistance predates the clinical use of antibiotics - NatureMethicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus appeared in European hedgehogs in the pre-antibiotic era as a co-evolutionary adaptation to antibiotic-producing dermatophytes and have spread within the local hedgehog populations and between hedgehogs and secondary hosts.
Read more »