We never stopped evolving.
Are humans still evolving? This question is a mystery for many, as about seven million years have passed since humans left the chimpanzee lineage. The factors that forced us to adapt, evolve, and survive harsh environments in the past are no longer relevant.
Today, humans have much longer lifespans and advanced healthcare facilities at their disposal. We live in a comfortable and protected environment almost all the time. The external factors that previously kept us in continuous survival mode don't affect us anymore.A team of researchers from Trinity College Dublin and Alexander Fleming Biomedical Sciences Research Center in Greece explored this question in detail.
They emerged from segments of unique DNA. The significance of these new genes can be understood from the fact that 44 out of the 155 genes were found to be linked to growth anomalies in cell cultures. So they could help us spot growth defects and ensure the optimum health of living systems. The patterns in the unique DNA also suggested that the newFor instance, the researchers noticed three genes with DNA markers related to disorders such as rod-cone dystrophy,The authors suggested that one particular gene of this new collection originated in humans as soon as our ancestors broke out from the gorilla lineage. This gene is now linked to human heart tissue development.
While highlighting the importance of the newly identified genes, senior author and geneticist at TCD, Aoife McLysaght, said, "These genes are convenient to ignore because they're so difficult to study, but I think it'll be increasingly recognized that they need to be looked at and considered. If we're right in what we think we have here, there's a lot more functionally relevant stuff hidden in the human genome."Diagram depicting new genes in humans.
United States Latest News, United States Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 The water you drink is 4.5 billion years old, scientists revealIt all began with a cloud that was mostly hydrogen with a touch of helium, oxygen, and carbon. It then evolved through four key steps to become today's water.
The water you drink is 4.5 billion years old, scientists revealIt all began with a cloud that was mostly hydrogen with a touch of helium, oxygen, and carbon. It then evolved through four key steps to become today's water.
Read more »
 Scientists Discover a New Daily Rhythm Providing Insight Into How Brain Activity Is Fine-TunedA new study explores how new information is across the sleep-wake cycle. Researchers discovered a new daily rhythm in a kind of synapse that dampens brain activity using a mouse model. These neural connections, known as inhibitory synapses, are rebalanced as we sleep to allow us to consolidate new
Scientists Discover a New Daily Rhythm Providing Insight Into How Brain Activity Is Fine-TunedA new study explores how new information is across the sleep-wake cycle. Researchers discovered a new daily rhythm in a kind of synapse that dampens brain activity using a mouse model. These neural connections, known as inhibitory synapses, are rebalanced as we sleep to allow us to consolidate new
Read more »
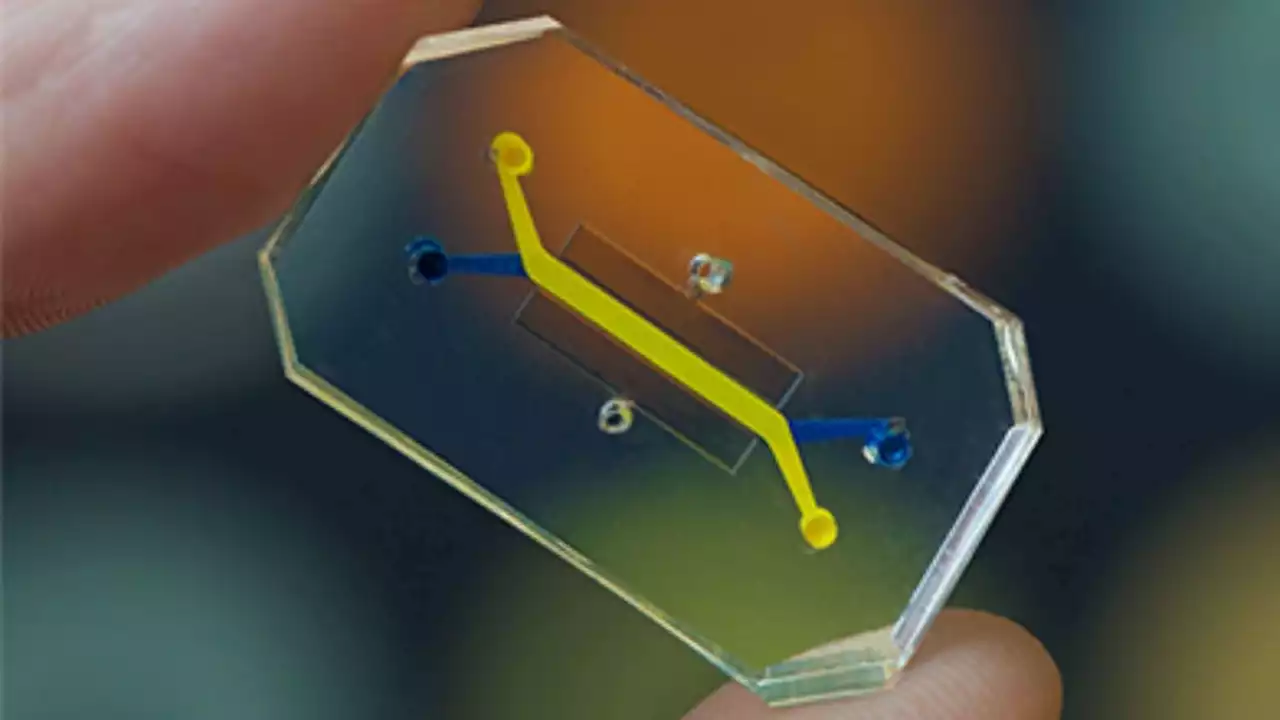 Scientists invent 1st 'vagina-on-a-chip'The first vagina-on-a-chip replicates the cellular environment of the vagina.
Scientists invent 1st 'vagina-on-a-chip'The first vagina-on-a-chip replicates the cellular environment of the vagina.
Read more »
 To save Yosemite’s bats, scientists need help finding themA deadly fungus has killed millions of bats across North America over the past decade. To protect the bats in the park, biologists first need to document the many places they roost.
To save Yosemite’s bats, scientists need help finding themA deadly fungus has killed millions of bats across North America over the past decade. To protect the bats in the park, biologists first need to document the many places they roost.
Read more »
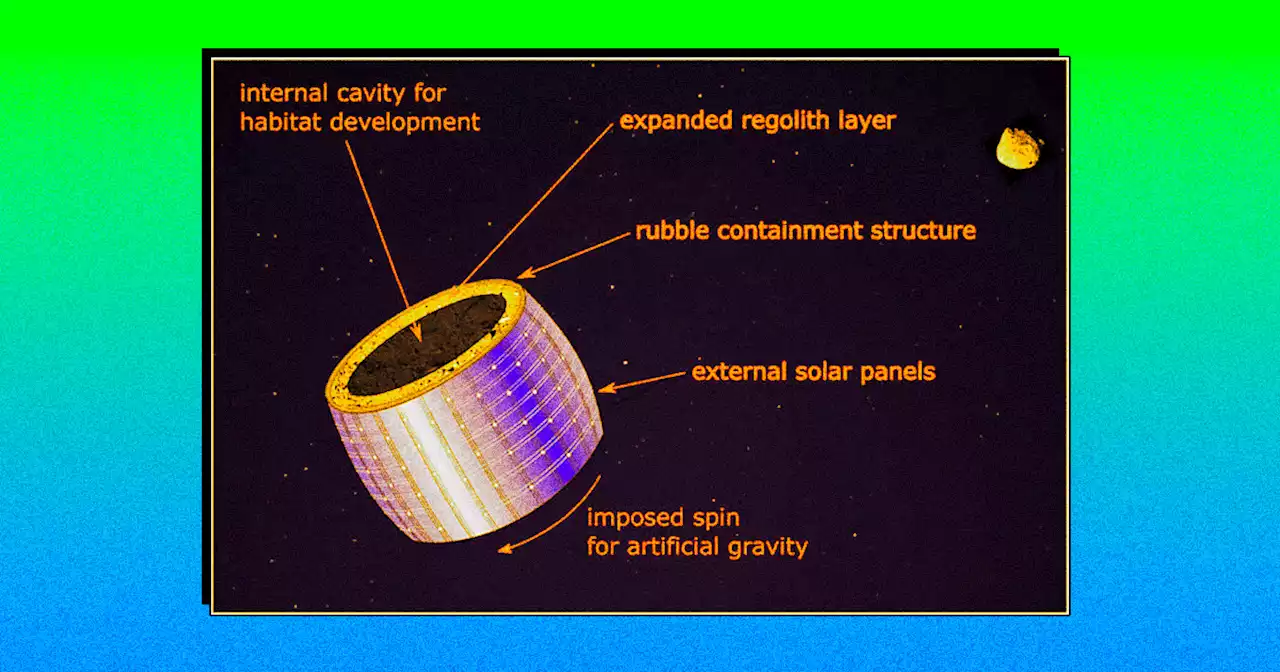 Scientists Propose Building City Inside Giant Bag Around Entire AsteroidResearchers have admitted that it's 'theoretical' to put a giant mesh bag around an asteroid to build space cities — but that it's technically feasible.
Scientists Propose Building City Inside Giant Bag Around Entire AsteroidResearchers have admitted that it's 'theoretical' to put a giant mesh bag around an asteroid to build space cities — but that it's technically feasible.
Read more »
 Scientists warn Great Lakes might become more acidic from atmospheric carbonScientists are building a sensor network to spot Lake Huron water chemistry trends. It’s a first step toward a hoped-for system that would track carbon dioxide and pH in all five Great Lakes.
Scientists warn Great Lakes might become more acidic from atmospheric carbonScientists are building a sensor network to spot Lake Huron water chemistry trends. It’s a first step toward a hoped-for system that would track carbon dioxide and pH in all five Great Lakes.
Read more »
